 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 33(3); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
Sow milk (SM) may not be able to meet the pigletŌĆÖs nutritional needs in late lactation. Hence, this study was conducted to investigate the effects of early commercial milk (CM) supplement on the mucosal morphology, bacterial community and bacterial metabolites in jejunum of piglets.
Methods
Ten litters of newborn piglets ([Yorkshire├ŚLandrace]├ŚDuroc) were randomly divided into 2 groups of 5 litters. The piglets in the control group were suckled by the sow (SM), while the piglets in the treatment group (CM supplement) were supplemented with a CM supplement along with suckling from d 4 to d 28 of age.
Results
No significant differences were observed about jejunal mucosal morphology on d 28 and d 35 between two groups. On d 28, the activity of lactase in the jejunum was significantly decreased in the CM group, while the activity of sucrase and the ratio of maltase to lactase were significantly increased (p<0.05). On d 35, the activity of maltase in the jejunum was significantly increased in the CM group (p<0.05), and maltase to lactase ratio tended to increase in the CM group (p = 0.065). In addition, piglets in the CM group had a higher abundance of Clostridium XI, Tuicibater, and Moraxella in the jejunum on d 28, while the abundance of Lactobacillus was significantly increased on d 35 (p<0.05).
The small intestine (especially jejunum) is the main site of digestion and absorption, where adequate absorptive capacity depends on the maintenance of mucosal integrity constantly challenged by bacteria [1]. Although the low pH value and rapid flow of digesta in the jejunum leads to lesser numbers of bacteria compared with the hindgut, the jejunal bacterial community is important for host immunity and nutritional metabolism [2]. The jejunal beneficial bacteria could directly help inhibit pathogens colonization, or indirectly promote the jejunum epithelial cell growth and differentiation, and improve internal environment in jejunum by producing bacteria-derived metabolites, such as lactic acid and short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) [3,4]. Hence, jejunum and its microbiota are critical for maintaining intestinal homeostasis.
Breast milk is the best source of nutrients for neonatal growth and gut development [5]. Due to genetic selection and artificial rearing systems, the number of piglets delivered by sow has increased, which challenges the raising ability of sow [6]. Hence, the early commercial milk (CM) supplement could be beneficial for piglets and sows. Previous studies suggested that the early CM supplement could reduce the nutritional digestive capacity of the small intestine in piglets [7,8]. However, another study revealed that the piglets fed the CM supplement grew faster and were heavier than unsupplemented piglets [9]. While few researches are available regarding how the CM supplement affects the jejunal function and microbial community, which are highly related to the safe application of CM supplement in piglets. Therefore, we hypothesized that an early CM supplement could affect jejunal function and change the microbial community. To verity this hypothesis, jejunal morphology, disaccharidase activity, bacterial community and bacterial metabolites were investigated in this study.
The animal experiment was approved by the Animal Experiment Committee of Nanjing Agricultural University (Nanjing, Jiangsu province, China), in accordance with the Regulations for the Administrations of Affairs Concerning the Experimental Animals (The State Science and Technology Commission of China, 1988). All experiments were performed in accordance with the approved guidelines and regulations.
Ten Yorkshire├ŚLandrace sows were artificially inseminated by one Duroc boar. The sows had delivered on the same day. The piglets suckled the colostrum for three days after birth. On the 4th day after birth, the piglets were adjusted to 8 per litter; the average weight of piglets was 1.87┬▒0.05 kg. Ten litters of piglets were randomly divided into the control group (sow milk, SM) and the treatment group (CM), with 5 litters in each group (n = 5). The piglets in the SM group were reared only by the sow, while the piglets in the CM group were supplemented with a CM supplement along with suckling from d 4 to d 28 of age. Piglets in the CM group had ad libitum access to milk supplement via a nipple system. The CM supplement was dissolved in 50┬░C warm water (150 g/L) and was provided via a nipple system twice a day. At 9:00 and 19:00 every day during the experimental period, we supplemented the milk supplement with a weight that is same amount of average daily feed intake (ADFI) in the nipple system, and then weighed the rest milk supplement in the nipple system when we added milk supplement next time. Then, we calculated the intake of CM supplement every day. On d 28, one piglet was randomly picked from each litter, and then slaughtered for sampling (n = 5). The remaining piglets were weaned, and the piglets in the same litter were housed in a pen, therefore each group had five pens (n = 5). All the piglets were switched to a common diet for 7 days. On d 35, one piglet was randomly picked from each litter, and then slaughtered for samples (n = 5). The piglets had free access to feed and water throughout the experimental period. The body weight (BW) of each piglet in the SM group or CM group was individually recorded on d 4, 14, 21, 28, and 35. Then, we utilized those data to calculate average daily gain (ADG) of the SM group and CM groups. The nutritional values of the milk supplement and SM are shown in Table 1 [10ŌĆō13].
At days 28 and 35, after fasting overnight, one piglet from each litter (5 piglets from each group, n = 5) was euthanised with sodium pentobarbital (100 mg/kg BW). The abdomen was opened and the segments (stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, and colon) were identified and ligated before separation. The digesta in the jejunum was collected and mixed for measuring the pH value. Then, the digesta was immediately stored in liquid nitrogen for further analysis. Five cm jejunum tissue were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (100 mmol/L phosphate buffer, pH 7.4) for morphology analysis. The mucosa was isolated by gentle scraping with a glass slide, snap frozen in liquid nitrogen, and then stored in ŌłÆ80┬░C for future disaccharidase activities and gene expression analysis.
After fixing for 24 h, formalin-fixed samples were embedded in paraffin, sectioned at a 5 ╬╝m thickness, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histologic examination to determine villus length, crypt depth. The villus height and crypt depth were measured and analyzed by using NIS-Elements BR software (version 2.20; Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
Each sample was homogenized in 1.0 mL cold saline mixed with protease inhibitors (Roche, Shanghai, China) on ice. Protein concentration was determined using a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China). The activity of the disaccharidase (maltase, lactase, and sucrase) was determined using commercial kits (Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China). Enzyme activity was described as U per mg of protein.
The concentration of lactic acid was determined using commercial kits (Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China). The ammonia N concentration was determined by the colorimetric method described by Nyachoti et al [14]. The concentrations of SCFAs including acetate, propionate, butyrate, valerate and branched chain fatty acids were analyzed by gas chromatography (Shimadzu GC-14B, Tokyo, Japan) [15]. A Nukol Capillary GC Column (Sigma-Aldrich, Milwaukee, WI, USA) and an FID detector were used as described by Mao et al [16]. The temperature of injector, column and detector were 110┬░C, 150┬░C, and 180┬░C, respectively.
The total bacterial DNA was extracted from the jejunal digesta (0.1 g) according to a bead beating method described by Zoetendal et al [17]. The concentration of extracted DNA was determined using a Nano-Drop 1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific Inc., Wilmington, DE, USA). To analyze the taxonomic composition of bacterial community in the jejunal digesta, universal primers 319F (ACTCCTACGGGA GGCAGCAG) and 806R (GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT) targeting the V3ŌĆōV4 region of the 16S rRNA gene were chosen for the amplification and subsequent pyrosequencing of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products. The PCR amplification was performed using the following program: initial denaturation step at 95┬░C for 2 min, followed by 25 cycles at 95┬░C for 30 s, 55┬░C for 30 s, and 72┬░C for 30 s and a final extension at 72┬░C for 5 min. All amplicons were visualized on 2% agarose gels and were purified using the Axyprep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union City, CA, USA) following the recommended instructions and were quantified using Quantifluor TM-ST (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The purified amplicons were paired-end sequenced on an Illumia Miseq platform according to a standard protocol [18].
Raw fastq files were de-multiplexed and quality-filtered using QIIME (version 1.70, CU-Boulder, CO, USA) with standard criteria as described by Sun et al [19]. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were clustered with a 97% similarity cut-off using UPARSE (version 7.1 http://drive5.com/uparse/), and the chimeric sequences were identified and removed using UCHIME. The bacterial diversity was assessed using the observed species, Simpson, Chao1 and Shannon indices.
The raw sequencing data were submitted to the Sequence Read Archive under accession number SRP107026. The data were analyzed with SPSS 20.0 and shown as the means with standard error of the mean. The studentŌĆÖs t-test and Mann-Whitney U test were used to assess the differences between treatments, with the litter as the experimental unit for growth performance, and the piglet as the experimental unit for other indices (n = 5). The normality of the distribution of variables was tested by the Shapiro-Wilk test. The variables that had a non-normal distribution were analyzed using the nonparametric methods. The t-test and the Mann-Whitney U test were used to analyze the data that had a normal (the data of jejunal morphology, disaccharidase activities and the gene expression) or non-normal distribution (microbial data) on d 28 and d 35, respectively. Significant differences were declared when p<0.05, while p values between 0.05 and 0.10 were considered to be a tendency.
The villus height, crypt depth and villus height to crypt depth ratio are shown in Table 2. On d 28 and d 35 of age, no significant difference in villus height, crypt depth and villus height to crypt depth ratio was observed between the CM group and the SM group.
The disaccharidase activities in jejunal mucosa of piglets are presented in Figure 1. On d 28 of age (Figure 1A), the activity of lactase in the jejunum was significantly decreased in the CM group, while the activity of sucrase and maltase to lactase ratio were significantly increased (p<0.05). On d 35 of age, the activity of maltase in the jejunum was significantly increased in the CM group (p<0.05), and maltase to lactase ratio tended to increase in the CM group (p = 0.065, Figure 1B).
The bacterial metabolites in jejunal digesta are presented in Table 3 and 4. On d 28 (Table 3), the concentrations of acetate and the total SCFAs were significantly increased in the jejunal digesta in the CM group (p<0.05). Piglets in the CM group had increased lactic acid concentration (p = 0.07). On d 35 of age (Table 4), the pH value significantly decreased in the jejunal digesta, and the concentration of lactic acid in the jejunal digesta statistically increased in the CM group (p = 0.04). Moreover, no obvious difference was observed in the concentrations of ammonia N and total SCFAs in the jejunal digesta of the piglets in the SM group and CM group.
In this study, the number of average raw sequences detected in each group was at least 52,629 reads with 51,369 valid sequences (Supplementary Table S1). The overall number of OTUs detected was 17,756 at least in each sample, based on a 97% sequence similarity between reads. The rarefaction curves (Supplementary Figure S1) were generated by MOTHUR via plotting the number of reads versus the number of observed species and tended to approach the saturation plateau. The curves show that the sequencing amount was sufficient to evaluate the bacterial community in both groups. As shown in Supplementary Table S2, on d 28 of age, no statistical difference was observed in the diversity indices (Simpson) and richness estimators (observed species and Chao 1) of jejunal bacteria between SM group and CM group (p>0.05). However, compared with the SM group, the indices (Shannon) tended to increase in the CM group (p = 0.07). On d 35, no statistical difference was observed in the diversity indices (Shannon and Simpson) and richness estimators (observed species and Chao 1) of jejunal bacteria between the SM group and the CM group.
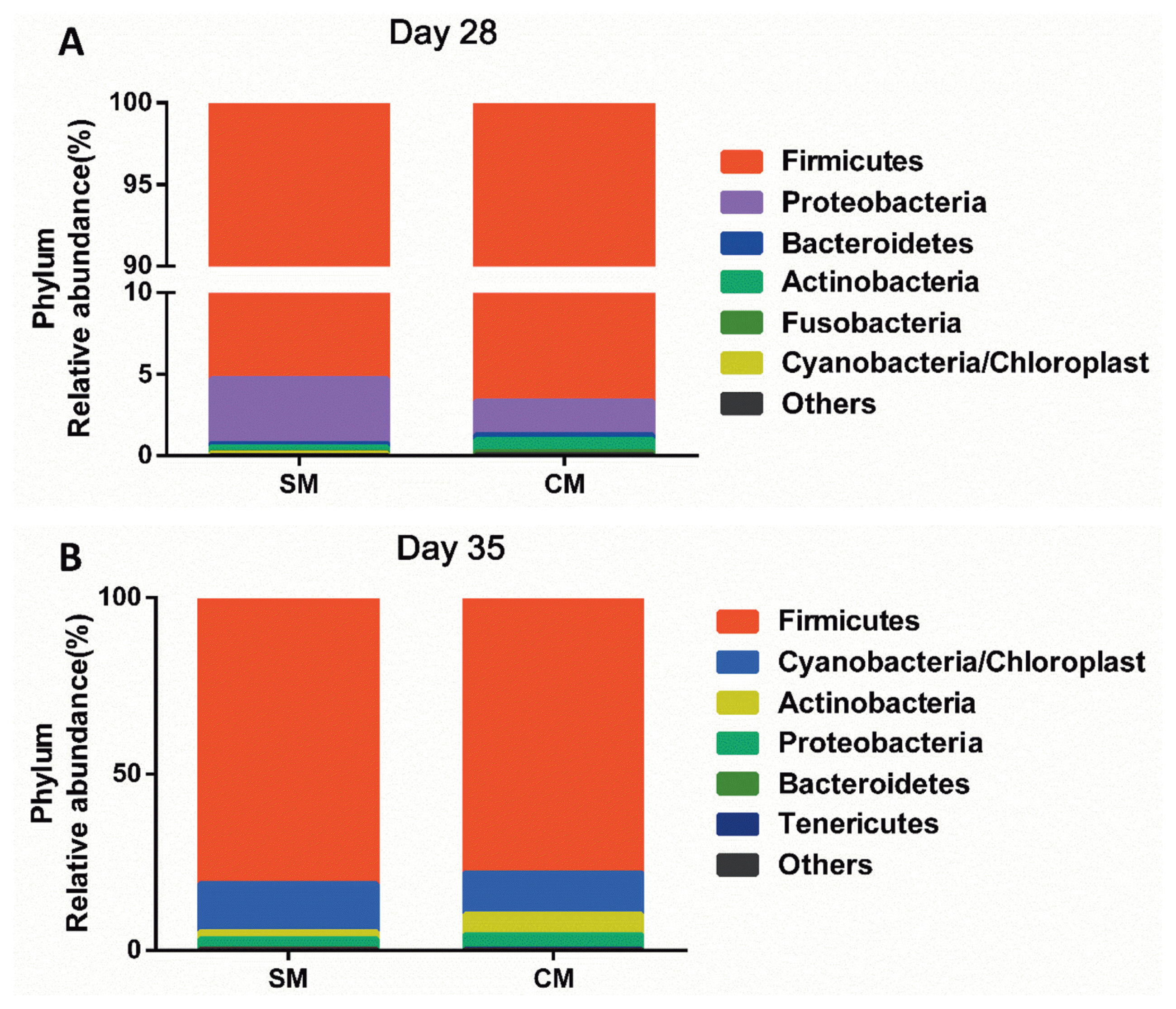
The bacterial community was assessed at different taxonomic levels. At the phylum level, as shown in Figure 2, the Firmicutes was the predominant phylum in all samples by d 28 of age, accounting for 95.97% of the total 16S rRNA gene sequences. Proteobacteria was the second dominant phylum, represented by 3.00% of total 16S rRNA gene sequences, followed by the bacteria from phyla Bacteroidetes (0.25%), and Actinobacteria (0.54%). By d 35 of age, the Firmicutes was the predominant phylum in all samples, accounting for 77.97% of the total 16S rRNA gene sequences. Cyanobacteria/Chloroplast was the second dominant phylum, represented by 11.78% of total 16S rRNA gene sequences, followed by the bacteria from phyla Actinobacteria (5.72%), Proteobacteria (4.09%). No statistical difference in the bacterial community at the phylum level was observed between the SM group and the CM group.
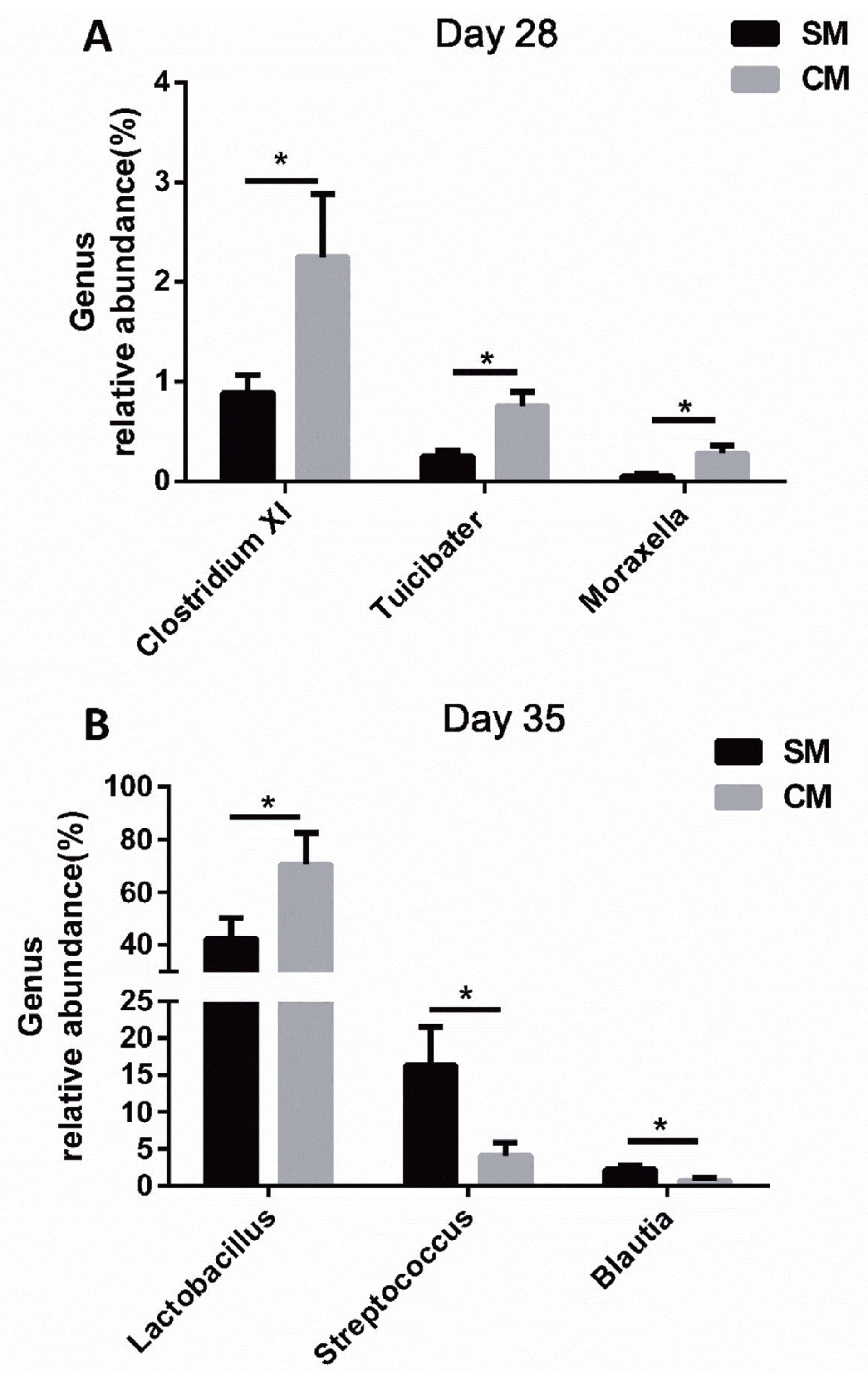
At the genus level, as shown in Figure 3, by d 28 of age, the predominant genera were the Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Veillonella, and Clostridium XI, while, there was no statistical difference between the SM group and the CM group (p>0.05). By d 28 of age (Figure 4A), piglets in the CM group had a higher abundance of Clostridium XI, Tuicibater, and Moraxella in the jejunum than those of piglets in the SM group (p<0.05). By d 35 of age (Figure 4B), the Lactobacillus, Streptophyta, Streptococcus, and Clostridium XI were predominant. In addition, the abundance of Lactobacillus was significantly increased, while the abundance of Streptococcus and Blautia was statistically decreased in the CM group by d 35 of age (p<0.05).
Previous study revealed that an early CM supplement could challenge the gut function, and damage the host health [20]. In our study, we revealed that milk supplement numerically increased the litter weight, but the difference was not significant, and no significant difference was observed in ADG and ADFI between two groups during experiment period [21]. The villus height and the crypt depth are useful criterions to evaluate the nutrient digestion and absorption capacity of the jejunum [22]. In the present study, no significant difference was observed in jejunal morphology (villus height and the crypt depth) between the SM group and CM group on d 28 and d 35 of age, indicating that the early milk supplement has no effect on the jejunal mucosa structure. It is noteworthy that disaccharidases localized on the jejunal microvilli could promote the newbornŌĆÖs development by contributing to the carbohydrate digestion and absorption [23]. In the present study, the piglets in the CM group had a higher sucrase activity and lower lactase activity than those in the SM group by d 28 of age, which suggested that the CM supplement could alter the absorption of different sugars in piglets. In addition, the piglets in the CM group had higher maltase activity than those in the SM group by d 35. The maltase to lactase ratio, an index of gut maturation, was increased in the CM group by d 28 and d 35 of age, suggesting that CM supplement contributes to gut maturation [24]. Therefore, the early CM supplement not only had no negative effect on the growth performance and the jejunal morphology, but also promoted the maturity of jejunum to some extent by altering the disaccharidases activities.
The bacterial community is important to the host intestinal physiology, affecting morphology, nutrient digestion, and metabolism [25]. Early nutritional composition is the major factor influencing the bacterial community [26]. In the present study, the Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria were the predominant bacteria at the phylum level, which is consistent as reported by Cao et al [27]. At the genus level, the piglets in the CM group had a higher abundance of Clostridium XI, Tuicibater, and Moraxella in the jejunum than those of piglets in the SM group by d 28 of age. Clostridium XI belonging to the Firmicutes contributes to the increase of ╬▓-glucuronidase activity, which is conductive to nutrient utilization and gut health [28]. Moreover, the CM piglets had a higher abundance of Lactobacillus than the SM piglets by d 35 of age, indicating that the early CM supplement could help maintain the intestinal homeostasis by increasing the abundance of beneficial bacteria [29]. The microbial stability in the gut plays a critical role in maintaining the health status of the host gut by impacting nutrient utilization, enhancing gut barrier function and simulating immune development [30]. Thompson et al [31] revealed that the early CM supplement may shape colonization of microbiota and increase the diversity of microbiota. Consistent with the previous research, piglets in the CM group had an increased tendency of microbial diversity in the present study by d 28 of age, suggesting that the early CM supplement could make the jejunal bacterial community more stable. Therefore, the early CM supplement changed the jejunal bacterial community and benefitted the stability of the jejunal bacterial community by increasing diversity of microbiota.
The bacteria could modulate the gut physiology by ferment ing simple structure carbohydrates to produce the metabolites, such as the SCFAs and lactate, which could promote the energy intake, stimulate water and sodium absorption, and low the luminal pH value [30,32]. In our study, the increased total SCFAs (mainly the acetate) in the CM group by d 28 of age indicated that the bacterial fermentation ability was enhanced. Previous research revealed that Clostridium XI had the SCFA-producing ability, which may be the reason for the increasing total SCFAs in the present study [33]. Increased SCFAs could keep the homeostasis of the intestinal environment and improve the gut immune system [34]. In addition, the lactic acid concentration was statistically increased, and the pH value was significantly decreased in the CM group by day 35 of age. The increased lactic acid concentration and decreased pH value were probably caused by the increased abundance of Lactobacillus, as the Lactobacillus is the major lactic acid bacteria and the increased lactic acid leaded to the decrease of pH [29]. The low pH value in jejunum is conducive to maintain the integrity of the mucosal morphology, partially inhibit harmful bacteria, and promote the colonization of beneficial bacteria [35]. The fermentation products from these facultative anaerobes is available to the host epithelial cells as an additional energy source, and can also serve as the substrates for other microbes, such as Veillonella species which could utilize the lactic acid as a carbon and energy source to provide energy for the host [36]. Therefore, these results showed that the early CM supplement could help maintain a stable jejunum internal environment via producing the metabolites and decreasing the pH value.
The early CM supplement had no effect on the jejunal mucosal morphology in piglets but improved the maturation of the jejunum to some extent by enhancing the maltase and sucrase activities. Moreover, the early CM supplement induced a more stable bacterial community by increasing the diversity indices with changing the bacterial composition. Finally, the early CM supplement promoted the homeostasis of internal environment in jejunum by increasing the microbial-derived metabolites, such as acetate and lactate.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank National Center for International Research on Animal Gut Nutrition for financial support.
This study was supported by National Key R &D Program of China 2017YFD0500505 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China (KYZ201722).
Figure┬Ā1
Effects of early commercial milk supplement on disaccharidase activities in the jejunum of piglets on day 28 and day 35. (A) Disaccharidase activities on day 28, (B) Disaccharidase activities on day 35. Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars, n = 5. * Means are different (p<0.05) between the SM group and CM group. The SM group are the piglets reared by the sows, the CM group are the piglets supplemented with a commercial milk along with suckling.

Figure┬Ā2
Relative abundance of microbiota at the phylum level. (A) On day 28; (B) On day 35. Values are means, n = 5. The SM group are the piglets reared by the sows, the CM group are the piglets supplemented with a commercial milk supplement along with suckling.
Figure┬Ā3
Relative abundance of microbiota in jejunal digesta at the genus level on day 28 and day 35. Values are means, n = 5.

Figure┬Ā4
Effects of early commercial milk supplement on the significantly changed genera in jejunal digesta. (A) On day 28; (B) On day 35; values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars, n = 5. * Means are different (p<0.05) between the SM group and CM group. The SM group are the piglets reared by the sows, the CM group are the piglets supplemented with a commercial milk supplement along with suckling.
Table┬Ā1
The nutrient composition of the commercial milk supplement (air-dry basis) and sow milk
| Items | Milk supplement | Sow milk1) |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient (%) | ||
| ŌĆāCorn | 39.20 | - |
| ŌĆāWhey powder | 18.95 | - |
| ŌĆāSoybean meal | 18.43 | - |
| ŌĆāExtruded soybean | 15.38 | - |
| ŌĆāFish meal | 6.23 | - |
| ŌĆāDicalcium phosphate | 0.38 | - |
| ŌĆāSodium chloride | 0.50 | - |
| ŌĆāL-lysine | 0.50 | - |
| ŌĆāDL-methionine | 0.30 | - |
| ŌĆāZinc chloride | 0.10 | - |
| ŌĆāVitamins | 0.03 | - |
| ŌĆāPhytase | 0.01 | - |
| Calculated composition (%) | ||
| ŌĆāCrude protein | 20.63 | 5.31 to 15.33 [10] |
| ŌĆāCrude fibre | 1.64 | - |
| ŌĆāCrude ash | 5.67 | 0.89 to 1.20 [11] |
| ŌĆāCalcium | 0.76 | 0.07 to 0.17 [12] |
| ŌĆāPhosphorus | 0.64 | 0.11 to 0.13 [12] |
| ŌĆāNaCl | 0.60 | - |
| ŌĆāLysine | 1.50 | 0.35 to 1.05 [13] |
| ŌĆāMoisture | 6.90 | - |
Table┬Ā2
Effects of the early commercial milk supplement on the mucosal morphology in jejunum of piglets on the day 28 and 35
| Items | Treatments1) | SEM | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||
| SM | CM | |||
| day 28 | ||||
| ŌĆāVillus height (╬╝m) | 321.34 | 307.85 | 26.09 | 0.786 |
| ŌĆāCrypt depth (╬╝m) | 105.34 | 96.16 | 9.79 | 0.407 |
| ŌĆāVillus height:crypt depth (%) | 3.02 | 3.33 | 0.45 | 0.592 |
| day 35 | ||||
| ŌĆāVillus height (╬╝m) | 259.01 | 274.83 | 29.27 | 0.611 |
| ŌĆāCrypt depth (╬╝m) | 91.06 | 97.47 | 10.74 | 0.568 |
| ŌĆāVillus height:crypt depth (%) | 2.87 | 2.83 | 0.21 | 0.833 |
Table┬Ā3
The pH value and the concentrations of the lactic acid, ammonia N, different SCFAs and total SCFAs in the jejunal digesta of piglets on day 28
| Items | Treatments1) | SEM | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||
| SM | CM | |||
| pH value | 5.89 | 5.97 | 0.04 | 0.251 |
| Acetate (╬╝mol/g) | 0.30 | 0.56 | 0.06 | 0.004 |
| Propionate (╬╝mol/g) | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.528 |
| Butyrate (╬╝mol/g) | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.932 |
| Valerate (╬╝mol/g) | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.267 |
| BCFAs (╬╝mol/g)2) | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.334 |
| Total SCFAs (╬╝mol/g)3) | 0.58 | 0.90 | 0.09 | 0.011 |
| Ammonia N (╬╝mol/g) | 28.17 | 21.54 | 5.64 | 0.314 |
| Lactic acid (mmol/L) | 1.14 | 1.39 | 0.13 | 0.072 |
Table┬Ā4
The pH value and the concentrations of the lactic acid, ammonia N, different SCFAs and total SCFAs in the jejunal digesta of piglets on day 35
| Items | Treatments1) | SEM | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||
| SM | CM | |||
| pH value | 6.33 | 5.79 | 0.15 | 0.032 |
| Acetate (╬╝mol/g) | 0.41 | 0.57 | 0.11 | 0.258 |
| Propionate (╬╝mol/g) | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.317 |
| Butyrate (╬╝mol/g) | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.944 |
| Valerate (╬╝mol/g) | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.713 |
| BCFAs (╬╝mol/g)2) | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.676 |
| Total SCFAs (╬╝mol/g)3) | 0.69 | 0.89 | 0.24 | 0.448 |
| Ammonia N (╬╝mol/g) | 16.62 | 13.94 | 5.88 | 0.664 |
| Lactic acid (mmol/L) | 1.02 | 1.31 | 0.12 | 0.041 |
REFERENCES
1. Peterson LW, Artis D. Intestinal epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol 2014; 14:141ŌĆō53. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3608



2. El Aidy S, van den Bogert B, Kleerebezem M. The small intestine microbiota, nutritional modulation and relevance for health. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2015; 32:14ŌĆō20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.09.005


3. Chen H, Mao XB, Che LQ, et al. Impact of fiber types on gut microbiota, gut environment and gut function in fattening pigs. Anim Feed Sci Technol 2014; 195:101ŌĆō11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2014.06.002

4. Sommer F, B├żckhed F. The gut microbiota--masters of host development and physiology. Nat Rev Microbiol 2013; 11:227ŌĆō38. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2974



5. Theil PK, Lauridsen C, Quesnel H. Neonatal piglet survival: impact of sow nutrition around parturition on fetal glycogen deposition and production and composition of colostrum and transient milk. Animal 2014; 8:1021ŌĆō30. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731114000950


6. Foxcroft GR. Reproduction in farm animals in an era of rapid genetic change: will genetic change outpace our knowledge of physiology? Reprod Domest Anim 2012; 47:313ŌĆō9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0531.2012.02091.x

7. Thymann T, Burrin DG, Tappenden KA, Bjornvad CR, Jensen SK, Sangild PT. Formula-feeding reduces lactose digestive capacity in neonatal pigs. Br J Nutr 2006; 95:1075ŌĆō81. https://doi.org/10.1079/BJN20061743


8. De Vos M, Huygelen V, Willemen S, et al. Artificial rearing of piglets: Effects on small intestinal morphology and digestion capacity. Livest Sci 2014; 159:165ŌĆō73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2013.11.012

9. Wolter BF, Ellis M, Corrigan BP, Dedecker JM. The effect of birth weight and feeding of supplemental milk replacer to piglets during lactation on preweaning and postweaning growth performance and carcass characteristics. J Anim Sci 2002; 80:301ŌĆō8. https://doi.org/10.2527/2002.802301x



10. Yang YX, Heo S, Jin Z, et al. Effects of lysine intake during late gestation and lactation on blood metabolites, hormones, milk composition and reproductive performance in primiparous and multiparous sows. Anim Reprod Sci 2009; 112:199ŌĆō214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2008.04.031


11. Aguinaga MA, G├│mez-Carballar F, Nieto R, Aguilera JF. Production and composition of Iberian sowŌĆÖs milk and use of milk nutrients by the suckling Iberian piglet. Animal 2011; 5:1390ŌĆō7. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731111000474


12. Hu P, Yang H, Lv B, Zhao D, Wang J, Zhu W. Dynamic changes of fatty acids and minerals in sow milk during lactation. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 2019; 103:603ŌĆō11. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpn.13040

13. Daza A, Riop├®rez J, Centeno C. Changes in the composition of sows milk between days 5 to 26 of lactation. Span J Agric Res 2004; 2:333ŌĆō6. http://dx.doi.org/10.5424/sjar/2004023-102

14. Nyachoti CM, Omogbenigun FO, Rademacher M, Blank G. Performance responses and indicators of gastrointestinal health in early-weaned pigs fed low-protein amino acid-supplemented diets. J Anim Sci 2006; 84:125ŌĆō34. https://doi.org/10.2527/2006.841125x



15. Zhou L, Fang L, Sun Y, Su Y, Zhu W. Effects of the dietary protein level on the microbial composition and metabolomic profile in the hindgut of the pig. Anaerobe 2016; 38:61ŌĆō9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2015.12.009


16. Mao SY, Zhang G, Zhu WY. Effect of disodium fumarate on ruminal metabolism and rumen bacterial communities as revealed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of 16S ribosomal DNA. Anim Feed Sci Technol 2008; 140:293ŌĆō306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2007.04.001

17. Zoetendal EG, Akkermans ADL, De Vos WM. Temperature gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of 16S rRNA from human fecal samples reveals stable and host-specific communities of active bacteria. Appl Environ Microb 1998; 64:3854ŌĆō9.

18. Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J 2012; 6:1621ŌĆō4. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2012.8




19. Sun Y, Zhou L, Fang L, Su Y, Zhu W. Responses in colonic microbial community and gene expression of pigs to a long-term high resistant starch diet. Front Microbiol 2015; 6:877https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00877



20. Sangild PT, Thymann T, Schmidt M, Stoll B, Burrin DG, Buddington RK. Invited review: the preterm pig as a model in pediatric gastroenterology. J Anim Sci 2013; 91:4713ŌĆō29. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2013-6359




21. Niu Q, Wang J, Shi C, Wang J, Zhu W. Effect of early supplementary feeding milk replacer on pigletsŌĆÖ ileum bacterial community and bacterial metabolites. Anim Husb Vet 2017; 49:17ŌĆō24.
22. Xiong X, Yang HS, Wang XC, et al. Effect of low dosage of chito-oligosaccharide supplementation on intestinal morphology, immune response, antioxidant capacity, and barrier function in weaned piglets. J Anim Sci 2015; 93:1089ŌĆō97. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2014-7851


23. Commare CE, Tappenden KA. Development of the infant intestine: implications for nutrition support. Nutr Clin Pract 2007; 22:159ŌĆō73. https://doi.org/10.1177/0115426507022002159


24. Yang C, Zhu X, Liu N, et al. Lactoferrin up-regulates intestinal gene expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factors BDNF, UCHL1 and alkaline phosphatase activity to alleviate early weaning diarrhea in postnatal piglets. J Nutr Biochem 2014; 25:834ŌĆō42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.03.015


25. Hermann-Bank ML, Skovgaard K, Stockmarr A, et al. Characterization of the bacterial gut microbiota of piglets suffering from new neonatal porcine diarrhoea. BMC Vet Res 2015; 11:139https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-015-0419-4




26. Wang M, Radlowski EC, Monaco MH, Fahey GC, Gaskins HR, Donovan SM. Mode of delivery and early nutrition modulate microbial colonization and fermentation products in neonatal piglets. J Nutr 2013; 143:795ŌĆō803. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.112.173096



27. Cao KF, Zhang HH, Han HH, Song Y, Bai XL, Sun H. Effect of dietary protein sources on the small intestine microbiome of weaned piglets based on high-throughput sequencing. Lett Appl Microbiol 2016; 62:392ŌĆō8. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12559


28. Laparra JM, Sanz Y. Interactions of gut microbiota with functional food components and nutraceuticals. Pharmacol Res 2010; 61:219ŌĆō25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2009.11.001


29. van Baarlen P, Wells JM, Kleerebezem M. Regulation of intestinal homeostasis and immunity with probiotic lactobacilli. Trends Immunol 2013; 34:208ŌĆō15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2013.01.005


30. Loh G, Eberhard M, Brunner RM, et al. Inulin alters the intestinal microbiota and short-chain fatty acid concentrations in growing pigs regardless of their basal diet. J Nutr 2006; 136:1198ŌĆō202. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/136.5.1198



31. Thompson AL, Monteagudo-Mera A, Cadenas MB, et al. Milk- and solid-feeding practices and daycare attendance are associated with differences in bacterial diversity, predominant communities, and metabolic and immune function of the infant gut microbiome. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2015; 5:3https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2015.00003



32. Marques TM, Wall R, Ross RP, Fitzgerald GF, Ryan CA, Stanton C. Programming infant gut microbiota: influence of dietary and environmental factors. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2010; 21:149ŌĆō56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2010.03.020


33. P├®rez-Cobas AE, Artacho A, Ott SJ, Moya A, Gosalbes MJ, Latorre A. Structural and functional changes in the gut microbiota associated to Clostridium difficile infection. Front Microbiol 2014; 5:335https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00335



34. Oude Elferink SJWH, Krooneman J, Gottschal JC, Spoelstra SF, Faber F, Driehuis F. Anaerobic conversion of lactic acid to acetic acid and 1, 2-propanediol by Lactobacillus buchneri. Appl Environ Microbiol 2001; 67:125ŌĆō32. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.1.125-132.2001



35. Barrow PA, Brooker BE, Fuller R, Newport MJ. The attachment of bacteria to the gastric epithelium of the pig and its importance in the microecology of the intestine. J Appl Bacteriol 1980; 48:147ŌĆō54.


36. Daly K, Darby AC, Hall N, Nau A, Bravo D, Shirazi-Beechey SP. Dietary supplementation with lactose or artificial sweetener enhances swine gut Lactobacillus population abundance. Br J Nutr 2014; 111:S30ŌĆō5. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114513002274








 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement
Supplement Print
Print





