 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 33(5); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Figure┬Ā1
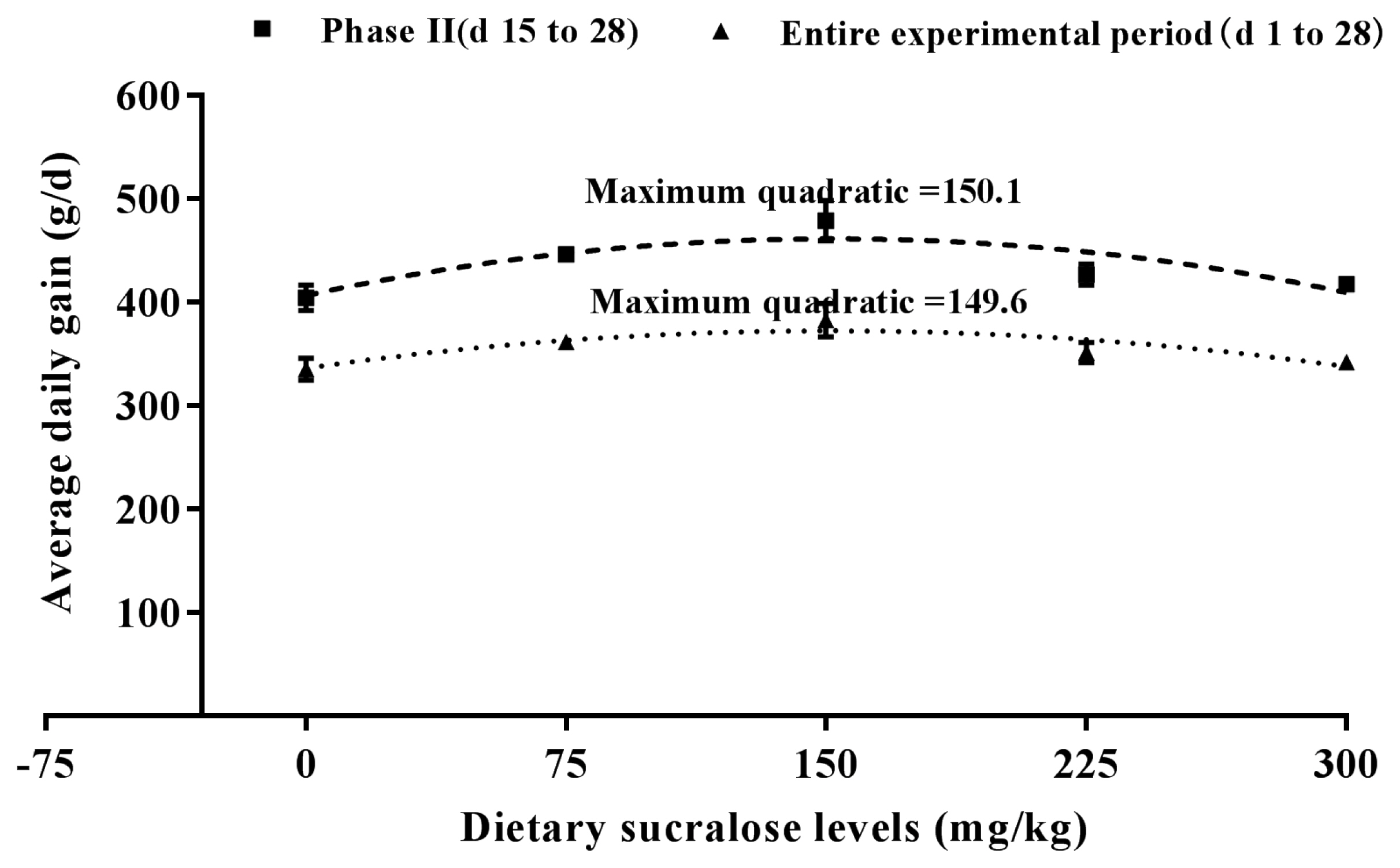
Figure┬Ā2
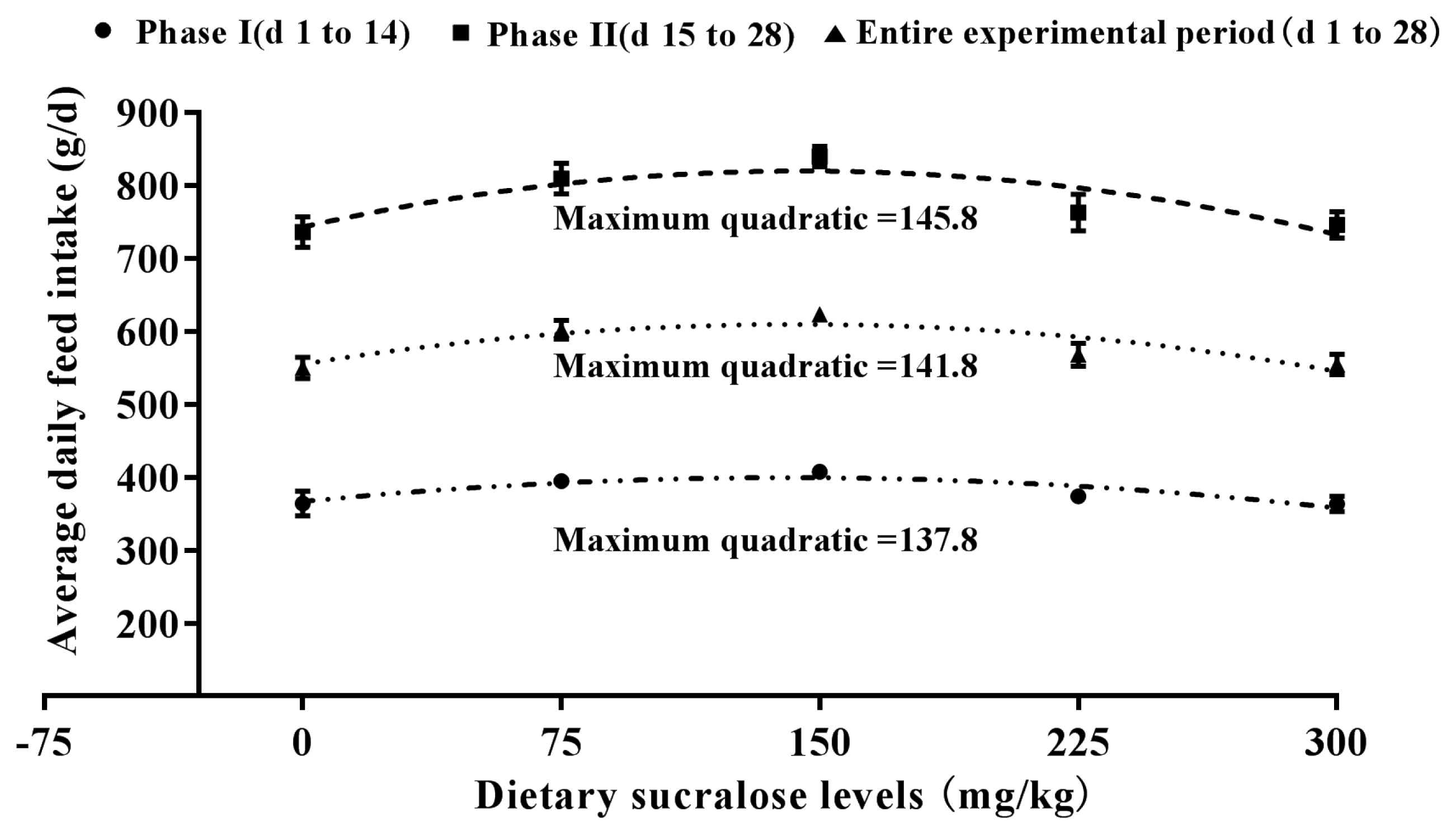
Figure┬Ā3
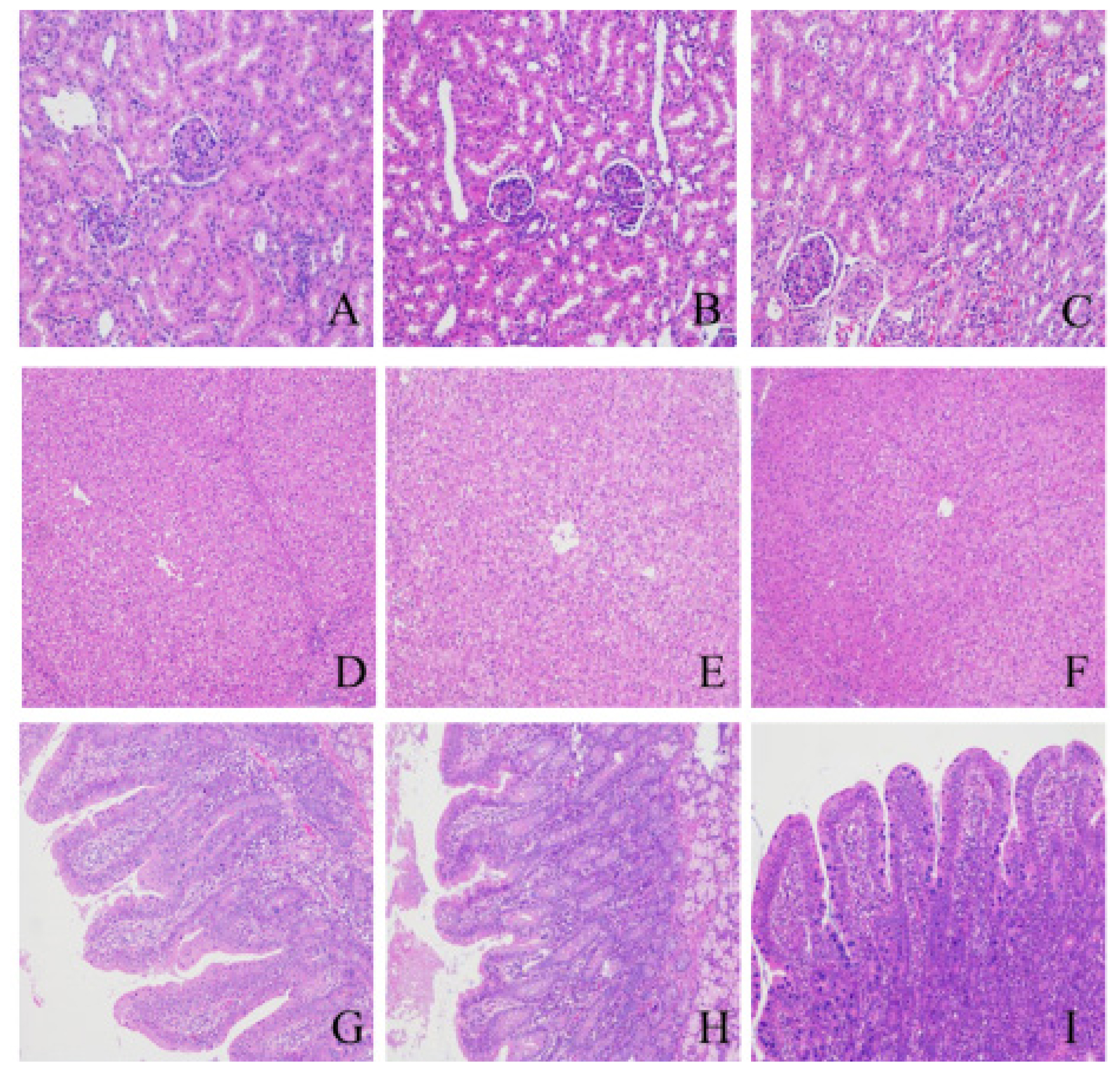
Table┬Ā1
| Items | Basal diet | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Phase I | Phase II | |
| Ingredient | ||
| ŌĆāGround corn | 533.8 | 581.6 |
| ŌĆāSoybean meal (46% crude protein) | 177.5 | 159.0 |
| ŌĆāExpanded soybean | 163.5 | 130.0 |
| ŌĆāDried whey (12% crude protein) | 46.4 | 62.1 |
| ŌĆāFish meal | 27.4 | 26.5 |
| ŌĆāSoybean oil | 16.9 | 10.2 |
| ŌĆāDicalcium phosphate | 11.2 | 10.0 |
| ŌĆāGround limestone | 7.4 | 5.0 |
| ŌĆāSalt | 2.3 | 3.0 |
| ŌĆāL-Lysine HCl | 3.5 | 3.8 |
| ŌĆāL-Threonine | 1.3 | 1.2 |
| ŌĆāDL-Methionine | 1.8 | 1.6 |
| ŌĆāCholine chloride | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| ŌĆāVitamin-mineral premix2) | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Chemical analysis | ||
| ŌĆāDigestible energy3) (MJ/kg) | 14.9 | 14.7 |
| ŌĆāCrude protein | 209.9 | 193.3 |
| ŌĆāLysine | 14.6 | 13.8 |
| ŌĆāMethionine | 4.4 | 3.9 |
| ŌĆāMethionine+cysteine | 7.4 | 6.8 |
| ŌĆāThreonine | 7.9 | 7.7 |
| ŌĆāCalcium | 8.5 | 8.2 |
| ŌĆāTotal phosphorus | 6.6 | 6.0 |
1) In experiment 1, the basal diet was supplemented with 150 mg/kg sucralose. In experiment 2, the basal diets were supplemented with 75, 150, 225, or 300 mg/kg sucralose (Phase I and II). In experiment 3, the basal diets were supplemented with 150, or 1,500 mg/kg sucralose (Phase I and II).
2) Provided per kg of diet: vitamin A, 12,000 IU; vitamin D3, 2,000 IU; vitamin E, 30 IU; vitamin K3, 2.5 mg; thiamin, 2.5 mg; riboflavin, 4 mg; pyridoxine, 3 mg; vitamin B12, 20 ╬╝g; niacin, 40 mg; pantothenic acid, 12.5 mg; folic acid, 0.7 mg; biotin, 0.07 mg; Fe as iron sulfate, 100 mg; Cu as copper sulfate, 90 mg; Zn as zinc sulfate, 80 mg; Mn as manganese sulfate, 30 mg; I as potassium iodide, 0.25 mg; Se as sodium selenite, 0.15 mg.
3) Calculated value according to DE value of each ingredient provided by NRC [19].






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





