 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 32(11); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to measure genetic diversity and to determine the relationships among fourteen goose breeds.
Methods
Microsatellite markers were isolated from the genomic DNA of geese based on previous literature. The DNA segments, including short tandem repeats, were tested for their diversity among fourteen populations of geese. The diversity was tested on both breeds and loci level and by mean of unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean and structure program, phylogenetic tree and population structure were tested.
Results
A total of 108 distinct alleles (1%) were observed across the fourteen breeds, with 36 out of the 108 alleles (33.2%) being unique to only one breed. Genetic parameters were measured per the 14 breeds and the 9 loci. Medium to high heterozygosity was reported with high effective numbers of alleles (Ne). Polymorphic information contents (PIC) of the screened loci was found to be highly polymorphic for eleven breeds; while 3 breeds were reported moderately polymorphic. Breeding coefficient (FIS) ranged from −0.033 to 0.358, and the pair wise genetic differentiation (FST) ranged from 0.01 to 0.36 across the fourteen breeds; for the 9 loci observed and expected heterozygosity, and Ne were same as the breeds parameters, PIC of the screened loci reported 6 loci highly polymorphic and 3 loci to be medium polymorphic, and FIS ranged from −0.113 to 0.368. In addition, genetic distance estimate revealed a close genetic distance between Canada goose and Hortobagy goose breeds by 0.04, and the highest distance was between Taihu goose and Graylag goose (anser anser) breed by 0.54.
Geese play a minor role in meat and egg production compared to chicken worldwide. On the other hand, the nutrition values of protein, vitamin A, vitamin B, niacin and sugar content are higher in goose meat, than that in pork or mutton. The energy content is 30% to 63% greater than that of other poultry with the advantage of low-fat and cholesterol content [1,2]. Geese have many other economic benefits such as: their large body size, strong adaptability to extensive management, high reproduction rate, along with good disease resistance [3]. For all these reasons, geese production is of considerable importance and of great commercial interest.
In the past few decades, extensive production systems have been instituted by many countries aiming for high quality and quantity of meat as their primary breeding objective. As a direct result of these systems, some goose breeds with specific features either have declined or their breed characteristics diluted to improve their genetic admixture [4,5].
The evaluation of genetic variation can be done using several techniques. One of the most important techniques is the usage of microsatellites. Microsatellites have many advantages including their large number of polymorphisms, abundance, co-dominant inheritance, analytical simplicity, and transferability [6–8]. In recent years, microsatellite-based studies have been used for the genetic evaluation and mapping between local geese breeds in China, revealing that some geese breeds are at risk of becoming genetically homogenous [9]. The development of effective and appropriate breeding management practices is needed to maintain the genetic diversity and structure of these breeds [4,10,11]. Genetic structure of 14 grey goose breeds was studied using 31 microsatellite markers. A total of 25 were moderately polymorphic, and the phylogenetic tree was completed through analysis of unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) revealing three main branches, two for Chinese breeds and one for the Yili goose (Yi) breed [12].
In recent studies the genetic diversity among geese populations in Taiwan were evaluated along with industrial white Rom farms revealed unified genetic structures in their breeders, ensuring more stable and better performing populations. However, Chinese breeds raised at private farms revealed an uneven structure, indicating that breeding management requires urgent care to ensure stable production, maintain genetic resources, and develop hybrid geese for better meat quality [13].
The mitochondrial DNA control region sequence variation of domestic geese was analyzed to evaluate the main matrilineal components and their phylogenetic relationships. Our results supported that Chinese domestic goose breeds (except the Yi breed) originated from the Swan goose (Anser cygnoides) (Sw); while European goose breeds originated from Graylag goose (Anser anser) (Gray) [13,14].
In the present study, we used 14 goose breeds. They were classified according to their geographical distribution into: four Chinese breed (Yangzhou, Shitou, Yili, and Taihu); five Europeans (Landes, Roman, Leime, Carolas, and Hortobagy); 2 African Egyptian breeds; 2 wild (graylag and white swan and one American breed [Canada]). We evaluated both the genetic diversity and genetic relationship between these populations. In order to give recent information about genetic diversity among, and within these breeds to optimize the utilization of goose genetic resources, and permit efficient genetic improvement for both production and conservation needs.
DNA samples [15] were obtained from 599 unrelated individuals representing 12 domestic and 2 wild geese populations; described as follow: 70 samples Landes goose (Land), 30 Roman goose (Rom), 30 Leime goose (Leim), 75 Yangzhou goose (Yang), 50 Shitou goose (Shi), 65 Yili goose (Yi), 48 Carlos goose (Ca), 48 Taihu goose (Tai), 30 Canada goose (Can), 30 Graylag goose (Gray), 30 Swan goose (Sw), 68 Hortobagy goose (Hort), 60 Egyptian goose (black variety) (Egy B), and 60 Egyptian goose (grey variety) (Egy G).
Nine species-specific microsatellite markers, isolated from geese, were chosen from GenBank and related articles [12,13] and used for geese breed genotyping. The primers were synthesized by Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Shanghai, China. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification was carried out in a 20 μL mixture containing 2 μL of 10×PCR (Mg+2) buffer, 2 μL of 10 mmol/L dNTPs, 1 μL of 10 μmol/μL forward primers, 1 μL of 10 μmol/μL reverse primers, 0.2 μL of 5.0 U/μL Taq DNA polymerase, and 1 μL of 100 ng/μL DNA template, and completed by adding 12.8 μL of double distilled water. After a denaturing step for 5 min at 95°C, samples were processed through 35 cycles of 45 s at 94°C, 45 s at an optimal annealing temperature (55°C to 64°C), and 45 s at 72°C. The last elongation step was extended to 10 min at 72°C, and preserved at 4°C as shown in (Table 1).
After electrophoresis, the 9 fluorescent microsatellite primers were mixed according to their groups as shown in Table 1. DNA Analyzer fluorescence was measured by automatic sequencing of PCR products of short tandem repeat type. The PCR products were sent to Beijing New Industry Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) (TSIGNKE). The independent documents were automatically generated by GeneMapper4.0 software containing fragment length, height of peak, and size of peak area.
The allelic data obtained through individual genotyping were analyzed by using different analytical software. MS toolkit (http://dscar.gene.ie-tcd./microsatellitetoolkit/m) program [16] was implemented to calculate allelic frequency, expected and observed heterozygosity (He and Ho) and polymorphic information content (PIC).
The indices of inbreeding (FIS) and genetic differentiation (FST) were analyzed by FSTAT Weir [17]. Structure software was used for clustering analysis [18]. The Markov chain Monte Carlo procedure was used and 10 independent runs of each K were implemented with 1×106 iterations after a burn-in period of 1×105 iterations for 14 populations. The most likely number of populations (K) was determined according to the procedure explained by [19]; Dispan Procedures [20] and UPGMA to measure standard genetic distance, and genetic distance (DA) and Xlstat to construct Dendrograms of relationships based on these two kinds of genetic distances. Effective numbers of alleles (Ne) was calculated according to the equation stated by [21].
The present study assessed the level of genetic diversity and the population structure of different geese breeds; genetic diversity was measured in terms of allelic frequency, Ho and He, PIC, Ne and inbreeding coefficient (FIS) over the fourteen breeds and the nine microsatellite loci.
The data set was analyzed to calculate allelic frequency, and to determine the presence of private alleles. A total of 108 distinct alleles (1%) were observed across the fourteen breeds, with 36 out of the 108 alleles (33.2%) unique to only one breed as shown in Table 2. With the highest 32% (Land at 152 bp) and the lowest 0.6% (Yang at 146 bp). Meanwhile, one locus G10 and four geese breeds Rom, Leim, Shi, and Egy B did not have any unique alleles.
MATLAB software [22] was used to provide a platform for data visualization and construction of heat map representing allele frequency for all 9 loci in the 14 populations as presented in Figure 1. The interpretation of the color intensity was as follows: the lighter color means low frequency (as light yellow mean 0%), the gradual increase in color density means the increase in the allele frequency until reaching a red color, which indicates the highest value of allele frequency.
Goose populations: Genetic parameters were calculated for the fourteen geese breeds as shown in Table 3. Moderate to high level of average genetic diversity for both He and Ho were recorded; He ranged from 0.482 (Hort) to 0.69 (Sw and Gray), while Ho ranged from 0.345 (Hort) to 0.65 (Can). The PIC were found to be highly polymorphic for eleven breeds, while Hort, Can, and Tai. Were reported to be moderately polymorphic. The Ne ranged from 2.5 (Gray) to 3.39 (Yi). Breeding coefficient (FIS) revealed statistically significant differentiation (p<0.01) among the studied populations. The mean values of FIS ranged from −0.033 (Ca) to 0.358 (Land).
Microsatellite loci: Same parameters were calculated per the nine loci as shown in Table 4. Low to high level of average expected heterozygosity (Exp He) and observed heterozygosity (Obs He) were recorded; He ranged from 0.28 (CKW13) to 0.848 (TTUCG5). Ho ranged from 0.26 (CKW13) to 0.6 (CKW21). PIC across the screened loci reported 6 loci highly polymorphic (PIC>0.5) for G1O, CKW21, TTUCG5, CKW49, GO7, and CKW32 and 3 loci reported medium polymorphic (PIC>0.25) for WWX1, CKW14, and CKW13. The Ne ranged from 1.39 (CKW13) to 6.294 (TTUCG5). The FIS revealed statistically significant differentiation (p<0.01) among the nine loci and ranged from −0.113 (CKW14) to 0.368 (GO7).
Genetic differentiation (FST): The values of genetic differentiation (FST) for each tested population pair are sum-marized in Table 5. It ranged from 0.01 (between Can and Hort) to 0.36 (between Hort and Egy B); and reported to be highly significant (p<0.01).
Genetic distance and phylogenetic tree: The Nei’s [23] DA was calculated to analyze the distance between groups, using Dispan Software, as shown in Table 5. It ranged from 0.04 (between Can and Hort) to 0.54 (between Tai and Gray). Later on, the DA matrix of these populations was used to build phylogenetic trees by mean of the UPGMA. Using this technique as shown in Figure 2 the 14 geese breeds were divided into two clusters, one cluster contained breeds from Chinese origin (Tai, Yang, and Shi), along with Sw and Egy G breed and the second cluster was subdivided into two clades first one contained Hort, Can, Caro, Yi, Leim, Gray, and Rom while second clade contained Egy B and Land geese breed.
The STRUCTURE software [18] program using Bayesian model-based clustering algorithms of multi-locus genotypes was utilized to assign individuals into populations via estimated individual admixture proportions and to infer the number of populations (K) for a given sample. The results from the analysis of all the populations for K = 10 to K = 14 are shown in (Figure 3). Some groups revealed a visual cluster but with interference of other groups.
When K = 10 there was a clear clustering for Hort, Can, Egy G, Gray, Sw, Yang, Shi, Leim, Ca, and Land. K = 11 was the same as K = 10 except for more interference between the breeds. K = 12 the clusters with clear identification were Gray, Sw, Yang, Shi, Leim, Ca, and Land. K = 13 can see clusters for only Gray, Sw, Yang, Leim, Ca, and Land. K = 14 the clearest clusters were for Gray, Sw, Yang, Shi, Ca, and Land.
It is difficult and time-consuming to distinguish indigenous goose breeds on morphological characteristics alone, for this reason it is important to develop molecular markers to aid in goose breeds identification. This will also help in designing an effective breeding program to improve productivity of these breeds, and protect them from becoming extinct.
Allele frequency is defined as the relative frequency of an allele at a particular locus in a population, expressed as a fraction or percentage [24]. The change in allele frequencies that occurs over time within a population leads to genetic diversity. It is the base from which the other genetic parameters can be determined. Presence of private allele can be used as a tool to identify different goose breeds in agreement with [9,12–14].
Heterozygosity, reflects genetic variation in a tested locus among a population. High heterozygosity indicates low genetic uniformity thus high genetic diversity. The mean heterozygosity across all 14 populations and 9 loci in the present work ranged from medium at Hort 0.48 to high at the two wild breeds Sw and Gray 0.69; same as per loci medium at CKW13 0.28±0.12 to high at TTUCG5 0.84±0.03. Medium heterozygosity might be due to inbreeding in population because of the relatively small group in a breeding farm.
On the other hand, high heterozygosity was attributed to direct result of a breeding program based on selection to improve the genetic admixture for some breeds [4,5,25]. Observations of excess heterozygosity are not uncommon in geese, this was consistent with [12,26].
The PIC is a good index for gene fragment polymorphism. The PIC index can be used to evaluate the level of gene variation: when PIC<0.25, the locus has low polymorphism; when PIC>0.5, the locus has high polymorphism; and when PIC ranged between 0.25 and 0.5, the locus has intermediate polymorphism [27]. The PIC were found to be highly polymorphic for eleven breeds; while Hort, Can, and Tai were reported to be moderately polymorphic. In the same context, PIC reported CKW21, G10, TTUCG5, CKW49, G07, and CKW32 of high polymorphism and WWX1, CKW13, and CKW14 of medium polymorphism. This is in consistent with the sampling strategy to fully reflect the population genetic diversity information of the 14 populations. This also is in agreement with [10–14].
The effective population size (Ne) is the number of individuals in the idealized Wright Fisher [28] population that retains the same amount of genetic variation and experiences equally much genetic drift as an actual population irrespective of census size. The high Ne decreases genetic drift, which in turn increases heterozygosity. As mentioned by [1,10].
Population analysis F-statistics are a way of partitioning variances in gene frequencies among subpopulations by using ratios of different variances [29]. The relatively low but positive FIS average, might indicate non-random mating, also these examined loci might be under morphological or productive traits of selective interest. Moreover, FIS is used to obtain a deeper insight to appraise the degree of in-breeding and endangerment potentiality and is considered as an important tool to judge the conservation priority [30]. Accordingly, when FIS is less than 0.05, the breeds are not in danger as in case of Ca breed; between 0.05 to 0.15, they are potentially endangered; between 0.15 to 0.25, they are minimally endangered as in case of Sw, Gray, Leim, Egy G, Egy B, Can, and Tai, breeds; between 0.25 to 0.40, they are endangered as in case of Hort, Rom, Yang, Shi, Yi, and Land breeds; and more than 0.40, they are critically endangered [31]. The FIS results could be related to different factors such as population sub structuring or recent population growth [29]. These findings were the same as [9,12–14].
Genetic differentiation (FST): The pairwise genetic differentiation (FST) is a measure of population differentiation due to genetic structure it ranges from 0 to 1. When FST = 0, there is no differentiation between the subpopulation. When FST = 1, all the alleles in the subpopulation are different [24,31]. The FST value across the 14 studied population showed low (0.01) to moderate mean (0.36) indicating that there is genetic differentiation among the 14 breeds for these values as FST was higher than 0.25 [29], this was recorded in both Egyptian breeds. While in Tai breed, this came along with a heterozygosity record indicating there is some migration occurring; which is an important mechanism for transferring genetic diversity among populations. This may result in a change in allele frequencies affecting the distribution of genetic diversity within the populations, due to new genetic variants be added to the established gene pool of a particular population. This comes in agreement with [9,12,24,30,31].
Genetic distance and phylogenetic tree: The project of breed protection and a plan of breeding can be made by analyzing genetic distance. Genetic distance should be an index for group structure and breeds diversity when breed conservation decisions are being made. Microsatellite allelic gene frequency analysis was one of the best methods at present, as it can reflect the time of diversity as well as genetics and variation among breeds [24].
A variety of genetic distances are currently available, but Nei DA is the most commonly used [23]. The DA was estimated for the 14 studied geese populations across the 9 microsatellite loci. The closest pairwise was recorded between Can and Hort (0.04) and this was supported by clustering in the neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree (Figure 2). The close relationship between Can and Hort can be attributed to the migrating nature of both breeds with the possibility of hybridization between both. Also the close genetic distance between Chinese breeds (Yang, Shi, and Tai) indicates the production system used by China aimed for high quality and quantity of meat [4,5]. On contrary, the widest genetic distance was recorded between Tai and Gray breeds was 0.54.
The clustering based on UPGMA and Nei’s distance is the best method for analyzing genetic diversity in different breed population. Nei [23] discovered that the correct topological tree is more effectively obtained from DA than other genetic distances, when he adopted infinite-allele model for computer simulation; 14 goose breeds were clustered into 2 main branches, which later on divided to four groups. This process reflected their relationship on geographical distribution and origin to some degree. The same findings were found in the previous literature suggesting that Chinese goose breeds (Tai, Yang, and Shi) were derived from the Sw, except for Yi breed, and European goose breeds (Hort, Can, Rom, and Leim) along with Yi breed were derived from the Gray. This assumption is based on morphology and plumage patterns; while for Yi breed this can be attributed to being in conservation zone and under the management of breeding program to improve its low performance [12,14].
The Structure program is based on the Bayesian probability theory and uses the Markov-Monte Carlo simulation algorithm. When the program runs, a mixed model is used to set the number of classification K of the detected population. All individuals can be divided to reflect the genetic structure of the population, especially for the population genetic structure and individual differentiation, migration and other aspects of the study. The structure program can also infer individuals with complex genetic background or migrating individuals in a population based on the number of individual alleles [19]. The attribution judgment of individuals in a group is not possible by ordinary genetic distance-based clustering methods. In this study, 14 groups were analyzed using the Structure program, the population structure was inferred, the accurate population structure map was obtained, K = 10, K = 11, K = 12, K = 13, and K = 14. These values are consistent with the results calculated by genetic distance and phylogenetic tree structure although it was reported that the most probable population structure was at K = 10 (Figure 3), at which the Chinese goose breeds (Tai, Yang, Shi, and Yi) were clustered together forming admixed mosaic cluster. A probable explanation for Yi breed to be interfered with other lines from other populations is that the breed is in conservation zone and under the management of breeding program to improve its low performance [14]; this comes in agreement with the other parameters of the breed (He 0.63 and PIC 0.59). The high genetic admixture and migrations between Egy B and interference from other Chinese and European breeds strains could contribute them forming the admixed mosaic cluster with no clear cluster for the breed.
Microsatellite markers are the more credible tool for the research of breed origins. This is due to the evolution of breeds in nature, and artificial selection had a little effect on the structure of Microsatellite locus. The clustering results support the hypothesis that geographical distance is an important factor influencing the genetic relatedness of populations’ and provided some useful data for evaluation of breeding programs results.
Figure 1
Heat map representing allele frequency for 9 loci in all 14 population as the gradual increase in color density from lighter color
 to darker color
to darker color
 means the increase in the allele frequency as the red color, which indicates the highest value of allele frequency.
means the increase in the allele frequency as the red color, which indicates the highest value of allele frequency.
 to darker color
to darker color
 means the increase in the allele frequency as the red color, which indicates the highest value of allele frequency.
means the increase in the allele frequency as the red color, which indicates the highest value of allele frequency.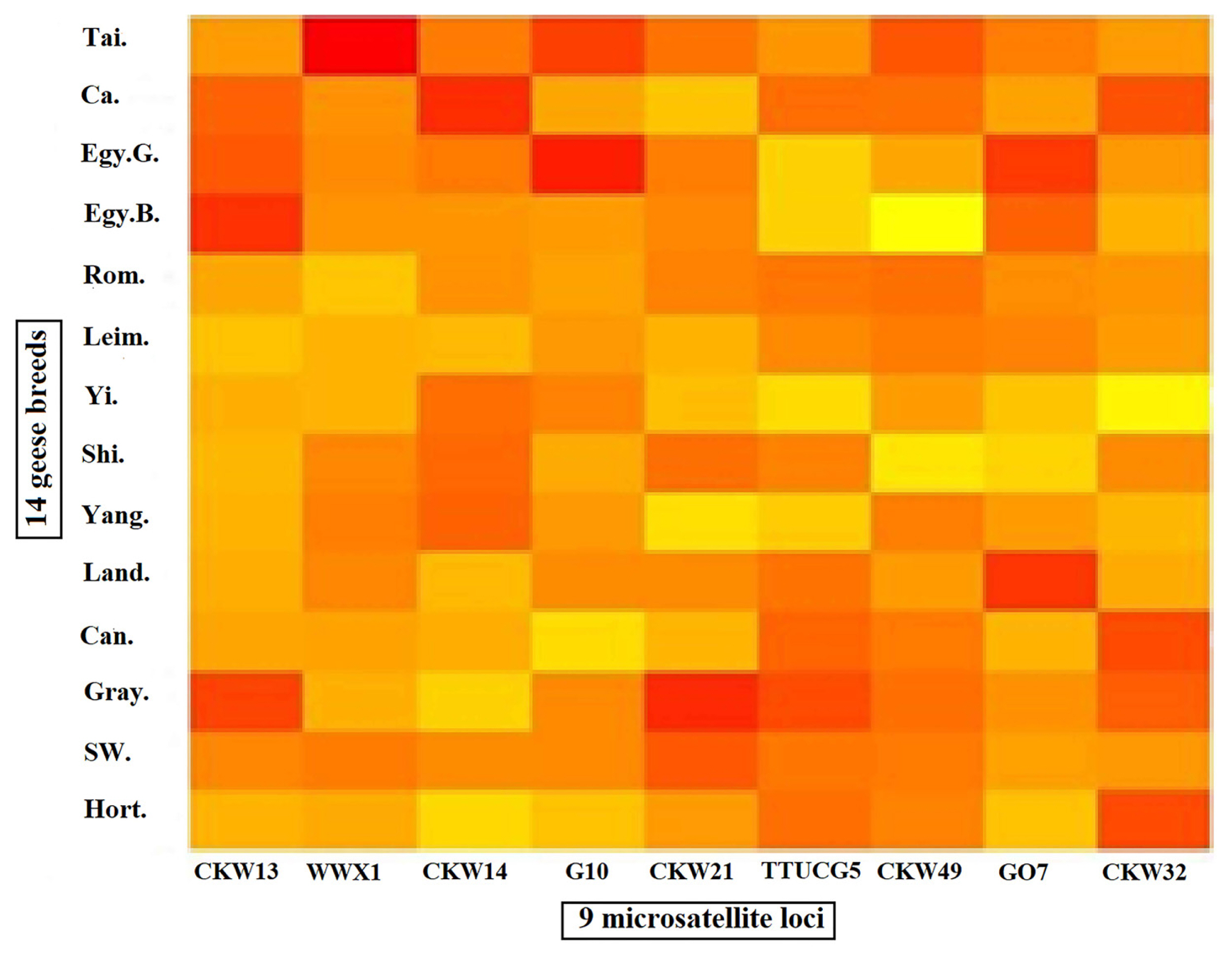
Figure 2
Unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) dendrogram based on genetic distance deriving from analysis of 9 microsatellite loci for the wild and hatchery populations of 14 geese breeds, which were divided into two clusters, one cluster contained breeds from Chinese origin Yangzhou goose (Yang), Shitou goose (Shi) and Taihu goose (Tai), along with swan (Sw) and Egyptian goose (grey variety) (Egy G) and the second cluster was subdivided into two clades first one contained Roman goose (Rom), Leime goose (Leim), Yili goose (Yi), Carlos goose (Ca), Canada goose (Can), Graylag goose (Gray) and Hortobagy goose (Hort), while second clade contained Egyptian goose (black variety) (Egy B), and Landes goose (Land).

Figure 3
Structural analyses of goose populations. Each genotyped goose is represented by a single vertical line divided into K colors, where K is the number of clusters assumed in each structure analysis. Each vertical bar represents an individual goose. The colors on a vertical bar represent the probability that an individual belongs to that cluster. The Clustering diagrams of 14 goose breeds obtained from K = 10 to K = 14 using Q matrices of runs with best similarities When K = 10 there was a clear clustering for Hort, Can, Egy G, Gray, Sw, Yang, Shi, Leim, Ca, and Land. K = 11 was the same as K = 10 except for more interference between the breeds. K = 12 the clusters with clear identification were Gray, Sw, Yang, Shi, Leim, Ca, and Land. K = 13 can see clusters for only Gray, Sw, Yang, Leim, Ca, and Land. K = 14 the clearest clusters were for Gray, Sw, Yang, Shi, Ca, and Land. Hort, Hortobagy goose; Can, Canada goose; Egy G, Egyptian goose (grey variety); Gray, Graylag goose; Sw, along with swan; Yang, Yangzhou goose; Shi, Shitou goose; Leim, Leime goose; Ca, Carlos goose; Land, Landes goose.
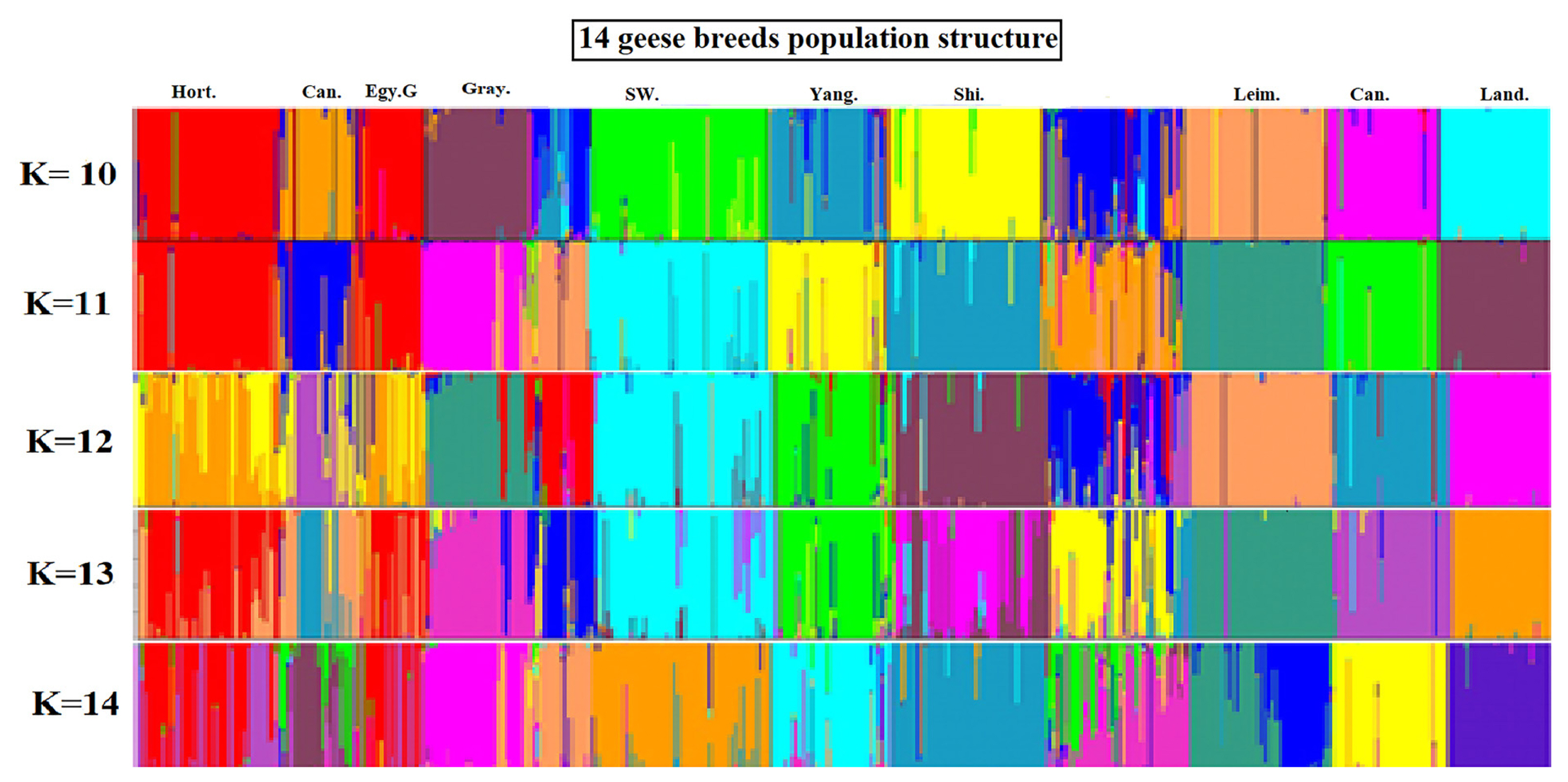
Table 1
Characterization of the nine microsatellites loci used for short tandem repeat genotype
Table 2
Mean number of alleles per locus for private allele across 14 geese population
Table 3
Mean estimates of expected (He), observed (Ho) heterozygosity, effective numbers of alleles (Ne), polymorphic information content (PIC), and FIS estimates per breed
| Geese breeds | He | Ho | PIC | Ne | FIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hort | 0.482±0.252 | 0.345±0.224 | 0.449±0.24 | 2.54±1.533 | 0.287** |
| Sw | 0.69±0.14 | 0.6±0.1 | 0.73±0.17 | 3.66±1.9 | 0.179** |
| Gray | 0.69±0.17 | 0.5±0.2 | 0.64±0.15 | 2.5±1.45 | 0.17** |
| Can | 0.51±0.225 | 0.4±0.272 | 0.464±0.221 | 2.609±1.58 | 0.216** |
| Land | 0.64±0.173 | 0.414±0.121 | 0.603±0.172 | 3.366±1.445 | 0.358** |
| Yang | 0.61±0.179 | 0.422±0.153 | 0.57±0.172 | 3.042±1.32 | 0.309** |
| Shi | 0.59±0.178 | 0.429±.163 | 0.549±0.175 | 2.948±1.384 | 0.286** |
| Yi | 0.63±0.199 | 0.463±0.145 | 0.593±0.195 | 3.39±1.67 | 0.263** |
| Leim | 0.61±0.173 | 0.507±0.129 | 0.557±0.173 | 3.114±1.781 | 0.168** |
| Rom | 0.61±0.161 | 0.437±0.144 | 0.557±0.156 | 2.908±1.193 | 0.286** |
| Egy B | 0.61±0.196 | 0.463±0.141 | 0.567±0.196 | 3.333±2.036 | 0.249** |
| Egy G | 0.62±0.132 | 0.5±0.14 | 0.564±0.145 | 3±1.408 | 0.199** |
| Ca | 0.63±0.121 | 0.65±0.11 | 0.572±0.138 | 3.066±1.468 | −0.033** |
| Tai | 0.522±0.228 | 0.394±0.22 | 0.488±0.221 | 2.73±1.614 | 0.248** |
Table 4
Mean estimates of expected (He), observed (Ho) heterozygosity, effective numbers of alleles (Ne), polymorphic information content (PIC) and FIS estimates per selected fluorescence primer loci
Table 5
The Nei’s genetic distance (upper diagonal) and genetic differentiation FST between different populations (lower diagonal)
REFERENCES
1. Zhu W, Chen K, Li H, et al. Two maternal origins of the Chinese domestic grey goose. J Anim Vet Adv 2010; 9:2674–8.

2. Ding N, Han Q, Li Q, et al. Comprehensive analysis of Sichuan white geese (Anser cygnoides) transcriptome. Anim Sci J 2014; 85:650–9.


3. Xu GF, Chen KW. Photograph album of Chinese indigenous poultry breeds. Beijing, China: Chinese Agriculture Publisher; 2004.
4. Li HF, Chen KW, Yang N, Song WT, Tang QP. Evaluation of genetic diversity of Chinese native geese revealed by microsatellite markers. Worlds Poult Sci J 2007; 63:381–90.

5. Tang Q, Zhang S, Guo J, Chen K, Lu H, Su J. Microsatellite DNA typing for assessment of genetic variability in Taihu goose: a major breed of China. J Anim Vet Adv 2009; 8:2153–7.
6. Gholizadeh M, Mianji GR. Use of microsatellite markers in poultry research. Int J Poult Sci 2007; 6:145–53.

7. Chistiakov DA, Hellemans B, Volckaert FA. Microsatellites and their genomic distribution, evolution, function and applications: a review with special reference to fish genetics. Aquaculture 2006; 255:1–29.

8. Wang ML, Barkley NA, Jenkins TM. Microsatellite markers in plants and insects. Part I: Applications of biotechnology. Genes Genomes Genomics 2009; 3:54–67.
9. Li J, Yuan Q, Shen J, et al. Evaluation of the genetic diversity and population structure of five indigenous and one introduced Chinese goose breeds using microsatellite markers. Can J Anim Sci 2012; 92:417–23.

10. Chen KW, Song WT, Xu WJ, Zhu WQ, Li HF, Tang QP. Assessment of genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of chinese native goose using microsatellite markers. Chinese J Anim Vet Sci 2009; 3:007
11. Liu S, Li P, Song Y, Li SZ, Wei CB, Yang HM. Analysis of genetic variations in different goose breeds using microsatellite markers. Yi Chuan 2006; 28:1389–95.


12. Tu Y, Chen K, Zhang S, Tang Q, Gao Y, Yang N. Genetic diversity of 14 indigenous grey goose breeds in China based on microsatellite markers. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2006; 19:1–6.


13. Lai FY, Tu PA, Ding ST, et al. Survey of genetic structure of geese using novel microsatellite markers. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2018; 31:167–79.



14. Tu Y, Chen K, Tang Q, et al. Genetic diversity of 13 indigenous grey goose breeds in China based on microsatellite markers. Biodivers Sci 2006; 14:152–8.

15. Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1989.
16. Park SDE. Trypanotolerance in West African cattle and the population genetic effects of selection [Ph D thesis]. Dublin, Ireland: University of Dublin; 2001.
17. Goudet J. FSTAT, a program to estimate and test gene diversities and fixation indices 2.9.3.2. Lausanne, Switzerland: Institute of Ecology and Evolution, University of Lausanne; 2002.
18. Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000; 155:945–59.




19. Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 2005; 14:2611–20.


20. Ota T. DISPAN: genetic distance and phylogenetic analysis. University Park, PA, USA: Pennsylvania State University; 1993.
21. Karlin S. Rates of approach to homozygosity for finite stochastic models with variable population size. Am Nat 1968; 102:443–55.

22. Murphy K. The bayes net toolbox for matlab. Comput Sci Stat 2001; 33:1024–34.
24. Ibeagha-Awemu E, Erhardt G. Genetic structure and differentiation of 12 African Bos indicus and Bos taurus cattle breeds, inferred from protein and microsatellite polymorphisms. J Anim Breed Genet 2005; 122:12–20.


25. Cathey J, DeWoody J, Smith L. Brief communication. Microsatellite markers in Canada geese (Branta canadensis). J Hered 1998; 89:173–5.


26. Gillespie JH. Population genetics: a concise guide. Baltimore, MD, USA: Johns Hopkins University Press; 2010.
28. Wright S. Evolution and the genetics of populations, volume 3: experimental results and evolutionary deductions. Chicago, IL, USA: University of Chicago Press; 1984.
29. Ramadan S, Kayang BB, Inoue E, et al. Evaluation of genetic diversity and conservation priorities for Egyptian chickens. Open J Anim Sci 2012; 2:183–90.

- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles
-
Genetic variation analysis of Guanling cattle based on whole-genome resequencing






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print




