 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 33(7); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producing bacteria (GPB) on in vitro rumen fermentation and on the growth performance and meat quality of Hanwoo steers.
Methods
The effects of GPB (Lactobacillus brevis YM 3-30)-produced and commercially available GABA were investigated using in vitro rumen fermentation. Using soybean meal as a substrate, either GPB-produced or commercially available GABA were added to the in vitro rumen fermentation bottles, as follows: control, no additive; T1, 2 g/L GPB; T2, 5 g/L GPB; T3, 2 g/L autoclaved GPB; T4, 5 g/L autoclaved GPB; T5, 2 g/L GABA; and T6, 5 g/L GABA. In addition, 27 Hanwoo steers (602.06±10.13 kg) were subjected to a 129-day feeding trial, during which they were fed daily with a commercially available total mixed ration that was supplemented with different amounts of GPB-produced GABA (control, no additive; T1, 2 g/L GPB; T2, 5 g/L GPB). The degree of marbling was assessed using the nine-point beef marbling standard while endotoxin was analyzed using a Chromo-Limulus amebocyte lysate test.
Results
In regard to in vitro rumen fermentation, the addition of GPB-produced GABA failed to significantly affect pH or total gas production but did increase the ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) concentration (p<0.05) and reduce total biogenic amines (p<0.05). Animals fed the GPB-produced GABA diet exhibited significantly lower levels of blood endotoxins than control animals and yielded comparable average daily gain, feed conversion ratio, and beef marbling scores.
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system that has other known physiological functions, including etiotropic effects on the health status and growth rates of calves [1] and protective effects against neurotoxicant-induced cell death [2]. The GABA is considered as a potent bioactive compound [3] that is synthesized through the irreversible α-decarboxylation of L-glutamic acid, which is catalyzed by glutamic acid decarboxylase [2]. In recent years, researchers have primarily focused on the production of GABA by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) because it possess special physiological activities that could also be used as functional starters [4]. In addition, the production of GABA by LAB is considered safe and eco-friendly [5]. Some LAB species can produce high concentrations of GABA, and the most commonly used bacteria in GABA production are Lactococcus lactis, Lactobacillus brevis, Lb. paracassei, and Lb. delbrüeckii subsp. bulgaricus [6]. One of these GABA-producing bacteria (GPB), namely Lb. brevis, was isolated from kimchi and produces GABA that may inhibit or regulate certain biogenic amine (BA) compounds, such as histamine and tyramine [7].
Owing to the potential of GPB to be used in animal feeding, the present study was conducted to evaluate the ability of the GPB Lb. brevis YM 3-30 to reduce BAs and increase antioxidative substances, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), using an in vitro fermentation technique. In vitro gas production has been used as a valuable tool for evaluating the nutritional value of feedstuffs [8] and techniques for mitigating methane production among ruminants [9]. In the present study, soybean meal, which is a by-product of soybean oil extraction and the most important source of high-quality vegetable protein in animal feed, was used as a fermentation substrate. Furthermore, an in vivo feeding trial was conducted to determine the blood endotoxin level and performance of Hanwoo steer provided with GPB-produced GABA-supplemented feed, in terms of average daily gain (ADG), feed conversion ratio (FCR), and marbling score.
The feeding trial on animal growth performance was conducted at the Sunchon National University (SCNU) animal farm while the laboratory experiments was conducted at the Ruminant Nutrition and Anaerobe Laboratory, Department of Animal Science and Technology, SCNU, Jeonnam, South Korea that were reviewed and approved by the Sunchon National University Animal Research Ethics Committee (SCNU IACUC, approval number: SCNU IACUC-2012-04).
The fermentation processes that occur inside the rumen were simulated using an in vitro ruminal fermentation technique. The GPB Lb. brevis YM 3-30 was isolated from kimchi and anaerobically cultivated in deMan, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) broth (Becton-Dickinson and Company, Difco, Sparks, MD, USA; pH 5.0) that was supplemented with 5% monosodium glutamate (MSG) at 32°C for 48 h. The GPB had an optical density of 1.8 at 600 nm, which corresponded to 107 colony-forming unit (CFU)/mL and a GABA concentration of 45 mg/mL. Using soybean meal as a substrate, either GPB-produced or commercially available GABA were added to the in vitro rumen fermentation bottles, as follows: control, no additive; treatment 1 (T1), 2 g/L GPB; treatment 2 (T2), 5 g/L GPB; treatment 3 (T3), 2 g/L autoclaved GPB; treatment 4 (T4), 5 g/L autoclaved GPB; treatment 5 (T5), 2 g/L GABA; treatment 6 (T6), and 5 g/L GABA. Fresh GPB culture was added to treatments 1 and 2, whereas autoclaved (121°C for 15 min) GPB was added to treatments 3 and 4, and commercially available GABA (99.9%; Sigma-Aldrich, Ltd., St. Louis, Mo, USA) was added to treatments 5 and 6.
Ruminal contents were collected from three 48-month-old ruminally cannulated Hanwoo steers with body weights of 600±47 kg. The contents were squeezed, and the extracted fluids were strained through cheesecloth that had been folded four times. The extracted and strained fluids were then transferred to a glass bottle and maintained at 39°C in a water bath. The upper residue of the rumen fluid was removed using a vacuum pump, whereas the middle portion was collected and used in the experiment. The pooled, particle-free rumen fluid was transferred to a buffer medium [10] (pH 6.7) that was prepared according to the method described by Russell and Van Soest [10].
Next, the buffered rumen fluid (50 mL) was anaerobically transferred under a constant flow of CO2 gas to 160-mL serum bottles that contained soybean meal (2% dry matter [DM] basis; particle size: 2 mm). The bottles that contained the mixed substrate and buffered rumen fluid were sealed using rubber stoppers and aluminum caps and were incubated at 39°C for 12, 24, or 48 h in a shaking incubator (100 rpm). Three replicates were performed for each treatment and incubation period, and the total gas (TG), pH, ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), BA, SOD, and GSH-Px were analyzed after each incubation period. Duplicates of one ml sample were also collected from each of the serum bottles and kept at −50°C until analyses for volatile fatty acids (VFAs) and NH3-N.
The TG production was measured in each of the serum bottles using a press and sensor machine (Laurel Electronics, Inc., Costa Mesa, CA, USA). After TG measurement, the bottles were uncapped, and the pH of each bottle was measured using a Pinnacle series M530p meter (Schott Instruments, Mainz, Germany). Rumen fluid was collected, transferred to Eppendorf tubes, centrifuged, and the NH3-N concentration of the resulting supernatant was measured using the methods developed by Chaney and Marbach [11]. Meanwhile, the VFAs and other metabolites were measured using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC; Agilent Technologies 1200 series, Waldbronn, Baden-Wuttemberg, Germany), according to the methods described by Han et al [12] and Tabaru et al [13], and BA concentrations were measured using Waters Liquid Chromatography (Waters Ltd., Milford, MA, USA) with a Varian column (Pursuit × Rs 5u C-18 250 × 4.6 mm; Varian, Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA) [7]. Finally, total SOD activity was determined by measuring the inhibition of pyrogallol autoxidation (with and without sample) while the GSH-Px was determined by the presence of reduced glutathione and hydrogen peroxide as described in our previous study [7].
Twenty-seven 24- to 25-month-old Hanwoo steers, with an average initial weight of 602.06±10.13 kg, were subjected to a 129-day feeding trial. The animals were randomly selected and equally distributed among the following three groups: control, T1, and T2. During the experiment, the animals were housed in separate pens. The initial weights were measured upon commencement of the feeding trial (day 1), whereas final weight measurement and blood collection for endotoxin analysis were conducted at the termination of the feeding trial (day 129).
Each steer was fed daily with 13 kg commercially available total mixed ration. The feed was divided into morning and afternoon feeding. The feed and chemical composition was shown in Table 1. The GPB Lb. brevis YM 3-30 was cultivated using MRS broth (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Sparks, MD, USA; pH 5.0) that was supplemented with 5% MSG at 32°C or 48 h, and fresh GPB broth cultures with similar bacterial densities and GABA concentrations were added to the animals’ feed. The GABA produced by GPB were evaluated and these were: control, T1, T2. To evenly distribute the GPB within the feed, the amount of GPB to be fed to each animal was mixed into 200 g of either soybean meal (first 60 d) or wheat bran (last 69 d) prior to feeding, and the GPB were added to the feed by sprinkling the inoculated mixtures onto the TMR offered during the morning.
The weight gain of the experimental animals was calculated as the difference between initial weight, which was measured on day 1, and the final weight, which was measured on day 129, whereas ADG was calculated by dividing the weight gain by 129, and FCR was calculated as the ratio of DM intake (DMI) to ADG. Experimental animals were slaughtered after completion of the feeding trial, at which time the degree of marbling was assessed, using the nine-point beef marbling standard, which is regularly used to estimate the quality of Korean beef carcasses. In this grading system, which was established by the Korea Institute of Animal Products Quality Evaluation, a score of 9 indicates very abundant marbling, whereas a score of 1 indicates little or no marbling [14].
For the determination of the plasma endotoxin levels, 3 mL blood was extracted from each animal, by tail venipuncture, on the last day of the feeding trial (day 129) and then centrifuged. The resulting plasma (1.5 mL) was transferred to a microtube and sent to Woojung Bio Co., Ltd. Inc. (Suwon, Korea) for endotoxin analysis, using a Chromo-LAL (Limulus amebocyte lysate) test. Briefly, co-lyophilized LAL and substrate reagent were mixed with a test sample in a microplate and incubated in a reader at 37°C±1°C. Absorbance measurements were then collected at various times following the addition of Chromo-LAL and analyzed. The time (onset time) required for a sample to reach a specified absorbance (onset optical density) was calculated, after which a standard curve that represented the linear correlation between log onset time and log concentration of standard endotoxin was generated. The maximum range of endotoxin concentrations for the standard curve was 0.005 to 50 EU/mL, and the maximum sensitivity (λ) of the assay was defined as the lowest concentration used in the standard curve (0.005 EU/mL).
Data were analyzed by analysis of variance using the general linear model for randomized complete block design. All treatments in in vitro and in vivo studies were conducted in three and nine replications, respectively, and Duncan’s multiple range test was used to identify differences between specific treatments. A significance value of p<0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. All analyses were carried out using Statistical Analysis Systems (SAS) version 9.4 [15].
As shown in Table 2, pH decreased significantly as incubation time increased, with the lowest pH being obtained at 24 and 48 h. Meanwhile, TG production and NH3-N concentration exhibited increasing trends from 12 to 48 h of incubation (p<0.05). The TG produced after 48 h of incubation by the GABA in T6 tended to be higher than other treatments, however, did not differ significantly from that of the control, whereas NH3-N concentration was lowest in the control (p<0.05) and greatest in the T6 treatment (p<0.05), at levels of 107.80 and 158.20 mg/dL, respectively. However, the treatments failed to significantly affect the concentrations of acetate, propionate, or butyrate or the acetate:propionate ratio (Table 3). Notably, higher total VFA production at 48 h in non-autoclaved GPB-produced GABA than autoclaved GPB-produced GABA. Furthermore, the greatest total VFA production at 48 h (108.31 mM) was observed in the T6 treatment and was 11.63 mM greater than that of the control (p<0.05).
The total BA (Table 4) was highest after 48 h of incubation, and the control group yielded the highest concentration (17.22 mM), whereas the treatment groups that contained non-autoclaved GPB-produced GABA and GABA (T1, T2, T5, and T6) yielded the lowest concentrations (10.62 to 11.21 mM; p<0.05). In addition, the control group produced the most histamine (15.99 mM). In contrast, treatment failed to significantly affect the production of SOD or GSH-Px, even though the groups without GPB-produced GABA or GABA exhibited the lowest SOD and GSH-Px levels (55.06 and 27.32 U/mL, respectively). As shown in Figure 1, antioxidant enzyme levels decreased over time, with the highest levels of both SOD and GSH-Px being observed after 48 h of incubation (p<0.05).
As shown in Table 5, the Hanwoo steers fed with GPB-produced GABA exhibited superior weight performance than the control animals. The mean weight gains of the T1 and T2 groups were 6.50 and 18.34 kg greater than those of the control group, respectively, which resulted in higher, but not significantly so, ADG values in the T1 (0.76 kg) and T2 (0.85 kg) groups than in the control (0.71 kg). Treatment also failed to affect the marbling score of the meat. However, as shown in Table 5, the T1 and T2 groups exhibited lower blood endotoxin levels (17.23 and 16.42 EU/mL, respectively) than the control group (29.23 EU/mL; p<0.05).
The significant effects of GABA treatment on pH were only observed during the first 12 h of incubation, and then pH remained relatively stable for the next 36 h, as previously reported by Lounglawan and Suksombat [16], who found that the ruminal pH of dairy cows was not affected by either Lb. plantarum or Lb. acidophilus supplementation at 1×109 CFU/cow/d, when administered with 200 g/d soybean oil. The similar pH values of the control and GABA-treated groups in the present study suggest that the addition of GPB or GABA did not make the in vitro fermentation more acidic and, therefore, that the treatment would not reduce either fiber digestion or the number of fiber-degrading bacteria, both of which are negatively affected by low pH. In addition, the GPB used in the present study was a LAB that could elicit its mode of action as a direct-fed microbe through stabilization of ruminal pH [17] and, therefore, lessen the occurrence of ruminal acidosis.
The concentration of NH3-N also increased with incubation duration, which indicated N became available for microbial utilization and protein synthesis as the incubation period progressed. The NH3-N concentrations of the experimental rumen fluid were considered sufficient for the maximum growth of rumen microbes, whereas a minimum of ~80 mg N/L was required to achieve maximum carbohydrate degradation [18]. The addition of GPB failed to significantly affect the production of individual VFAs, which confirms the findings of Raeth-Knight et al [19], who reported that supplementing the diet of Holstein dairy cows with Lb. acidophilus and Propionibacteria freudenreichii, did not affect ruminal fluid characteristics, at least in terms of individual and total VFA production. However, it was observed in this study that the non-autoclaved GPB-produced GABA had higher efficiency than autoclaved GPB-produced GABA by having higher total VFA production.
The apparently lower concentration of histamine and total BA in the GABA-treated groups than in the control indicates the positive effect of including GPB. This finding was unexpected since the addition of GPB-produced GABA tends to produce more GABA because LAB, such as Lb. brevis, decarboxylate amino acids from substrates to form BAs. Moreover, lower individual and total BA concentrations in the non-autoclaved GPB-produced GABA indicate higher efficiency than autoclaved GPB-produced GABA. In vivo studies conducted by Buchanan-Smith [20] revealed that the addition of BAs and GABA to a silage basal diet can reduce intake owing to the possible role of nitrogenous constituents. However, Dawson and Mayne [21] reported that amines, GABA, or silage juice, at concentrations of ≤2 g/kg, either added directly to the diet or administered via intraruminal infusion had no significant effect on the voluntary food intake of steer. A relationship between histamine concentration and hyperacidity during metabolic acidosis has also been reported by a variety of functional studies of non-ruminant gastrointestinal cuticles [22]. Moreover, Aschenbach and Gäbel [23] concluded that promotion of systemic acidosis by histamine absorption is due to luminal acidity-induced ruminal epithelial damage and not to histamine.
The SOD and GSH-Px are the primary oxygen free radical-eliminators that decrease during stressful environmental conditions. LeBlanc et al [24], who evaluated the anti-inflammatory effects of catalase (CAT)- or SOD-producing LAB on mice using a trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced Crohn’s disease murine model, reported that mice fed CAT- or SOD-producing LAB exhibited more rapid recoveries from initial weight loss, increased enzymatic activities in the gut, and less intestinal inflammation. Zhang et al [25] also reported that dietary GABA can improve antioxidation among heat-stressed laying hens, as indicated by a significant increase in SOD and GSH-Px activity.
Hanwoo steers fed GPB-produced GABA exhibited superior weight performance than the control animals, even though the difference was not statistically significant. Similar findings were reported by Cruywagen et al [26], who reported that supplementing a milk substitute with Lb. acidophilus did not significantly affect feed efficiency among pre-weaned calves that were older than 2 weeks of age. These findings suggest that animals will benefit most from GPB-produced GABA when supplementation is conducted during the early growth stages. Moreover, Ando et al [27] reported that the addition of LAB (Lb. plantarum and Lb. rhamnosus NGRI 0110) improved silage quality and increased both digestibility and voluntary intake. In addition, treatment did not affect the deposition of intramuscular fat, as indicated by the similar marbling scores of treated and control animals in this study.
It is unlikely that the lower plasma endotoxin levels of the steers fed GPB-produced GABA can be attributed to the reductions in rumen lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and histamine levels caused by GPB-produced GABA supplementation since plasma concentrations of LPS and histamine should not be significantly affected by rumen contents [28]. However, studies in rats suggest that the attenuation of bacteremia and endotoxemia by Lactobacilli administration could be partly attributed to enhanced intestinal motility [29] and protection of the liver against LPS-induced injury, both of which are thought to contribute to the systemic clearance and detoxification of LPS, via anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects [30].
The present study demonstrates the potential utility of GPB in the development of feed additives. In the in vitro fermentation experiments, the inclusion of GPB-produced GABA (2 g/L and 5 g/L) yielded the greatest reduction in BAs and greatest increase in NH3-N production and antioxidant activity. Moreover, the supplementation of cattle feed with GPB reduced plasma endotoxin levels. However, the possible role of the GPB in increasing NH3-N concentration and reducing BA production in vitro and reducing plasma endotoxin level in vivo has yet to be established, and the effects of GABA treatment on rumen microorganisms should be studied further to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the effects of GPB probiotics in cattle.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was funded by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, and Forestry, Republic of Korea (Project No. 317016-03-2-WT011).
Figure 1
Effect γ-aminobutyric acid on the antioxidant concentrations of in vitro fermentation. Con, 0 g/L GPB; T1, 2 g/L GPB; T2, 5 g/L GPB; T3, 2 g/L autoclaved GPB; T4, 5 g/L autoclaved GPB; T5, 2 g/L GABA; and T6, 5 g/L GABA. GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; GPB, GABA-producing bacteria; GSH-Px, glutathione peroxidase; SOD, superoxide dismutase. Values and error bars represent mean±standard deviation values (n = 3).
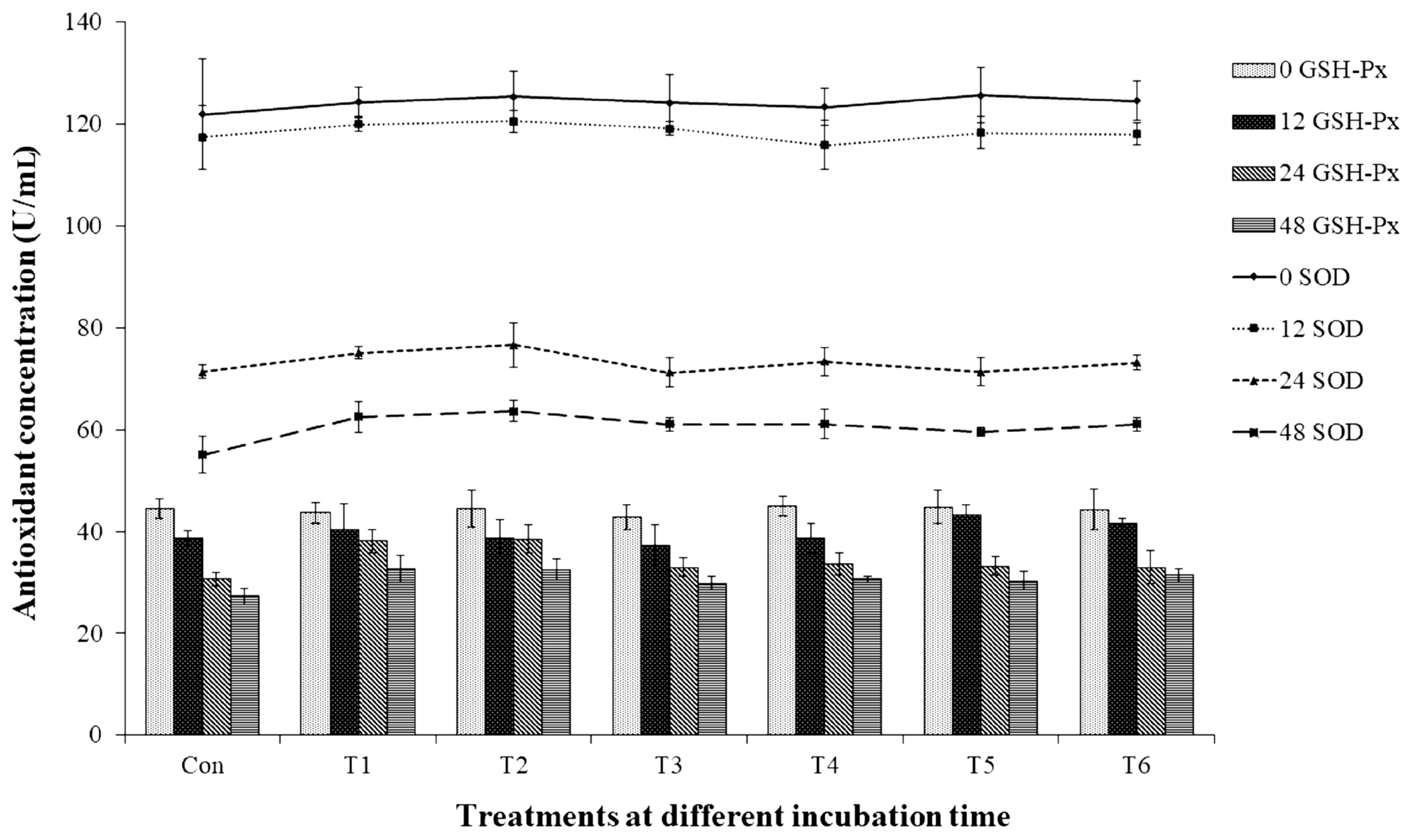
Table 1
Total mixed ration feed and chemical composition
| Items | As basis % |
|---|---|
| Ingredients | |
| Basal feed | 39.10 |
| Brewer’s grain | 14.00 |
| Soy sauce cake | 18.50 |
| Rice straw | 3.10 |
| Italian ryegrass | 20.00 |
| Alfalfa pellet | 5.00 |
| Yeast | 0.30 |
| Basal feed | |
| Corn | 49.50 |
| Molasses | 3.00 |
| Tapioca | 2.50 |
| Wheat bran | 9.00 |
| Corn gluten feed | 9.00 |
| Soybean meal | 6.00 |
| Rapeseed oil meal | 6.00 |
| Coconut meal | 6.00 |
| Palm kernel cake | 6.00 |
| Salt and vitamin premix1) | 3.00 |
| Chemical composition (% dry matter) | |
| Dry matter | 71.90 |
| Crude protein | 11.12 |
| Crude fat | 2.60 |
| Crude fiber | 9.44 |
| Ash | 8.63 |
| Calcium | 1.76 |
| Phosphorus | 0.39 |
1) Vitamin premix contained the following amount which was diluted in cellulose (g/kg premix): L-ascorbic acid, 121.2; DL-atocopherol acetate, 18.8; thiamin hydrochloride, 2.7; riboflavin, 9.1; pyridoxine hydrochloride, 1.8; niacin, 36.4; Ca-D-pantothenate, 12.7; myo-inositol, 181.8; D-biotin, 0.27; folic acid, 0.68; p-aminobenzoic acid, 18.2; menadione, 1.8; retinal acetate, 0.73; cholecalciferol, 0.003; cyanocobalamin, 0.003.
Table 2
Effect of γ-aminobutyric acid on the pH, gas production, and ammonia concentration of in vitro fermentation
| Time (h) | Treatment1) | Mean | p-value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||
| Con | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | |||
| pH | |||||||||
| 12 | 5.61c | 5.64abc | 5.64abc | 5.65ab | 5.68a | 5.66ab | 5.63bc | 5.64w | <0.001 |
| 24 | 5.49 | 5.45 | 5.46 | 5.48 | 5.50 | 5.45 | 5.45 | 5.46x | |
| 48 | 5.42 | 5.41 | 5.43 | 5.41 | 5.42 | 5.44 | 5.42 | 5.48x | |
| Total gas production (mL) | |||||||||
| 12 | 74.00b | 75.00b | 80.33a | 82.67a | 83.00a | 71.00b | 71.67b | 76.62x | <0.001 |
| 24 | 77.00 | 81.00 | 80.33 | 78.33 | 79.67 | 77.00 | 79.00 | 79.10x | |
| v48 | 96.50ab | 91.00b | 99.67ab | 99.67b | 102.33ab | 98.33ab | 108.00a | 99.43w | |
| NH3-N concentration (mg/dL) | |||||||||
| 12 | 75.55c | 79.00bc | 5.00abc | 90.73ab | 96.47a | 74.93c | 79.90bc | 83.06y | <0.001 |
| 24 | 96.10d | 104.10c | 104.07c | 104.33c | 103.57c | 105.43b | 110.13a | 103.93x | |
| 48 | 107.75c | 127.67b | 130.67b | 128.6.33b | 117.07bc | 118.70bc | 158.20a | 127.11w | |
Table 3
Effect γ-aminobutyric acid on volatile fatty acid production during in vitro fermentation
| Time (h) | Treatment1) | Mean | p-value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||
| Con | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | |||
| Acetate (mM) | |||||||||
| 12 | 44.92 | 41.43 | 44.03 | 42.11 | 44.23 | 43.02 | 42.70 | 43.21 | 0.412 |
| 24 | 41.98 | 45.86 | 43.56 | 43.55 | 44.01 | 45.75 | 44.13 | 44.12 | |
| 48 | 49.30ab | 49.15ab | 50.67ab | 48.61ab | 46.66b | 51.90a | 52.47a | 49.82 | |
| Propionate (mM) | |||||||||
| 12 | 16.43a | 14.77b | 15.35ab | 15.19ab | 15.98ab | 15.47ab | 15.78ab | 15.57 | 0.024 |
| 24 | 16.81 | 17.43 | 17.45 | 18.96 | 18.95 | 17.72 | 18.28 | 17.94 | |
| 48 | 22.20 | 23.98 | 23.07 | 26.61 | 23.85 | 23.75 | 24.96 | 24.06 | |
| Butyrate (mM) | |||||||||
| 12 | 8.59d | 9.67abcd | 10.83a | 10.36ab | 10.10abc | 9.46bcd | 8.91cd | 9.70 | 0.056 |
| 24 | 13.48 | 12.92 | 15.41 | 14.18 | 16.44 | 15.08 | 13.26 | 14.39 | |
| 48 | 25.19ab | 29.62a | 27.37ab | 21.61b | 21.14b | 21.40b | 30.88a | 25.31 | |
| Acetate:propionate ratio (mM) | |||||||||
| 12 | 2.73 | 2.80 | 2.87 | 2.77 | 2.77 | 2.78 | 2.71 | 2.78 | <0.001 |
| 24 | 2.50ab | 2.63a | 2.50ab | 2.30b | 2.32b | 2.58a | 2.41ab | 2.46 | |
| 48 | 2.22 | 2.05 | 2.20 | 1.83 | 1.96 | 2.19 | 2.10 | 2.08 | |
| Total volatile fatty acids (mM) | |||||||||
| 12 | 69.94cd | 65.87d | 70.21a | 67.65cd | 70.31ab | 67.95cd | 67.39bc | 68.47 | 0.473 |
| 24 | 72.27d | 76.21cd | 76.42abcd | 76.68abc | 79.40a | 78.55ab | 75.67bcd | 76.46 | |
| 48 | 96.68c | 102.75b | 101.11b | 96.84c | 91.65d | 97.04c | 108.31a | 99.20 | |
Table 4
Effect γ-aminobutyric acid on the concentration of biogenic amines during in vitro fermentation
| Time (h) | Treatment1) | Mean | p-value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||
| Con | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | |||
| Histamine (mM) | |||||||||
| 12 | 14.16a | 12.13ab | 11.01bc | 11.43bc | 10.55bc | 10.08bc | 9.66c | 11.29 | <0.001 |
| 24 | 14.72a | 9.41b | 10.42b | 11.19b | 10.95b | 9.98b | 9.36b | 10.86 | |
| 48 | 15.99a | 9.34c | 9.96c | 11.51b | 13.23b | 9.58c | 9.62c | 11.32 | |
| Methylamine (mM) | |||||||||
| 12 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.31y | <0.001 |
| 24 | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.33y | |
| 48 | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.49 | 0.36x | |
| Ethylamine (mM) | |||||||||
| 12 | 0.39ab | 0.33b | 0.38ab | 0.39ab | 0.43a | 0.30b | 0.31b | 0.36 | <0.001 |
| 24 | 0.46 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.40 | |
| 48 | 0.35c | 0.36c | 0.35c | 0.35c | 0.50a | 0.42b | 0.46ab | 0.40 | |
| Tyramine (mM) | |||||||||
| 12 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.37y | <0.001 |
| 24 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.39 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 0.38y | |
| 48 | 0.56 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.65 | 0.60 | 0.67 | 0.59 | 0.60x | |
| Total biogenic amines (mM) | |||||||||
| 12 | 15.25a | 13.09ab | 12.05b | 12.51b | 11.67b | 11.06b | 10.71b | 12.34xy | <0.001 |
| 24 | 15.86a | 10.47bc | 11.41bc | 12.44b | 12.08bc | 11.13bc | 10.41c | 11.97y | |
| 48 | 17.22a | 10.62c | 11.21c | 12.83b | 14.67b | 11.02c | 11.17c | 12.68x | |
Table 5
Effect γ-aminobutyric acid on the performance of Hanwoo steers
| Parameter | Treatment1) | Mean | SEM | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||
| Control | T1 | T2 | ||||
| Weight gain (kg) | 91.33 | 97.83 | 109.67 | 99.61 | 7.19 | 0.247 |
| Average daily gain (kg) | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.05 | 0.238 |
| Feed conversion ratio (kg feed/kg gain) | 13.7 | 12.47 | 11.42 | 12.53 | 0.94 | 0.280 |
| Marbling score | 6.17 | 7.17 | 5.50 | 6.28 | 0.62 | 0.199 |
| Blood endotoxins (U/mL) | 29.23a | 17.23b | 16.42b | 20.96 | 2.66 | 0.025 |
REFERENCES
1. Matsumoto D, Takagi M, Fushimi Y, et al. Effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid administration on health and growth rate of group-housed Japanese black calves fed using an automatic controlled milk feeder. J Vet Med Sci 2009; 71:651–6.
https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.71.651


2. Cho YR, Chang JY, Chang HC. Production of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by Lactobacillus buchneri isolated from Kimchi and its neuroprotective effect on neuronal cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol 2007; 17:104–9.

3. Diana M, Quílez J, Rafecas M. Gamma-aminobutyric acid as a bioactive compound in foods: a review. J Funct Foods 2014; 10:407–20.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2014.07.004

4. Vo T, Park JH. Characteristics of potential gamma-aminobutyric acid-producing bacteria isolated from Korean and Vietnamese fermented fish products. J Microbiol Biotechnol 2019; 29:209–21.
https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1811.09072



5. Li H, Cao Y. Lactic acid bacterial cell factories for gamma-aminobutyric acid. Amino Acids 2010; 39:1107–16.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0582-7



6. Mazur R, Kovalovská K, Hudec J. Changes in selectivity of gamma-aminobutyric acid formation effected by fermentation conditions and microorganisms resources. J Microbiol Biotechnol Food Sci 2011; 1:164–71.
7. Ku BS, Mamuad LL, Kim SH, et al. Effect of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) producing bacteria on in vitro rumen fermentation, biogenic amine production and anti-oxidation using corn meal as substrate. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2013; 26:804–11.
https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2012.12558




8. Murillo M, Herrera E, Reyes O, Gurrola JN, Gutierrez E. Use in vitro gas production technique for assessment of nutritional quality of diets by range steers. Afr J Agric Res 2011; 6:2522–6.
https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR10.753

9. Hassanat F, Benchaar C. Assessment of the effect of condensed (acacia and quebracho) and hydrolysable (chestnut and valonea) tannins on rumen fermentation and methane production in vitro
. J Sci Food Agric 2013; 93:332–9.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.5763


10. Russell JB, Van Soest PJ.
In vitro ruminal fermentation of organic acids common in forage. Appl Environ Microbiol 1984; 47:155–9.



11. Chaney AL, Marbach EP. Modified reagents for determination of urea and ammonia. Clin Chem 1962; 8:130–2.
https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/8.2.130



12. Han SK, Kim SH, Shin HS. UASB treatment of wastewater with VFA and alcohol generated during hydrogen fermentation of food waste. Process Biochem 2005; 40:2897–905.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.01.005

13. Tabaru H, Kadota E, Yamada H, Sasaki N, Takeuchi A. Determination of volatile fatty acids and lactic acid in bovine plasma and ruminal fluid by high performance liquid chromatography. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi [Internet] 1988; 50:1124–6.
https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms1939.50.1124

14. Jo C, Cho SH, Chang J, Nam KC. Keys to production and processing of Hanwoo beef: a perspective of tradition and science. Anim Front 2012; 2:32–8.
https://doi.org/10.2527/af.2012-0060


15. SAS Institute. SAS version 9.4. Carey, NC, USA: SAS Inst. Inc; 2012.
16. Lounglawan P, Suksombat W. Effect of soybean oil and lactic acid bacteria supplementation on performance and CLA accumulation in milk of dairy cows. J Anim Vet Adv 2011; 10:868–74.
https://doi.org/10.3923/javaa.2011.868.874

17. Seo JK, Kim SW, Kim MH, Upadhaya SD, Kam DK, Ha JK. Direct-fed microbials for ruminant animals. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2010; 23:1657–67.
https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2010.r.08


18. Dryhurst N, Wood CD. The effect of nitrogen source and concentration on in vitro gas production using rumen micro-organisms. Anim Feed Sci Technol 1998; 71:131–43.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-8401(97)00124-7

19. Raeth-Knight ML, Linn JG, Jung HG. Effect of direct-fed microbials on performance, diet digestibility, and rumen characteristics of Holstein dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 2007; 90:1802–9.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2006-643


20. Buchanan-Smith JG. An investigation into palatability as a factor responsible for reduced intake of silage by sheep. Anim Prod 1990; 50:253–60.
https://doi.org/10.1017/S0003356100004700

21. Dawson L, Mayne CS. The effects of either dietary additions or intraruminal infusion of amines and juice extracted from grass silage on the voluntary intake of steers offered grass silage. Anim Feed Sci Technol 1995; 56:119–31.
https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-8401(95)00809-2

22. Komuro Y, Ishihara K, Kojima Y, Saigenji K, Hotta K. Distinct effects of tetragastrin in rat gastroduodenal mucosa on mucin content and mucosal protective action against histamine-induced injury. Dig Dis Sci 1998; 43:1050–6.
https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018839003603


23. Aschenbach JR, Gäbel G. Effect and absorption of histamine in sheep rumen: significance of acidotic epithelial damage. J Anim Sci 2000; 78:464–70.
https://doi.org/10.2527/2000.782464x


24. LeBlanc JG, del Carmen S, Miyoshi A, et al. Use of superoxide dismutase and catalase producing lactic acid bacteria in TNBS induced Crohn’s disease in mice. J Biotechnol 2011; 151:287–93.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.11.008


25. Zhang M, Zou XT, Li H, Dong XY, Zhao W. Effect of dietary γ-aminobutyric acid on laying performance, egg quality, immune activity and endocrine hormone in heat-stressed Roman hens. Anim Sci J 2012; 83:141–7.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1740-0929.2011.00939.x


26. Cruywagen CW, Jordaan I, Venter L. Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus supplementation of milk replacer on preweaning performance of calves. J Dairy Sci 2010; 79:483–6.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(96)76389-0

27. Ando S, Ishida M, Oshio S, Tanaka O. Effects of isolated and commercial lactic acid bacteria on the silage quality, digestibility, voluntary intake and ruminal fluid characteristics. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2006; 19:386–9.
https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2006.386


28. Pilachai R, Schonewille JT, Thamrongyoswittayakul C, et al. Starch source in high concentrate rations does not affect rumen pH, histamine and lipopolysaccharide concentrations in dairy cows. Livest Sci 2012; 150:135–42.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2012.08.009

29. Thorlacius H, Nobaek S, Wang XD, et al. Lactobacilli attenuate bacteremia and endotoxemia associated with severe intra-abdominal infection. Surgery 2003; 134:467–73.
https://doi.org/10.1067/S0039-6060(03)00246-0


30. Wang Y, Li Y, Xie J, et al. Protective effects of probiotic Lactobacillus casei Zhang against endotoxin- and d-galactosamine-induced liver injury in rats via anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory capacities. Int Immunopharmacol 2013; 15:30–7.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2012.10.026








 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





