Ahhmed MA, Kawahara S, Muguruma M. 2009. Transglutaminate improves the textural and structural properties of chicken skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. In : Proceeding of the 55th International Congress of Meat Science and Technology; Copenhagen, Denmark.

Ahn DU, Ajuyah A, Wolf FH, Sim JS. 1993. Oxygen availability affects prooxidant catalyzed lipid oxidation of cooked turkey patties. J Food Sci 58:278–291.

AOAC. 2000. Official methods of analysis. 17th ednAssociation of Official Analytical Chemists; Gaithersburg, MD:
Arihara K, Nakashima Y, Mukai T, Ishikawa S, Itoh M. 2001. Peptide inhibitors for angiotensin I-converting enzyme from enzymatic hydrolysates of porcine skeletal muscle proteins. Meat Sci 57:319–324.


Bersuder P, Hole M, Smith G. 1998. Antioxidants from heated histidine-glucose model system. 1. Investigation of the antioxidant role of histidine and isolation of antioxidants by high performance liquid chromatography. J Am Oil Chem Soc 75:181–187.

Bhaskar N, Modi VK, Govindaraju K, Radha C, Lalitha RG. 2007. Utilization of meat industry by products: protein hydrolysate from sheep visceral mass. Bioresour Technol 98:388–394.


Buege JA, Aust SD. 1978. Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Meth Enzymol 52:302–310.

Daoud R, Dubios V, Bors-Dodita L, Nedjar-Arroume N, Krier F, Chihib NE. 2005. New antibacterial peptide derived from bovine hemoglobin. Peptides 26:713–719.


Escudero E, Sentandreu MA, Arihara K, Toldrá F. 2010. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides generated from
in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of pork meat. J Agric Food Chem 58:2895–2901.


Flaczyk E, Rudzinska M, Wasowicz E, Korczak J, Amarowicz R. 2006. Effect of crackling hydrolysates on oxidative stability of pork meatballs fat. Food Res Int 39:924–931.

Han-Ching L, Leinot A. 1993. Surimi composition and technology: present status and nutritional consideration. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 44:S1S55–S63.

Hughes E, Confrades S, Troy DJ. 1997. Effects of fat level, oat fibre and carrageenan on frankfurters formulated with 5, 12 and 30% fat. Meat Sci 45:273–281.


Hur SJ, Choi BD, Choi YJ, Kim BG, Jin SK. 2011. Quality characteristics of imitation crab sticks made from Alaska Pollack and spent laying hen meat. LWT-Food Sci Technol 44:1482–1489.

Jang A, Jo C, Kang KS, Lee M. 2008. Antimicrobial and human cancer cell cytotoxic effect of synthetic angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides. Food Chem 107:327–336.

Janitha PK, Wanasundara PD, Rose ARS, Amarowicz R, Ambrose SJ, Pegg RB. 2002. Peptides with angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity from defibrinated, hydrolyzed bovine plasma. J Agric Food Chem 50:6981–6988.


Jin SK, Kim IS, Choi YJ, Park GB, Yang HS. 2008. Quality characteristics of chicken breast surimi as affected by water washing time and pH adjustment. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 21:449–455.

Jin SK, Kim IS, Kim SJ, Jeong KJ, Choi YJ, Hur SJ. 2007. Effect of muscle type and washing times on physic-chemical characteristics and qualities of surimi. J Food Eng 81:618–623.

Kong BH, Xiong YL. 2006. Antioxidant activity of zein hydrolysates in a liposome system and the possible mode of action. J Agric Food Chem 54:6059–6068.


Kristinsson HG, Hultin HO. 2003. Role of pH and ionic strength on water relationships in washed minced chicken breast muscle gels. J Food Sci 68:917–922.

Lanier TC. 2000. Surimi gelation chemistry. Surimi and surimi seafood. Park JW, editorNew York: Marcel Dekker; p. 237–265.

Li B, Chen F, Xang X, Ji B, Wu Y. 2007. Isolation and identification of antioxidative peptides from porcine collagen hydrolysate by conseutive chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Chem 102:1135–1143.

Liu Q, Kong B, Jiang L, Cui X, Liu J. 2009. Free radical scavenging activity of porcine plasma protein hydrolysates determined by electron spin resonance spectrometer. LWT-Food Sci Technol 42:956–962.

Luo Y, Kuwahara R, Kaneniwa M, Murata Y, Yokoyama M. 2004. Effect of soy protein isolate on gel properties of Alaska Pollack and common carp surimi at different setting conditions. J Sci Food Agric 84:663–671.

Luo Y, Shen H, Pan D, Bu G. 2008. Gel properties of surimi from silver carp (
Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) as affected by heat treatment and soy protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll 22:1513–1519.

Morrissey PA, Sheehy PJA, Galvin K, Kerry JP. 1998. Lipid stability in meat and meat products. Meat Sci 49:73–86.

Nowasd AAAKM, Kanoh S, Niwa E. 2000. Thermal gelation characteristics of breast and thigh muscles of spend hen and broiler and their surimi. Meat Sci 54:169–175.


Park S, Brewer MS, Novakofski J, Bechtel PJ, McKeith FK. 1996. Process and characteristics for a surimi-like material made from beef or pork. J Food Sci 61:422–427.

Park JW, Morrissey MT. 2000. Manufacturing of surimi from light muscle fish. Surimi and surimi seafood. Park JW, editorNew York: Marcel Dekker; p. 23–58.
Pena-Ramos EA, Xiong YL. 2003. Whey and soy protein hydrolysates inhibit lipid oxidation in cooked pork patties. Meat Sci 64:259–263.


Phatcharat S, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W. 2006. Effects of washing with oxidizing agents on the gel-forming ability and physicochemical properties of surimi produced from bigeye snapper. Food Chem 98:431–439.

Saiga A, Tananbe S, Nishimura T. 2003a. Antioxidnat activity of peptides obtained from porcine myofibrillar proteins by protease treatment. J Agric Food Chem 51:3661–3667.


Saiga A, Okumura T, Makihara T, Katsuta S, Shinizu T, Yamada R, Nishimura T. 2003b. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in a hydrolyzed chicken breast muscle extract. J Agric Food Chem 51:1741–1745.


Sakanaka S, Tachibana Y. 2006. Active oxygen scavenging activity of egg-yolk protein hydrolysates and their effects on lipid oxidation in beef and tuna homogenates. Food Chem 95:243–249.

SAS Institute Inc. 2000. SAS/STAT user’s guide: Version 8.2. Cary, NC:
Shahidi F, Han X, Synowiecki J. 1995. Production and characteristics of protein hydrolysates from capelin (
Mallotus villosus). Food Chem 53:285–293.

Smith DM. 1987. Functional and biochemical change in deboned turkey due to frozen storage and lipid oxidation. J Food Sci 52:22–27.

Srinivasan S, Xiong YL. 1996. Gelation of beef heart surimi as affected by antioxidants. J Food Sci 61:707–711.

Sylvia SF, Claus JR, Mariott NG, Eigel WN. 1994. Low-fat, high-moisture frankfurters: Effects of temperature and water during extended mixing. J Food Sci 59:937–940.

Tornberg E. 2005. Effect of heat on meat proteins- Implications on structure and quality of meat products: A review. Meat Sci 70:493–508.


Uddin M, Okazaki E, Fukushima H, Turza S, Yumiko Y, Fukuda Y. 2006. Nondestructive determination of water and protein in surimi by near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem 96:491–495.

Vilhelmsson O. 1997. The state of enzyme biotechnology in the fish processing industry. Trends Food Sci Technol 8:266–270.

Wu HC, Chen HM, Shiau CY. 2003. Free amino acids and peptides as related to antioxidant properties in protein hydrolysates of mackerel (
Scomber austriasicus). Food Res Int 36:949–957.

Wu KC, Lin ZY, Chiang SH, Chang CY. 2004. Antioxidant properties of porcine blood proton before and after enzymatic hydrolysis. J Biomass Energ Soc China 23:79–85.
Yang TS, Froning GW. 1992. Selected washing processes affect thermal gelation properties and microstructure of mechanically separated chicken meat. J Food Sci 57:325–329.



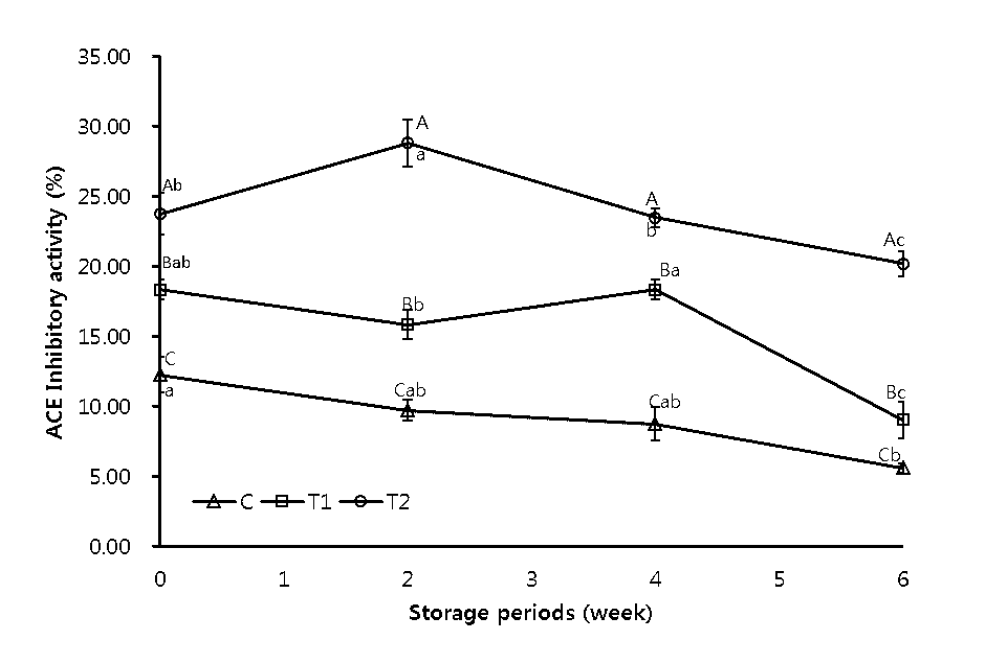





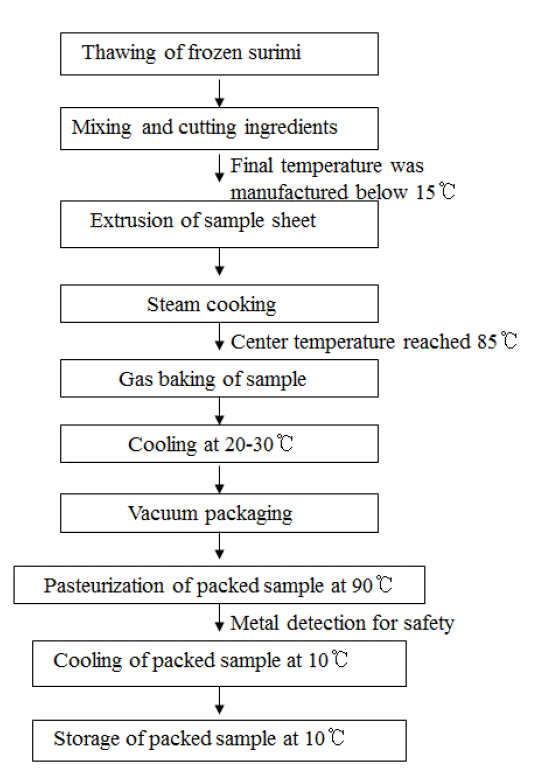
 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





