 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 37(2); 2024 Special Issue > Article |
|
Abstract
Ruminants possess a specialized four-compartment forestomach, consisting of the reticulum, rumen, omasum, and abomasum. The rumen, the primary fermentative chamber, harbours a dynamic ecosystem comprising bacteria, protozoa, fungi, archaea, and bacteriophages. These microorganisms engage in diverse ecological interactions within the rumen microbiome, primarily benefiting the host animal by deriving energy from plant material breakdown. These interactions encompass symbiosis, such as mutualism and commensalism, as well as parasitism, predation, and competition. These ecological interactions are dependent on many factors, including the production of diverse molecules, such as those involved in quorum sensing (QS). QS is a density-dependent signalling mechanism involving the release of autoinducer (AIs) compounds, when cell density increases AIs bind to receptors causing the altered expression of certain genes. These AIs are classified as mainly being N-acyl-homoserine lactones (AHL; commonly used by Gram-negative bacteria) or autoinducer-2 based systems (AI-2; used by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria); although other less common AI systems exist. Most of our understanding of QS at a gene-level comes from pure culture in vitro studies using bacterial pathogens, with much being unknown on a commensal bacterial and ecosystem level, especially in the context of the rumen microbiome. A small number of studies have explored QS in the rumen using ‘omic’ technologies, revealing a prevalence of AI-2 QS systems among rumen bacteria. Nevertheless, the implications of these signalling systems on gene regulation, rumen ecology, and ruminant characteristics are largely uncharted territory. Metatranscriptome data tracking the colonization of perennial ryegrass by rumen microbes suggest that these chemicals may influence transitions in bacterial diversity during colonization. The likelihood of undiscovered chemicals within the rumen microbial arsenal is high, with the identified chemicals representing only the tip of the iceberg. A comprehensive grasp of rumen microbial chemical signalling is crucial for addressing the challenges of food security and climate targets.
The rumen, the main fermentative compartment of the ruminant forestomach, hosts a complex and dynamic microbial population composed of bacteria, protozoa, fungi, archaea and bacteriophages [1,2]. The rumen microbial ecosystem is characterised by its high cell density, which plays a crucial role in the efficient breakdown of ingested plant material and the overall digestive processes of ruminant animals; mainly characterised as symbiosis [3]. The rumen ecosystem is also versatile, with much redundancy (overlap of function among multiple species) and resilience (resistance to, and capacity to recover from perturbation) observed [3]. The regulation and balance of ruminal fermentation are influenced by various factors, including nutrient balance and a wide range of ecological interactions among microbial populations such as, predation, competition, mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism and amensalism [3–7]. Within this highly complex rumen microbiome, there has been evidence of multiple mechanisms driving the ecological interactions, including use of chemical signalling. However, chemical signalling data in the rumen microbiome is scarce. In this review we focus on outlining the main quorum sensing (QS) systems currently known within the rumen context.
Based on pure bacterial culture studies, QS has been shown to be intrinsically linked to altered gene expression, through the intracellular synthesis of autoinducers (AIs) before their subsequent release and accumulation in the nearby external environment. Environmental concentrations of these AIs increase alongside increases in cell density, until they reach a detection threshold and begin binding to receptors, triggering transduction cascades and leading to the transcription of specific genes [8,9]. QS based systems have also been shown as being intrinsically important in biofilm formation and thereafter in the dispersion of bacteria from mature biofilms [10]. To date, there have been five types of discovered QS systems based on the AIs used, summarised as N-acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs), autoinducer-2 (AI-2), autoinducing peptides (AIPs), methyl dodecenoic acid, and quinolones [11].
Among those, AHLs are one of the most widely studied QS AI molecules, used mainly by Gram-negative bacterial species, possessing variations in carbon length and compound structure [9,12]. AHL-mediated QS was originally identified in Vibrio fischeri (Aliivibrio fischeri), best known as the LuxI/LuxR regulatory system. This two-component system comprises of the luxI and luxR genes, encoding the LuxI protein (which functions as the AHL synthase) and LuxR protein (acting as a signal receptor) respectively [12]. Briefly, AHLs are synthesised by the LuxI synthase, through upregulation of the luxI gene, the AHLs then diffuse into the environment. As the concentration of AHL increases in the local environment, more will diffuse into the cytoplasm of nearby cells, binding to the LuxR receptor, triggering the expression of select genes and behavioural changes (Figure 1; [13]). This QS system is thought to only enable intraspecies communication due to AHL molecules only being detected by species that produce that same type of AI [9]. In addition to AHL based QS, Vibrio harveyi can also utilise AI-2 based QS and are therefore capable of employing multiple QS systems [14]. Differently to the AHL based QS, the AI-2 based QS enable ‘universal’ interspecies communication and gene regulation [8]. In this QS system, the AI-2 based QS, is facilitated by LuxS (AI-2 synthase and exporter), encoded by the luxS gene. Many homologues of this gene have now been discovered in both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria (Figure 1). Once AI-2 signalling molecules are exported, and reach a threshold in the extracellular environment, they will bind to the LuxPQ complex. This then begins a phosphate transfer and the signal is transduced where LuxU is dephosphorylated leading to dephosphorylation of LuxO, resulting in increased LuxR concentrations and altered gene expression (Figure 1; [14]). Gram-positive bacteria, like Staphylococcus aureus, can also utilise short macrocyclic peptides known as AIPs [15]. These self-inducing AIPs can regulate gene receptors, often following one of the two common types of circuits known as Agr-like and RNPP-like [15]. Briefly, in Agr-like circuits the peptide signal is not physically transported, unlike in the RNPP-like circuits where the peptide signal will be physically imported before activating the transcription receptor [15,16].
Many reviews are available focusing on QS in pathogenic bacteria [e.g 17–20], however, this review introduces the concept of QS with a more system studies based approach, thereby enabling an in-depth discussion of QS systems in the rumen as outlined below.
The majority of studies to date regarding QS in the rumen have focused on laboratory pure cultures of bacteria, using in vitro assays and reporter strains for detection of AIs. These in vitro methods, including culture-dependent approaches, allow us to gain fundamental knowledge on how rumen bacteria utilise QS under tightly controlled and reproducible conditions [21]. Additionally, recent studies have demonstrated evidence of QS and potential impact on the microbiome by mining rumen bacterial genomes, metagenomes and metatranscriptomes [6,22–25].
Culture-dependent in vitro methods have been employed to investigate AHL-based QS in rumen isolate bacteria [26,27]. Erickson et al [26] used two AHL reporter systems, Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 and Agrobacterium tumefaciens (Agrobacterium radiobacter) A136 (pCF372)(pCF272) to detect AHLs. Although AHLs were detected in ruminal fluid samples, no AHLs were observed in the following pure rumen isolates cultures: Anaerovibrio lipolyticus 5S, Fibrobacter succinogenes S85, Megasphaera elsdenii LC1, Prevotella albensis 223/M2/7, Prevotella brevis GA33, Prevotella bryantii B14, Prevotella ruminicola 23, Prevotella ruminicola 85, Ruminobacter amylophilus 70, and WP109, Selenomonas ruminantium HD4, four more unnamed S. ruminantium strains, and Succinivibrio dextrinosolvens 24, as well as several strains of Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens (which stains Gram-negative but has a Gram-positive ultrastructure) [26]. The presence of AHL based QS activity in rumen fluid, but not in pure cultures tested, led the authors to hypothesise that either these pure culture bacteria were simply not AHL producers, or that QS only occurs in the density-dependent manner in mixed culture rumen microbiomes [26]. However, there has since been evidence that bacteria isolated from the rumen can produce AHLs in in vitro conditions, for example in Pseudomonas aeruginosa [27]. When Escherichia coli was transformed with the luxI gene homolog identified in the rumen isolated P. aeruginosa, changes in expressions were observed for the following genes fliC, gadA and sdiA [27]. These genes are known to be linked to motility, increased acid tolerance and QS respectively [28].
To date the findings from culture based and in vitro rumen fluid-based experiments remain highly variable. The methodologies employed can explain some of this variability, including experimental alterations such as primer differences, limitations of the bioassays for screening QS molecules and the difficulty of emulating the highly competitive rumen environment in vitro. For example, within the cattle gastrointestinal tract (GIT), current evidence suggests that AHL-based QS only occurs in the rumen, with no evidence of QS in other sites of the GIT [29]. However, limitations in our current QS molecule detection technologies could explain this apparent absence of AHLs in the lower GIT. Another potential reason for AHL absence, could be that the AHL-producing microbes are simply lacking in this area but are present in the rumen microbiome. An alternative reason could be due to the pH differences between the lower GIT and the rumen. The pH of the acidic rumen is the ideal environment where the homoserine ring of AHLs are stable, in comparison the alkaline pH of the lower GIT can lead to the hydrolysis of this ring, degrading the QS molecule and negating the effectiveness of the signal being generated [29]. The pH of the rumen can be driven by diet, with diet formulation including grain to roughage ratios having a great impact on pH and inappropriate diets leading to nutritional disorders in cattle such as ruminal acidosis [30]. Despite Erickson et al [26] finding that animals receiving concentrate diets tended to have longer chain AHLs in their rumen fluid in comparison to those receiving forage diets, overall AHL synthesis in the rumen was found not to be diet dependent and the impact of diet on QS in the rumen is yet to be clarified.
To date evidence of QS have been reported in the cattle ruminal fluid samples but not in the caprine ruminal fluid samples [29,31]. When the rumen fluid of Liuyang black goats was investigated, no evidence of QS, including AHLs and AI-2 activity, was identified [31]. In this study, the primary method utilised to identify AHLs was gas chromatography-mass spectrometric (GC-MS) and the authors highlighted potential problems with this method notably the short retention times of the AHLs standards, which potentially led to the lack of AHLs detected. This lack of QS evidence in this caprine rumen study could also be due to several reasons, for example that the rumen of goats did not harbour organisms that are capable of QS such as those seen in cattle [31]. In contrast, when considering other established molecular based methods, homologues of luxS found in P. ruminicola were identified both in vitro and in vivo from goat rumen fluid indicating that the rumen microbiomes of goats do have the potential ability to communicate through AI-2 QS [31] and that the detection method could play a crucial part in the detection of AHLs in the caprine rumen and should be considered further.
The variability of results in the above-mentioned experi ments highlights the need to employ both culture-dependent and culture-independent methods for investigating QS in the rumen. Indeed, numerous studies have now utilised genomic, metagenomic, or metatranscriptomic analysis, revealing a large diversity of potential QS mechanisms within the rumen [6,23,24]. For example, the advent of the Hungate collection, which sequenced 410 rumen bacteria and 21 archaea isolate cultures, allowed the mining of these genomes against known QS genes [23,32]. Won et al [23] found evidence of AHL QS, although not widespread, with only one species of Gram-negative bacteria, Citrobacter sp. NLAE-zl-C269, possessing an AHL synthase gene. Interestingly, this Citrobacter species genome also contained luxS and luxR genes representing the potential to engage in multiple QS systems, i.e., both AHL and AI-2 [23]. Liu et al [24] expanded this mining of rumen genomes to include 948 bacterial genomes and 33 archaeal genomes, sourced from Shi et al [33], Gharechahi et al [34], and GenBank [35]. In this study they found more extensive evidence of AHL QS, with 5 archaeal genomes (all from the genus Methanobrevibacter) and 58 bacterial genomes containing AHL genes, mainly harboured by the following orders; Eubacteriales, Bacteroidia, Clostridiales, and Selenomonadales [24].
In contrast to AHL based QS, evidence suggests AI-2 QS is far more widespread within the rumen. Through the utilisation of the V. harveyi BB170 bioluminescence assay, B. fibrisolvens, Eubacterium ruminantium, Ruminococcus flavefaciens, and Succinimonas amylolytica have been confirmed as producing AI-2 like molecules [36]. These findings, indicating that R. flavefaciens species are capable of AI-2 production, are further supported through genome sequencing of these isolates, confirming that they harbor luxS gene homologues [36]. In contrast, no luxS gene homologues were identified from the other 3 species that were identified as being capable of QS AI-2. Interestingly, luxS genes have been identified in P. ruminicola, yet this species did not produce AI-2 molecules under the experimental conditions employed by Mitsumori et al [36]. Further investigations on Prevotella species by Gorenc et al [37], utilising an optimised V. harveyi BB170 autoinducer bioassay, reported evidence of AI-2 type QS by P. ruminicola-like strain 223/M2/7A. Contrary to this, P. bryantii strains were unable to induce such a bioluminescence assay response, suggesting a lack of AI-2 QS system in this strain [37]. Additionally, the predominant rumen bacterium, Streptococcus bovis, has been identified as harbouring the QS luxS gene, through the use of S. bovis genomic DNA as a PCR template and degenerate primers for the luxS gene [38]. Through molecular techniques, including northern blot analysis, S. bovis was also found to be capable of transcribing the luxS gene, however the production of the LuxS protein was not found to be directly related to cell density [38]. In contrast, Mitsumori et al [36], did not detect the luxS gene in the genome of S. bovis. It should be noted that such differences in findings could potentially be due to primer or culturing differences or indeed strain differences [38].
Beyond pure culture experiments, there is evidence of AI-2 QS in rumen fluid using culture independent techniques [22–24]. Ghali et al [22] mined 3 bovine rumen metagenomic and one metatranscriptomic datasets for the presence of luxS genes, with 135 luxS genes identified predominantly from the phyla Bacteroidota (genus Prevotella mainly) and Firmicutes (Ruminococcus albus mainly), and to a lesser extent Fusobacteria and Actinomycetota. Further to this, through metatranscriptomic analysis, 34 luxS were expressed largely by Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes and Spirochaetes [22]. Another study, Won et al [23], prospecting the Hungate collection [32], found AI-2 lux-based genes in 191 bacterial genomes, across both Gram positive and negative, 139 and 53 genomes respectively, and were most abundant in Butyrivibrio, Prevotella, Ruminococcus, and Pseudobutyrivibrio genera, all of which are prevalent in the rumen. In the same study, metatranscriptomic datasets were prospected and showed that LuxS proteins were the most widespread followed by LuxR, while the LuxS synthase was highly expressed by Prevotella species [23]. Similarly, AI-2 genes were identified as highly expressed using metatranscriptomic based methods by Liu et al [24]. This study also detected that AI-2 genes are widespread across rumen bacterial genomes, with 680 out of the 948 ruminal bacteria genomes mined containing AI-2 genes, including the following genera of bacteria; Prevotella, Butyrivibrio, Ruminococcus, Oribacterium, Selenomonas, and Treponema genera [24].
In addition to AI-2 and AHL mediated communication, other methods of QS have been identified in pure cultures of ruminant bacteria, however, research into these mechanisms is still in its infancy. For example, S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus has been shown to have the ability to produce peptide pheromone competence-stimulating peptides, or CSP, involved in the ComABCDE QS pathway [39]. The peptide variant produced by S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus differs from those previously seen in others Streptococcus spp. The CSP produced by S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus is not thought to be involved in competence induction (as previously demonstrated by other S. gallolyticus subspecies) but instead plays a role in QS and regulation of bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances, suggesting that this QS system leads to a competitive advantage through the ability to eliminate close competitor species [39]. Additionally, autoinducing peptide, AIP, based QS genes have been identified in the genomes of ruminal bacteria, however evidence is limited [24]. AIP based QS genes, agrA/agrB, were identified in 199 rumen bacterial genomes, mainly all belonging to the Firmicutes phylum [24]. These genes are part of the Agr operon, agrB, agrD, agrC, and agrA, which together form a quorum-sensing circuit most widely studied in Staphylococci species [40]. This AgrBDCA QS system, requires the combination of AgrB and AgrB to process and secret AIPs, the two component signal transduction system, AgrAC, then responds to the AIPs [41,42]. This AIP detection then leads to the up-regulation of RNAIII, the agr effector molecule, which initiates regulatory changes in virulence gene expression in bacteria such as Streptococci spp. [40]. AIP QS has also been identified in Firmicutes (Bacillota), a dominant taxon in the rumen, in other cellulolytic environments [43]. Namely landfill leachate (liquid that passes through landfills and in the process extracts soluble or suspended solids, or any other component of the landfill), where uncultured clostridial species (Clostridium thermocellum-like [Acetivibrio thermocellus]) was identified as harbouring the agrC AIP gene [43].
Although there is now a range of evidence that QS is prevalent within the rumen microbiome there is still a limitation in our understanding of how QS influences gene regulation within this environment and consequently its impacts on rumen ecology and the host phenotype. However, limited data does exist that suggests QS can influence rumen colonisation [6,29,44]. For example, QS may play a key role in enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) cattle GIT colonisation. As the natural asymptomatic reservoir, the cattle GIT can be successfully colonised by EHEC, and this colonisation will result in the cattle shedding the pathogen into the environment. However, EHEC does not have its own luxI gene nor can it produce AHLs, instead relying on the AHLs produced by other bacteria, another indicator of interspecies QS mechanisms [45]. This interspecies QS by EHEC is enabled through the LuxR receptor homologue, SdiA, a transcription factor capable of sensing and reacting to environmental AHLs [28]. The AHLs present in rumen fluid can regulate the expression of genes associated with commensal EHEC colonisation ensuring the pathogen can successfully pass through the rumen and reach the desired colonisation site, the recto-anal junction [29,44,46]. AHLs can repress transcription of genes through SdiA, including the locus for enterocyte effacement gene cluster which are genes required for attaching and effacing (A/E) lesions, preventing EHEC colonisation in the hostile rumen environment. While SdiA simultaneously activates expressions of others such as gad genes, which allows for increased acid survival, enabling passage through the stomach [44–46].
Furthermore, multiple studies investigating the temporal colonisation of fresh perennial ryegrass (PRG) in the rumen, including the ability to form biofilms, have shown that colonisation is biphasic with similarities in attached communities from 0 to 4 h (primary colonisation) and thereafter from 4 to 24 h (secondary colonisation) a change in the attached community occurs [6,47–49; Figure 2). Likewise, such colonisation within the rumen is dominated by the biofilm phenotype [6,47–49]. The biofilm phenotype is intrinsically linked to QS, with QS known to be an essential a factor in biofilm formation, maturation and dispersion [10,50].
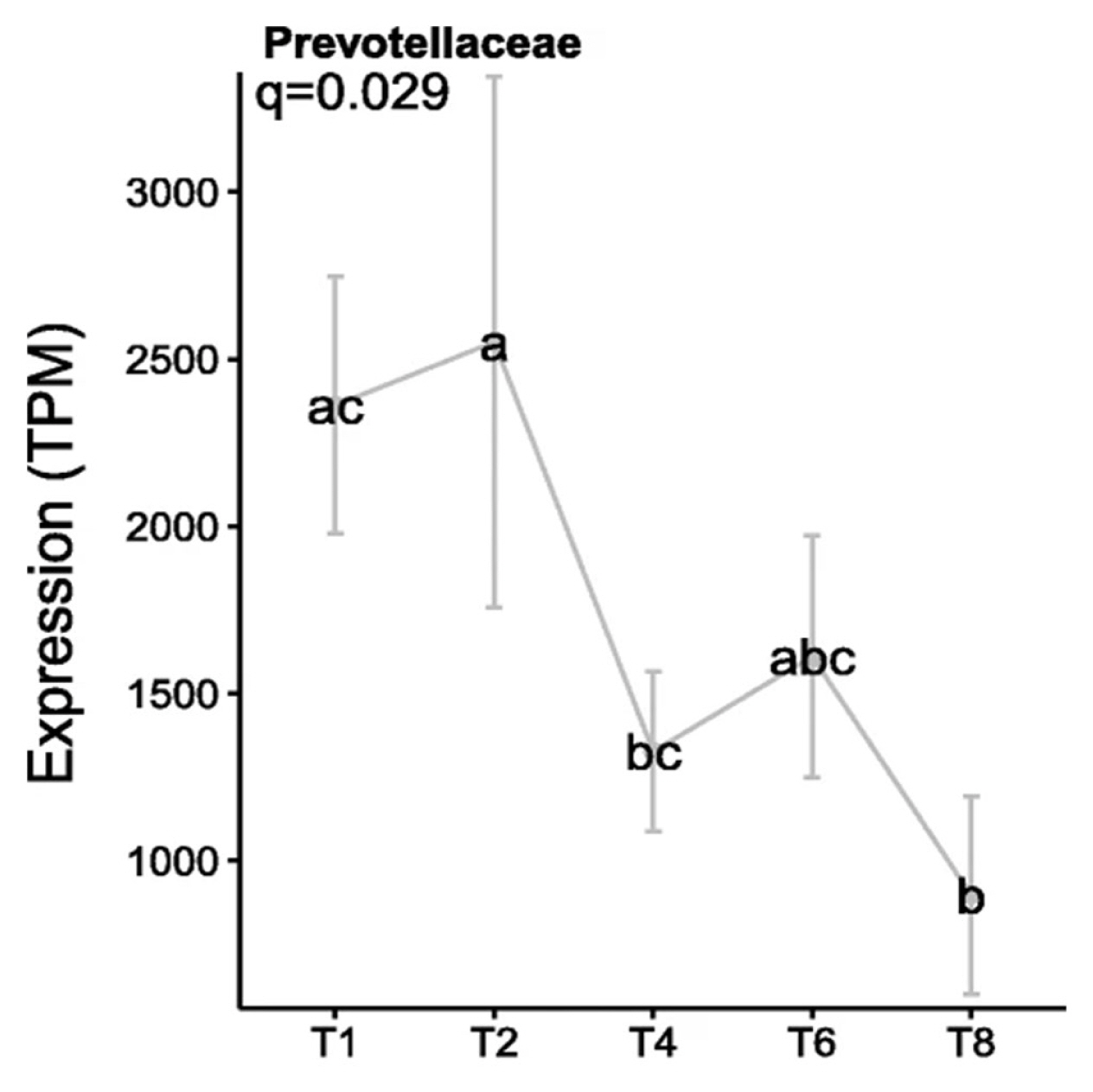
The factors which cause this change from the primary to secondary sub microbiomes were recently investigated using metatranscriptomics, with the resultant data showing that AHL was not identified as a QS mechanism in the PRG-colonising bacteria. In contrast, AI-2 QS appeared to be more abundant, which is perhaps unsurprising as this aligns with previous findings based on in vitro and genomic technologies [6,23,24]. In particular, the luxS gene was expressed abundantly by Prevotellaceae, specifically P. ruminicola 23, during primary colonisation, before decreasing during secondary colonisation (Figure 3). This suggests a role for QS as a driver for the switch between sub-microbiomes of primary and secondary colonisation [6].
When considering consequences of QS on the production of livestock, differing levels of QS, based on metagenomic techniques employed by Xie et al [25], has been linked to different animal phenotypes including residual feed intake (RFI). RFI is defined as “The difference between the actual and expected feed intake of an animal based on its body weight and growth rate over a specified period.” [51]. Therefore, an animal with high efficiency of feed conversion is expected to have a low RFI, with a high RFI indicating an inefficient animal. QS in the rumen was significantly higher in cattle with high RFI, specifically three genes, EC 4.1.1.15, EC 4.2.2.2 and EC 6.2.1.32, known to be regulated via QS systems were enriched in high RFI animals [25]. These enriched genes encoded the following enzymes; glutamate decarboxylase [52], pectate lyase [53] and acetate-CoA ligase [54]. These lower efficiency animals (high RFI) also had a significantly higher predicted methane production (p = 0.04) of 533 g/d when compared to the low RFI animals estimated to produce 506 g/d [25]. (A mathematical model was employed to predict methane production by the equation: CH4 (MJ/d) = 3.23 (±1.12)+0.81 (±0.086)×dry matter intake (kg/d) [55]). Animals with high RFI also had 6 methane metabolism genes, EC 1.5.98.1, EC 1.5.98.2, EC 2.1.1.248, EC 2.1.1.86, EC 2.1.1.90 and EC 2.3.1.101, enriched in their rumen microbiome [25]. In contrast, the more efficient animals, with lower RFI, were found to have lower levels of methanogenesis as well as lower abundances of Methanosphaera and Methanobrevibacter ruminantium [25]. Twenty-two bacterial species were identified as contributors to the differences observed in feed efficiency between the animals. These species were associated with both QS and carbohydrate metabolism capacity and included taxa belonging to the family Lachnospiraceae and included Ruminococcus torques, Blautia obeum, Blautia producta, Blautia schinkii, Blautia wexlerae, Dorea longicatena, Enterocloster clostridioformis (Clostridium clostridioforme), Clostridium symbiosum, Marvinbryantia formatexigens, and Lachnospiraceae bacterium [25]. Nonetheless, despite studies now showing the presence of QS in the rumen microbiome and correlating such activity to animal phenotype, the influence of QS on subsequent gene regulation is still unclear and requires further research.
Quorum sensing mechanisms play a crucial role in the rumen microbiome, impacting competition, symbiosis, and functional dynamics. However, studying QS in complex microbiomes, like the rumen, faces challenges due to the limitations associated with existing methodologies. To advance our understanding, we need comprehensive approaches like comparative genomics, refined anaerobic cultivation, and co-culture investigations. Despite significant strides in our knowledge of the rumen microbiome and its functionality, our comprehension of QS and its specific role within this niche remains understudied. Understanding these signalling pathways could empower us to manipulate the microbiome for animal and productivity benefits. This knowledge could contribute to developing direct-fed microbials, promoting sustainability, animal health, and enhanced productivity. Beyond reducing methane emissions, this approach aligns with planetary health goals by improving animal performance and meat quality. In summary, unravelling QS intricacies in the rumen microbiome is vital for advancing animal health and overall agricultural sustainability.
Notes
Figure 1
Simplified overview of AHL and AI-2 based quorum sensing mechanisms in Vibrio harveyi. The LuxR receptors are in dark blue, while other QS enzymes (LuxI, LuxS, LuxQ, LuxP, LuxU, and LuxO) are in light blue. Phosphate transfers in the signalling cascade are indicated by ‘P’ on dashed arrows, and black arrows show the movement and interaction of molecules. AHL QS: Produced by LuxI, AHL binds to LuxR at high concentrations, inducing target gene expression. AI-2 QS: Generated by LuxS, AI-2 interacts with the LuxPQ complex (LuxP as the periplasmic binding protein and LuxQ as the sensor kinase) at high concentrations. This triggers a dephosphorylation cascade, with LuxU as an intermediary, leading to the inactivation of LuxO, the repressor of LuxR. Inactivated LuxO allows LuxR to activate favouring the induction of target gene expression.
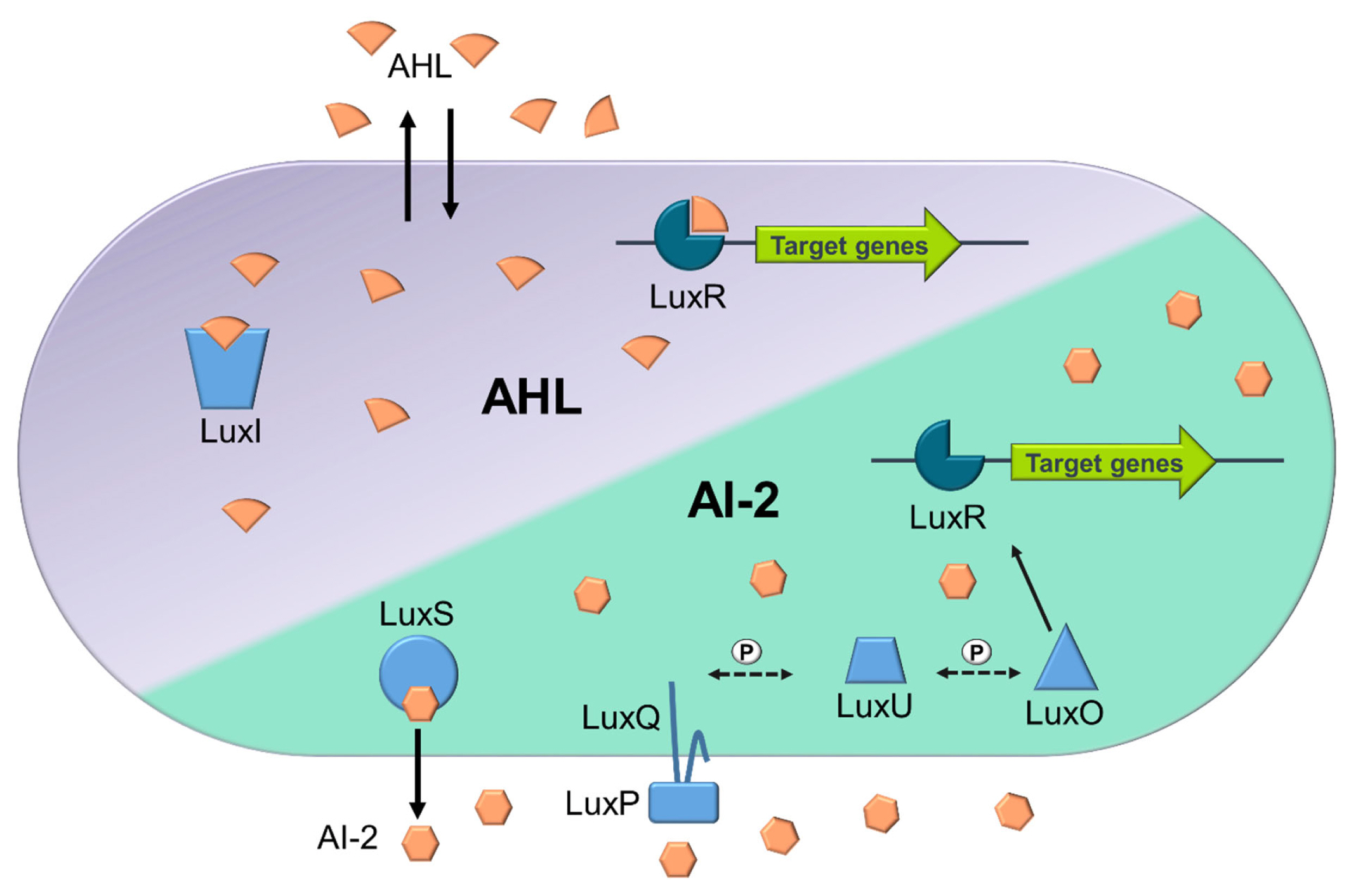
Figure 2
Biphasic colonization of fresh perennial ryegrass in the rumen. Putative coding sequences (CDS) were predicted in the de novo assembled transcriptomes obtained from the biofilm interface of fresh perennial ryegrass using an in sacco incubation approach. Subsequently, these CDS were taxonomically analysed at different time points during colonization, and the number of reads assigned to each taxon is presented at the family level., analysis completed by Huws et al [6] where error bars represent standard deviations.
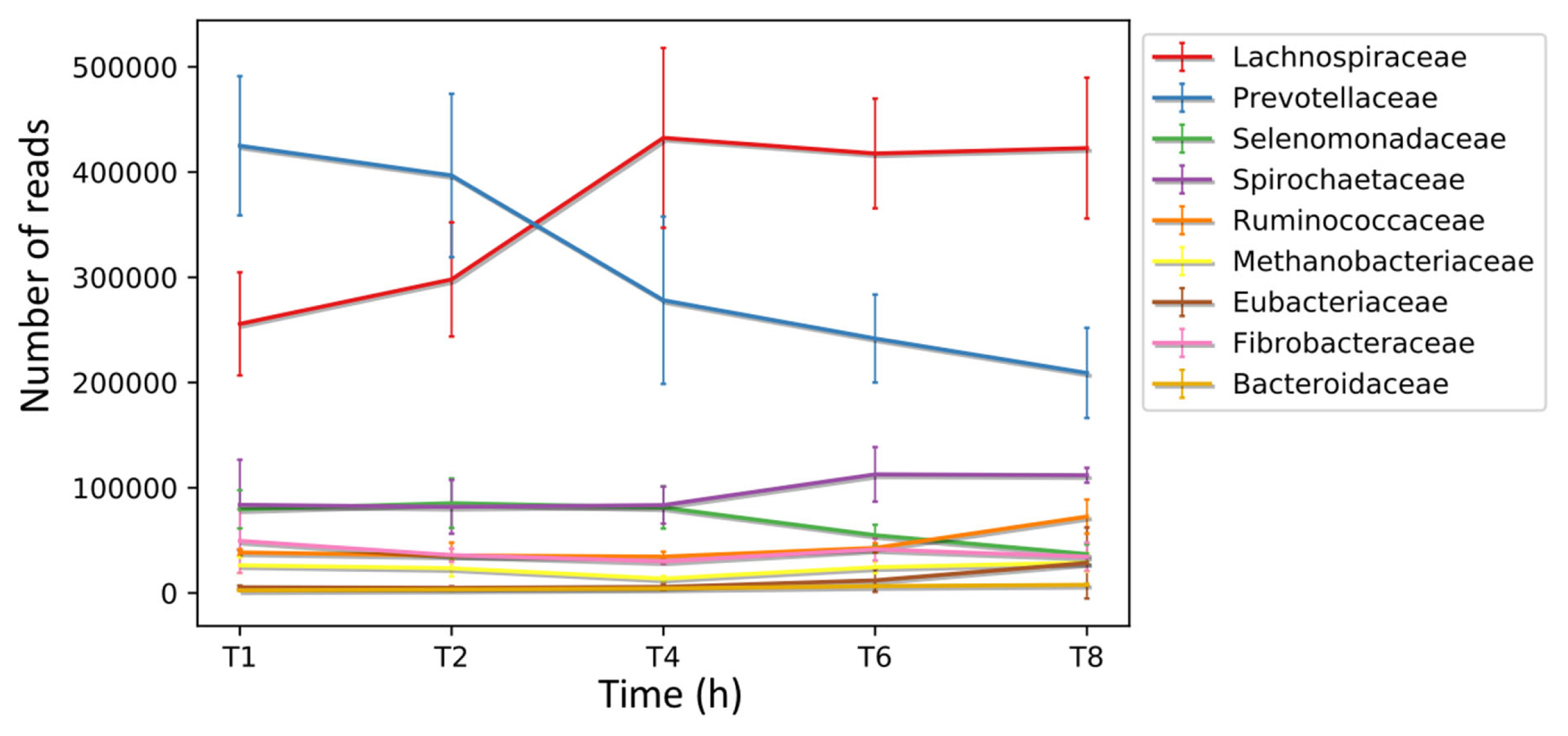
Figure 3
Expression levels of the luxS gene by Prevotellaceae colonising fresh perennial ryegrass (transcripts per million, TPM). Using an in sacco incubation approach the biofilm interface of fresh perennial ryegrass was characterized by metatranscriptomic profiling over different incubation times. The incubation times (h) are indicated on the X axis, error bars represent standard deviation, while different letters (abc) indicate significance between time points, (Huws et al [6]; Figure 8).
REFERENCES
1. Huws SA, Creevey CJ, Oyama LB, et al. Addressing global ruminant agricultural challenges through understanding the rumen microbiome: past, present, and future. Front Microbiol 2018; 9:2161
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02161



2. Mizrahi I, Wallace RJ, Moraïs S. The rumen microbiome: balancing food security and environmental impacts. Nat Rev Microbiol 2021; 19:553–66.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00543-6


3. Weimer PJ. Redundancy, resilience, and host specificity of the ruminal microbiota: implications for engineering improved ruminal fermentations. Front Microbiol 2015; 6:296
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00296



4. Russell JB, Cotta MA, Dombrowski DB. Rumen bacterial competition in continuous culture: Streptococcus bovis versus Megasphaera elsdenii. Appl Environ Microbiol 1981; 41:1394–9.
https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.41.6.1394-1399.1981



5. Martin BD, Schwab E. Symbiosis: “Living together” in chaos. Stud Hist Biol 2012; 4:7–25.
6. Huws SA, Edwards JE, Lin W, et al. Microbiomes attached to fresh perennial ryegrass are temporally resilient and adapt to changing ecological niches. Microbiome 2021; 9:143
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-021-01087-w



7. Mulkern AJ, Oyama LB, Cookson AR, et al. Microbiome-derived antimicrobial peptides offer therapeutic solutions for the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2022; 8:70
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41522-022-00332-w



8. Waters CM, Bassler BL. Quorum sensing: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2005; 21:319–46.
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.012704.131001


9. Ng WL, Bassler BL. Bacterial quorum-sensing network architectures. Annu Rev Genet 2009; 43:197–222.
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-102108-134304



10. Solano C, Echeverz M, Lasa I. Biofilm dispersion and quorum sensing. Curr Opin Microbiol 2014; 18:96–104.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2014.02.008


11. Zhang Y, Li C, Yuan Z, Wang R, Angelidaki I, Zhu G. Syntrophy mechanism, microbial population, and process optimization for volatile fatty acids metabolism in anaerobic digestion. Chem Eng J 2023; 452:139137
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139137

13. Tarr PI, Gordon CA, Chandler WL. Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli and haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet 2005; 365:1073–86.
https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(05)71144-2


14. Miller MB, Bassler BL. Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 2001; 55:165–99.
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.165


15. McBrayer DN, Cameron CD, Tal-Gan Y. Development and utilization of peptide-based quorum sensing modulators in Gram-positive bacteria. Org Biomol Chem 2020; 18:7273–90.
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0OB01421D



16. Tal-Gan Y, Ivancic M, Cornilescu G, Blackwell HE. Characterization of structural elements in native autoinducing peptides and non-native analogues that permit the differential modulation of AgrC-type quorum sensing receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Org Biomol Chem 2016; 14:113–21.
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01735A



17. Winzer K, Williams P. Quorum sensing and the regulation of virulence gene expression in pathogenic bacteria. Int J Med Microbiol 2001; 291:131–43.
https://doi.org/10.1078/1438-4221-00110


18. De Kievit TR. Quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Environ Microbiol 2009; 11:279–88.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01792.x


19. Bhargava N, Sharma P, Capalash N. Quorum sensing in Acinetobacter: an emerging pathogen. Crit Rev Microbiol 2010; 36:349–60.
https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841x.2010.512269


20. Defoirdt T. Quorum-sensing systems as targets for antivirulence therapy. Trends Microbiol 2018; 26:313–28.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2017.10.005


21. Whiteley M, Diggle SP, Greenberg EP. Bacterial quorum sensing: the progress and promise of an emerging research area. Nature 2017; 551:313–20.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature24624



22. Ghali I, Shinkai T, Mitsumori M. Mining of luxS genes from rumen microbial consortia by metagenomic and metatranscriptomic approaches. Anim Sci J 2016; 87:666–73.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-13356


23. Won MY, Oyama LB, Courtney SJ, Creevey CJ, Huws SA. Can rumen bacteria communicate to each other? Microbiome 2020; 8:23
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-020-00796-y



24. Liu X, Liu Q, Sun S, et al. Exploring AI-2-mediated interspecies communications within rumen microbial communities. Microbiome 2022; 10:167
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-022-01367-z



25. Xie Y, Sun H, Xue M, Liu J. Metagenomics reveals differences in microbial composition and metabolic functions in the rumen of dairy cows with different residual feed intake. Anim Microbiome 2022; 4:19
https://doi.org/10.1186/s42523-022-00170-3



26. Erickson DL, Nsereko VL, Morgavi DP, Selinger LB, Rode LM, Beauchemin KA. Evidence of quorum sensing in the rumen ecosystem: detection of N-acyl homoserine lactone autoinducers in ruminal contents. Can J Microbiol 2002; 48:374–8.
https://doi.org/10.1139/w02-022


27. Yang Y, Zhou M, Hardwidge PR, Cui H, Zhu G. Isolation and characterization of N-acyl homoserine lactone-producing bacteria from cattle rumen and swine intestines. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2018; 8:155
https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2018.00155



28. Dziva F, van Diemen PM, Stevens MP, Smith AJ, Wallis TS. Identification of Escherichia coli O157: H7 genes influencing colonization of the bovine gastrointestinal tract using signature-tagged mutagenesis. Microbiology 2004; 150:3631–45.
https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.27448-0


29. Edrington TS, Farrow RL, Sperandio V, et al. Acyl-homoserine-lactone autoinducer in the gastrointestinal tract of feedlot cattle and correlation to season, E. Coli O157: H7 prevalence, and diet. Curr Microbiol 2009; 58:227–32.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-008-9312-8



30. González LA, Manteca X, Calsamiglia S, Schwartzkopf-Genswein KS, Ferret A. Ruminal acidosis in feedlot cattle: Interplay between feed ingredients, rumen function and feeding behavior (a review). Anim Feed Sci Technol 2012; 172:66–79.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2011.12.009

31. Ran T, Zhou CS, Xu LW, et al. Initial detection of the quorum sensing autoinducer activity in the rumen of goats in vivo and in vitro. J Integr Agric 2016; 15:2343–52.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61417-X

32. Seshadri R, Leahy SC, Attwood GT, et al. Cultivation and sequencing of rumen microbiome members from the Hungate 1000 Collection. Nat Biotechnol 2018; 36:359–67.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4110



33. Shi W, Moon CD, Leahy SC, et al. Methane yield phenotypes linked to differential gene expression in the sheep rumen microbiome. Genome Res 2014; 24:1517–25.
https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.168245.113



34. Gharechahi J, Vahidi MF, Bahram M, Han JL, Ding XZ, Salekdeh GH. Metagenomic analysis reveals a dynamic microbiome with diversified adaptive functions to utilize high lignocellulosic forages in the cattle rumen. ISME J 2021; 15:1108–20.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-00837-2



35. Sayers EW, Cavanaugh M, Clark K, et al. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 2022; 50:D161–4.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab1135



36. Mitsumori M, Xu L, Kajikawa H, et al. Possible quorum sensing in the rumen microbial community: detection of quorum-sensing signal molecules from rumen bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2003; 219:47–52.
https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1097(02)01192-8


37. Gorenc G, Lukas F, Avgustin G. Examination of ai-2 quorum sensing system in Prevotella bryantii and Prevotella ruminicola-like strains by using bioluminiscence assay. Acta Agric Slov 2007; 90:107–13.


38. Asanuma N, Yoshii T, Hino T. Molecular characterization and transcription of the luxS gene that encodes LuxS autoinducer 2 synthase in Streptococcus bovis. Curr Microbiol 2004; 49:366–71.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-004-4356-x


39. Harrington A, Tal-Gan Y. Identification of Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus (biotype I) competence-stimulating peptide pheromone. J Bacteriol 2018; 200:10–128.
https://doi.org/10.1128%2FJB.00709-17

40. Geisinger E, George EA, Muir TW, Novick RP. Identification of ligand specificity determinants in AgrC, the Staphylococcus aureus quorum-sensing receptor. J Biol Chem 2008; 283:8930–8.
https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M710227200



41. Gomes-Fernandes M, Laabei M, Pagan N, et al. Accessory gene regulator (Agr) functionality in Staphylococcus aureus derived from lower respiratory tract infections. PLoS One 2017; 12:e0175552
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0175552



42. Otto M. Critical assessment of the prospects of quorum-quenching therapy for staphylococcus aureus infection. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24:4025
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24044025



43. Burrell PC. The detection of environmental autoinducing peptide quorum-sensing genes from an uncultured Clostridium sp. in landfill leachate reactor biomass. Lett Appl Microbiol 2006; 43:455–60.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2006.01968.x


44. Hughes DT, Terekhova DA, Liou L, et al. Chemical sensing in mammalian host–bacterial commensal associations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2010; 107:9831–6.
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1002551107



45. Sperandio V. SdiA sensing of acyl-homoserine lactones by enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) serotype O157. Gut Microbes 2010; 1:432–5.
https://doi.org/10.4161/gmic.1.6.14177



46. Nguyen Y, Sperandio V. Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) pathogenesis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2012; 2:90
https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2012.00090



47. Huws SA, Mayorga OL, Theodorou MK, et al. Successional colonization of perennial ryegrass by rumen bacteria. Lett Appl Microbiol 2013; 56:186–96.
https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12033


48. Huws SA, Edwards JE, Creevey CJ, et al. Temporal dynamics of the metabolically active rumen bacteria colonizing fresh perennial ryegrass. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2016; 92:fiv137
https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiv137


49. Mayorga OL, Kingston-Smith AH, Kim EJ, et al. Temporal metagenomic and metabolomic characterization of fresh perennial ryegrass degradation by rumen bacteria. Front Microbiol 2016; 7:1854
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01854



50. Landini P, Antoniani D, Burgess JG, Nijland R. Molecular mechanisms of compounds affecting bacterial biofilm formation and dispersal. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2010; 86:813–23.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2468-8


51. Nkrumah JD, Okine EK, Mathison GW, et al. Relationships of feedlot feed efficiency, performance, and feeding behavior with metabolic rate, methane production, and energy partitioning in beef cattle. J Anim Sci 2006; 84:145–53.
https://doi.org/10.2527/2006.841145x


52. Yogeswara IBA, Maneerat S, Haltrich D. Glutamate decarboxylase from lactic acid bacteria—A key enzyme in GABA synthesis. Microorganisms 2020; 8:1923
https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121923



53. Skandamis PN, Nychas GJ. Quorum sensing in the context of food microbiology. Appl Environ Microbiol 2012; 78:5473–82.
https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00468-12



54. Goo E, An JH, Kang Y, Hwang I. Control of bacterial metabolism by quorum sensing. Trends Microbiol 2015; 23:567–76.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2015.05.007


55. Ellis JL, Kebreab E, Odongo NE, McBride BW, Okine EK, France J. Prediction of methane production from dairy and beef cattle. J Dairy Sci 2007; 90:3456–66.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2006-675


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 1,635 View
- 107 Download
- Related articles
-
— Invited Review — Ruminal ciliates as modulators of the rumen microbiome 2024 February;37(2)






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print




