4. Toomer OT, Livingston ML, Wall B, et al. Meat quality and sensory attributes of meat produced from broiler chickens fed a high oleic peanut diet. Poult Sci 2019; 98:5188ŌĆō97.
https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pez258


5. Kuttappan VA, Hargis BM, Owens CM. White striping and woody breast myopathies in the modern poultry industry: a review. Poult Sci 2016; 95:2724ŌĆō33.
https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pew216


7. Jung S, Bae YS, Kim HJ, et al. Carnosine, anserine, creatine, and inosine 5ŌĆÖ-monophosphate contents in breast and thigh meats from 5 lines of Korean native chicken. Poult Sci 2013; 92:3275ŌĆō82.
https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2013-03441


9. Zhou XJ, Zhu NH, Zhang RJ. Effect of breed, age and feeding method on inosinic acid and intramuscular fat content of chicken meat. Chin J Anim Nutr 2010; 22:1251ŌĆō6.
10. Sun YJ, Tian HS, Zhao GP, et al. Influence of different feeding methods on muscle flavor substances of Beijing You chicken. Chin Anim Husband Veteri Medic 2014; 41:89ŌĆō94.
11. Chen YB. Study on the relationship between the change rule of IMP content and correlation of related. Shaanxi, China: Shaanxi University of Technology; 2021. p. 53ŌĆō6.
12. Dalgaard LB, Rasmussen MK, Bertram HC, et al. Classification of wooden breast myopathy in chicken pectoralis major by a standardised method and association with conventional quality assessments. Int J Food Sci Technol 2018; 53:1744ŌĆō52.
https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13759

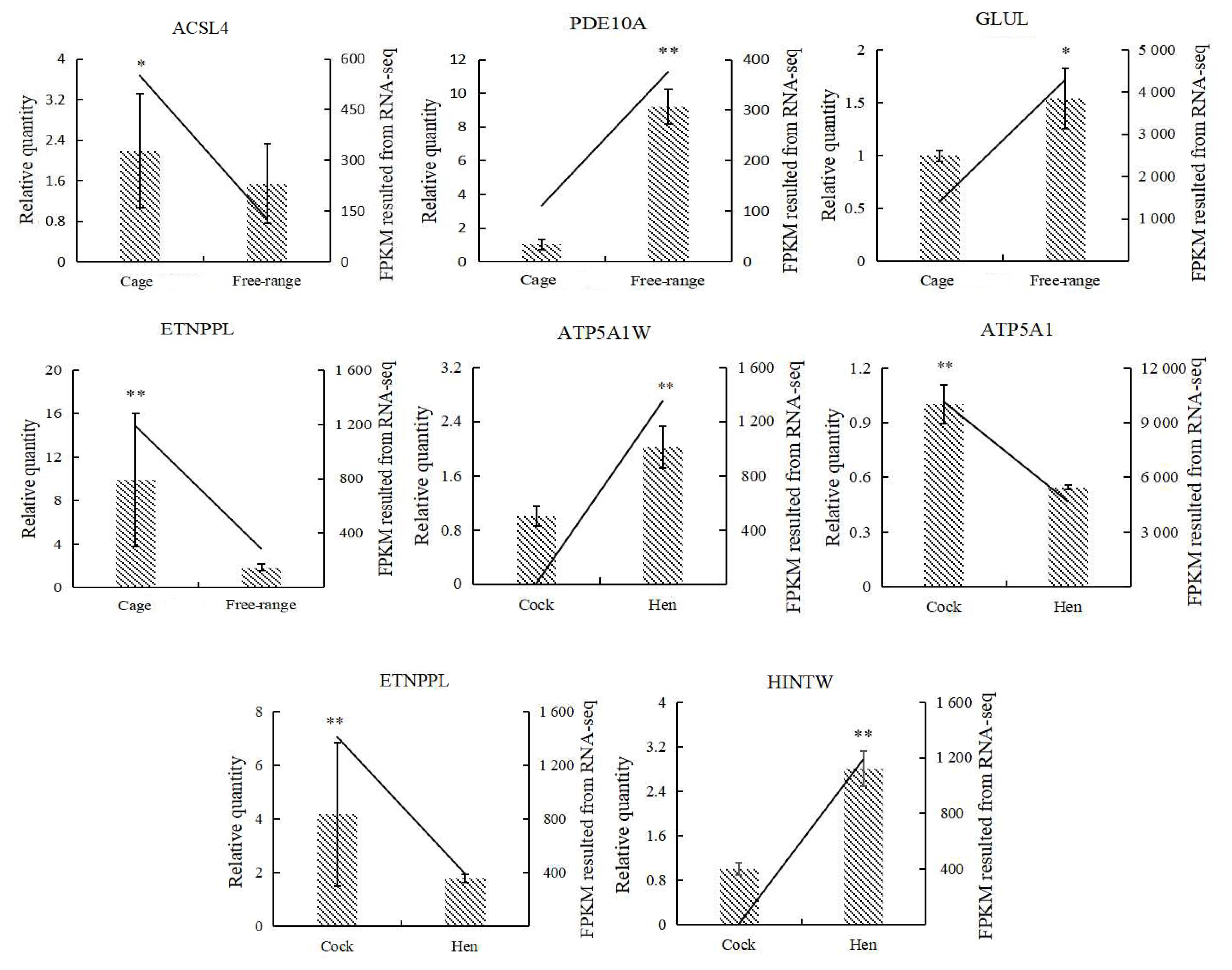
16. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(ŌłÆDelta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001; 25:402ŌĆō8.
https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262


17. Yan JS, Liu PF, Xu LM, et al. Effects of exogenous inosine monophosphate on growth performance, flavor compounds, enzyme activity, and gene expression of muscle tissues in chicken. Poult Sci 2018; 97:1229ŌĆō37.
https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pex415


18. K├╝├¦├╝k├Čzet AO, Uslu MK. Cooking loss, tenderness, and sensory evaluation of chicken meat roasted after wrapping with edible films. Food Sci Technol Int 2018; 24:576ŌĆō84.
https://doi.org/10.1177/1082013218776540


19. Musundire MT, Halimani TE, Chimonyo M. Physical and chemical properties of meat from scavenging chickens and helmeted guinea fowls in response to age and sex. Br Poult Sci 2017; 58:390ŌĆō6.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00071668.2017.1313961


23. Li Q, Zhang L, Lu H, Song S, Luo Y. Comparison of postmortem changes in atp-related compounds, protein degradation and endogenous enzyme activity of white muscle and dark muscle from common carp (cyprinus carpio) stored at 4┬░C. LWT-Food Sci Technol 2017; 78:317ŌĆō24.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.12.035

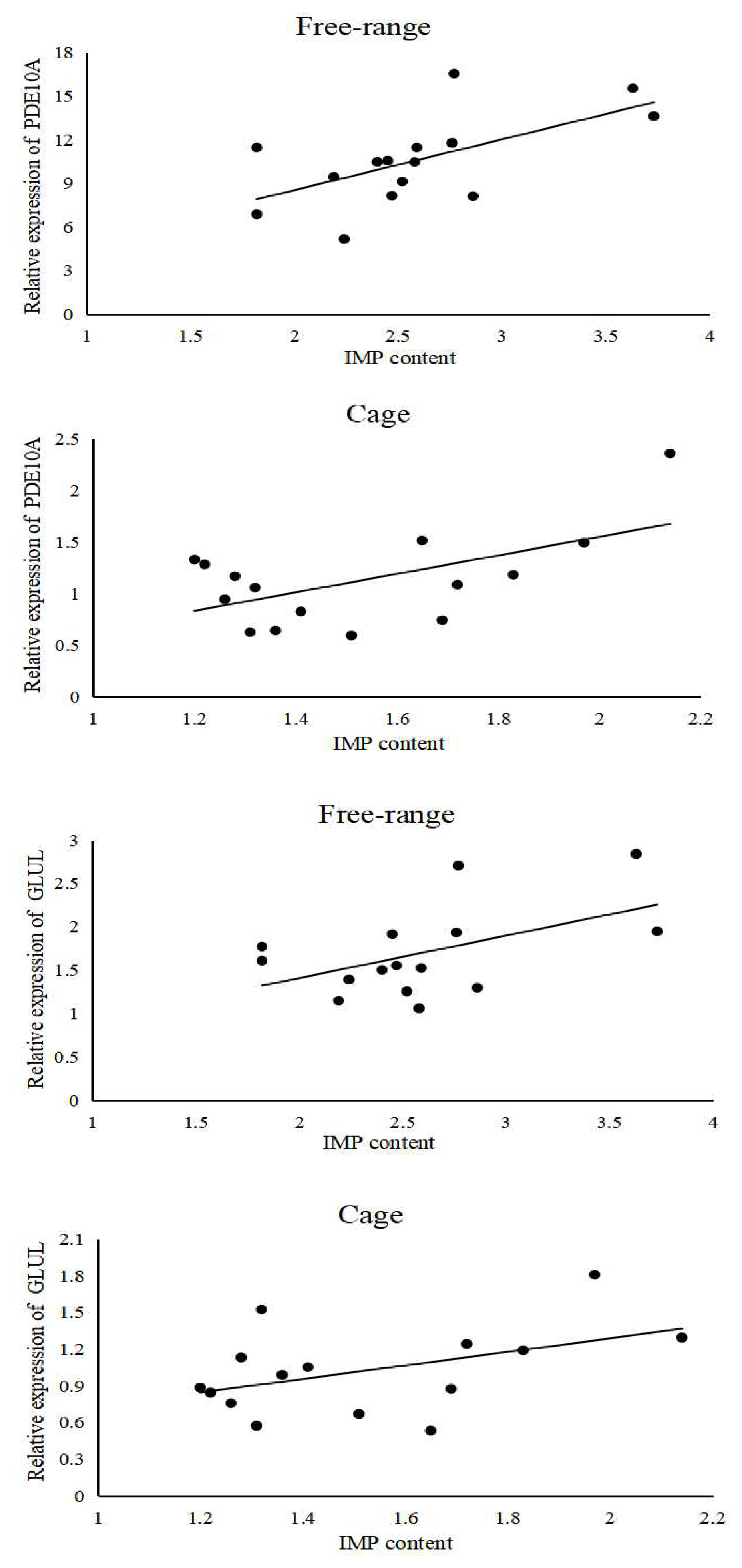
28. Fujishige K, Kotera J, Michibata H, et al. Cloning and characterization of a novel human phosphodiesterase that hydrolyzes both cAMP and cGMP (PDE10A). J Biol Chem 1999; 274:18438ŌĆō45.
https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.26.18438


29. Loughney K, Snyder PB, Uher L, Rosman GJ, Ferguson K, Florio VA. Isolation and characterization of PDE10A, a novel human 3ŌĆÖ, 5ŌĆÖ-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Gene 1999; 234:109ŌĆō17.
https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1119(99)00171-7


32. He YJ, Hakvoort TB, Vermeulen JL, Lamers WH, Van RMA. Glutamine synthetase is essential in early mouse embryogenesis. Dev Dyn 2007; 236:1865ŌĆō75.
https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.21185













 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





