 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 35(1); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
Intramuscular fat (IMF) is a critical economic indicator of pork quality. Studies on IMF among different pig breeds have been performed via high-throughput sequencing, but comparisons within the same pig breed remain unreported.
Methods
This study was performed to explore the gene profile and identify candidate long noncoding RNA (lncRNAs) and mRNAs associated with IMF deposition among Laiwu pigs with different IMF contents. Based on the longissimus dorsi muscle IMF content, eight pigs from the same breed and management were selected and divided into two groups: a high IMF (>12%, H) and low IMF group (<5%, L). Whole-transcriptome sequencing was performed to explore the differentially expressed (DE) genes between these two groups.
Results
The IMF content varied greatly among Laiwu pig individuals (2.17% to 13.93%). Seventeen DE lncRNAs (11 upregulated and 6 downregulated) and 180 mRNAs (112 upregulated and 68 downregulated) were found. Gene Ontology analysis indicated that the following biological processes played an important role in IMF deposition: fatty acid and lipid biosynthetic processes; the extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade; and white fat cell differentiation. In addition, the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-protein kinase B, and mammalian target of rapamycin pathways were enriched in the pathway analysis. Intersection analysis of the target genes of DE lncRNAs and mRNAs revealed seven candidate genes associated with IMF accumulation. Five DE lncRNAs and 20 DE mRNAs based on the pig quantitative trait locus database were identified and shown to be related to fat deposition. The expression of five DE lncRNAs and mRNAs was verified by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The results of qRT-PCR and RNA-sequencing were consistent.
Intramuscular fat (IMF), or marbling, which consists of white spots or stripes of adipose tissue in muscle fiber tracts, is a crucial index affecting meat flavor and tenderness. The IMF is also regarded as a pivotal characteristic to evaluate the quality of pork [1,2]. High IMF is an indicator of symbol of high-grade pork. Thus, to improve the IMF of pork, it is necessary to understand the molecular and cellular mechanisms of fat deposition in muscle. With the development of high-throughput sequencing, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) have been extensively used in recent years to identify genomic regions and candidate genes associated with a variety of pork traits [3ã5]. Furthermore, the appropriate analysis and reliable interpretation of the large datasets obtained by GWAS and RNA-seq is critical for gene expression studies.
Long noncoding RNA (lncRNAs) are vital noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) that regulate fat accumulation, including the processes of proliferation, differentiation, and hypertrophy of adipocytes [6,7]. Evidence has shown that lncIMF4 regulates porcine intramuscular preadipocytes by attenuating autophagy to inhibit lipolysis [8]. LncRNA IMFlnc1 increases caveolin-1 by sponging miR-199a-5p to promote porcine intramuscular adipocyte adipogenesis [9]. However, fat deposition disorder may also lead to obesity, diabetes, and atherosclerosis [10ã12] in humans. RNA-seq performed in humans has determined the molecular regulation mechanisms of fat accumulation between different groups of samples with different genetic backgrounds. For farm animals, RNA-seq conducted using samples obtained from full or half-sibs to control kinship obtains more rigorous data, which will help to elucidate the relatively accurate mechanism of adipogenesis and metabolism, thereby potentially identifying as well as find the novel methods to control fat deposition in meat.
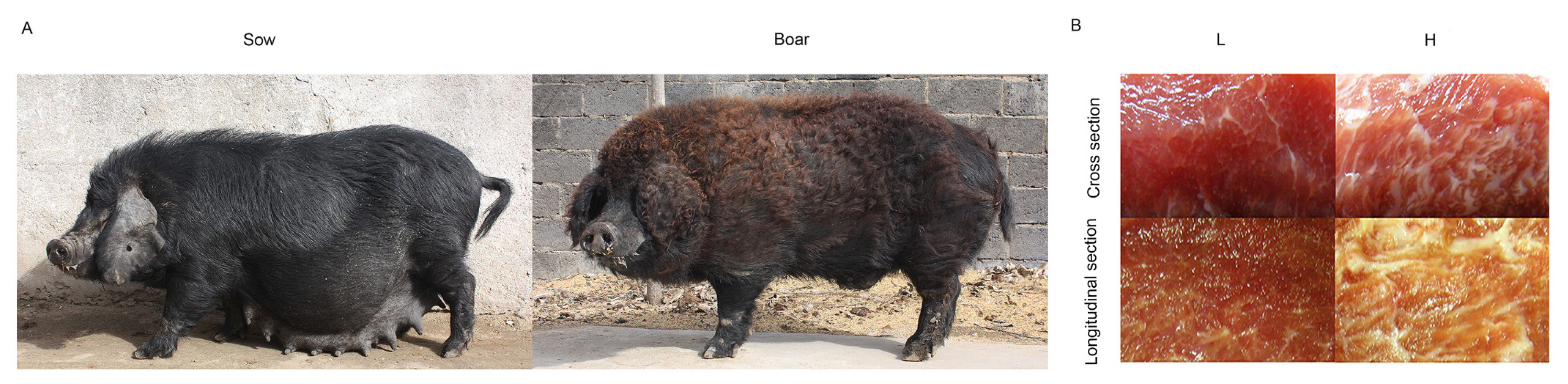
Laiwu pigs, an invaluable Chinese indigenous pig breed with high-quality pork, were selected in the present study to investigate the mechanisms of IMF differential expression among individuals [13] (Figure 1A). A previous study comparing Laiwu pigs and Yorkshire pigs has determined the IMF content of Laiwu pigs to be 13.83% [14]. We also found a wide range of variation (2.4% to 17.8%) in the IMF content in a study containing 333 Laiwu pigs [15]. This indicated that the content of IMF varies greatly among Laiwu pig individuals. In addition, few studies were reported on the comparison of gene expression and regulation from same breed, especially for Laiwu pigs. Therefore, based on these previous studies concerning the relationship between gene regulation and fat metabolism, the objective of the present study was to explore and identify valuable candidate lncRNAs and mRNAs associated with IMF accumulation in Laiwu pigs, which may be helpful for breeding pigs to produce high-quality pork. Here, individual Laiwu pigs with high or low IMF (Figure 1B) were identified and selected for analysis in this study. Transcriptomes of longissimus dorsi (LD) muscle samples from different Laiwu pig individuals were analyzed using RNA-seq to determine the differentially expressed (DE) lncRNAs and mRNAs from the different phenotypes of the same breed. This research may help to identify genes associated with IMF deposition and their functions in farm animals.
Twenty-nine male 300-d-old Laiwu pigs (approximately 96ôÝ 4 kg) reared at the Laiwu pig breeding farm in Jinan, Shandong Province, China, were selected for this study. All pigs were fed the same commercial pig diet and water ad libitum. After exsanguination, approximately 100 g of LD muscle from the last rib of each pig was obtained immediately for IMF content determination, RNA preparation, and oil red O staining analysis. For RNA isolation and protein analysis, samples were immediately placed into liquid nitrogen and stored at ã80ô¯C until analysis. Samples (1 cmû1 cmû0.5 cm) taken from the cross-section of the LD muscle and the liver were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (Solarbio, Beijing, China) for fatty analysis by oil red O staining. The remaining samples were stored at ã20ô¯C for the determination of fat content.
The IMF content evaluation was conducted 24 h after slaughter. Based on the ãTechnical regulation for determination of pork quality (NY/T 821-2004, China)ã, IMF content was determined using the Soxhlet petroleum-ether extraction method and expressed as the percentage of fat relative to wet muscle tissue. Specifically, the sample was mashed and dried to a constant weight at 105ô¯C. Following drying, the sample was continuously extracted in petroleum (Caratton, Tianjin, China) for 8 h using a Soxhlet flask. Then, all samples were removed and dried to a constant weight at 80ô¯C. According to the IMF content determined in LD muscle, eight half-sibs of Laiwu pigs were selected and divided into the following two groups: high IMF group and low IMF group, respectively.
Lipid accumulation was visualized by staining cells or tissue sections with the lipid-specific dye, oil red O (Solarbio, China). Tissue was first immersed in 30% isopropanol (Solarbio, China) until it sank to the bottom of the solution. After continuous 14 ö¥m tissue sectioning, sections were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde solution, washed with tap water for 30 min, and then washed with 60% isopropanol (Hushi, Shanghai, China). Staining was performed by immersing slides in oil red O solution for 30 min. Then, all slides were immersed again in 60% isopropanol, and nuclei were stained in alum hematoxylin (Solarbio, China) for 1 min, washed in distilled water and mounted in aqueous solution.
Total RNA was extracted with TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) from Laiwu pig muscle samples (stored at ã80ô¯C). One gram of total RNA was further treated with RNase-free DNase I (Accurate Biotechnology, Hunan, China) to eliminate genomic DNA contamination according to the manufacturerãs instruction. The integrity and quality of total RNA were evaluated using Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer (Santa Clara, CA, USA) and expressed using the RIN value. The results showed that all samples had RIN values greater than 8.2 (Supplementary Table S1), indicating that all RNA samples met the quality requirement of RNA-seq. All RNA samples were stored at ã80ô¯C before further processing.
For RNA-seq, 14 ö¥g of RNA per sample was used as input material for the RNA sample preparations. The RNA was fragmented into 250 to 300 bp fragments after removing the ribosomal RNA using the rRNA Removal Kit (Epicentre, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturerãs instruction. First-strand of cDNA was synthesized using fragmented RNA as a template and random oligonucleotides as primers. After purification, double-stranded cDNA was repaired at the end followed by the addition of A tail, and the DNA was connected with sequencing adapters. AMPure XP Beads were used to screen approximately 350 to 400 bp of cDNA. The USER enzyme (NEB, Ipswich, MA, USA) was used to degrade the second strand of cDNA containing U, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification was then performed to obtain the library. After library construction, the concentration of the library was measured by a Qubit fluorometer and adjusted to 1 ng/ö¥L. An Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer was utilized to examine 250 to 300 bp of the acquired library. Finally, the concentration of the cDNA library was verified using quantitative PCR (qPCR). Once the insert size and concentration of the library were greater than 2 nM, the samples were then subjected to sequencing.
Raw data (raw reads) in FASTQ format were first processed through in-house perl scripts. In this step, clean data (clean reads) were obtained by removing the following reads: i) reads with 5ãý adapter; ii) reads without 3ãý adapter or insert sequence; iii) reads with more than 10% N; iv) reads with more than 50% nucleotides with QphredãÊ20; and v) reads with poly A/T/G/C. Adapter trimming for the removal of adapter sequences from the 3ãý ends of reads was also performed. At the same time, the Q20, Q30, and GC contents of the clean data were calculated. Approximately 93.76% to 94.34% of clean reads were mapped to the reference genome of pigs and 80% of clean reads were uniquely mapped (Supplementary Table S1). All downstream analyses were based on clean data with high quality. Clean reads for each sample were first mapped to a reference genome with HISAT2 software [16]. Reads alignment results were transferred to the program StringTie for transcript assembly.
Quantification of the transcripts and genes was performed using StringTie software, and fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads was obtained. Cuffdiff or edgeR was used for differential expression analysis. The resulting p-values were adjusted using Benjamini and Hochbergãs approach for controlling the false discovery rate. All the transcripts were merged using Cuffmerge software, and then the selected lncRNAs were annotated using Cuffcompare. The reference genome version used for sequence alignment was GCF_000003025.6_Sscrofa11.1. Genes with |log2 (fold change)| >0 and padj<0.05 were assigned as DE. There were 17 DE lncRNAs, which included 11 upregulated and 6 downregulated lncRNAs. In addition, there were 180 DE mRNAs, which included 112 upregulated and 68 downregulated mRNAs (Supplementary Figure S1) (p<0.05).
Gene ontology (GO) analysis describes the functions of genes, and it is divided into the following three parts: molecular functions, biological processes and cellular components. Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) is a comprehensive database integrating genome, chemical, and system functional information [17]. GO seq software was used for GO enrichment analysis. Pathway enrichment analysis was performed using KOBAS (2.0) [18,19]. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses of target genes of DE lncRNAs were performed using the cluster Profiler R package, in which gene length bias was corrected. The enrichment was considered significant when the corrected p-value was less than 0.05.
The high- and low-IMF library preparation and sequencing were performed by Novogene Bioinformatics Technology Corporation. After library preparation, the samples were subjected to Illumina sequencing. A total of 12 Gb of raw data (Supplementary Table S1) for lncRNA-seq analysis were obtained using PE150 (paired-end 150 nt) sequencing.
The total RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA according to the manufacturerãs instructions of the PrimeScript RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (TaKaRa, Dalian, China). All quantitative real time-PCR (qRT-PCR) assays were performed using the Mx3000p Real-Time System (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA). Primers were obtained from Sheng Gong (Shanghai, China), and the sequences are shown in Table 1. The qRT-PCR was performed in triplicate with SYBR Premix Ex Taq (Takara, China) using the following program: 95ô¯C for 30 s; 40 cycles of 95ô¯C for 5 s, 58ô¯C for 30 s, and 72ô¯C for 30 s. To exclude between-run variations, all samples were amplified in triplicates and the means were used for further analysis. Data analyses were performed using the 2ãööCT method.
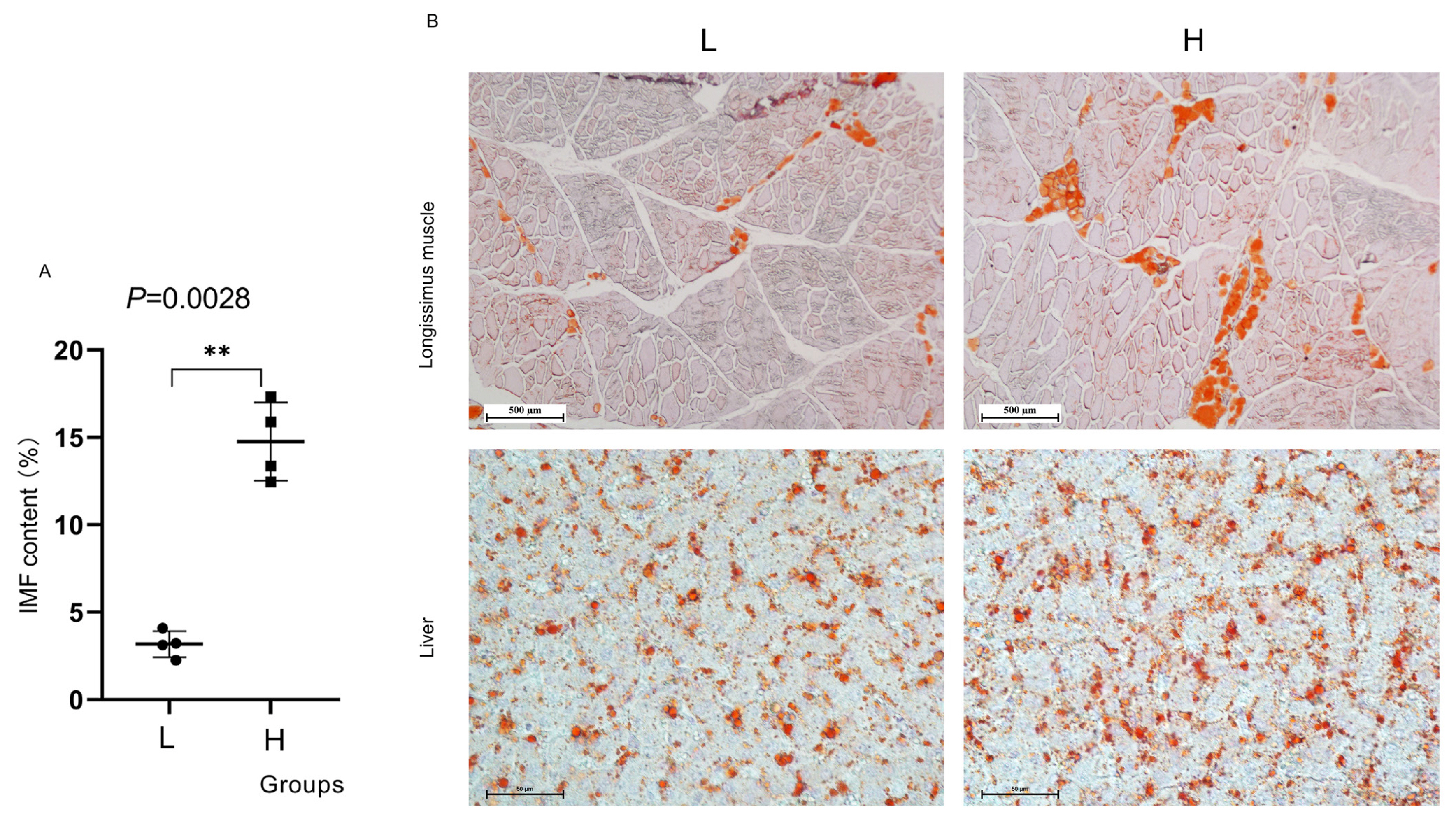
The IMF contents of LD muscle samples from the 29 pigs were determined (Supplementary Table S2), and samples from eight pigs were then selected and divided into two groups for further analysis. The two groups included the high IMF content group (>12%, in terms of H) and the low IMF content group (<5%, in terms of L). Figure 2A shows that the H group had significantly higher IMF content than the L group (p<0.05). To better visualize the differences in muscle and liver transection fat distribution, frozen sections were prepared, and oil red O Staining was performed to elucidate the differences in IMF content in more detail (Figure 2B). The results indicated that compared to the H group, the total area of fat stained by oil red O was larger than that of the L group.
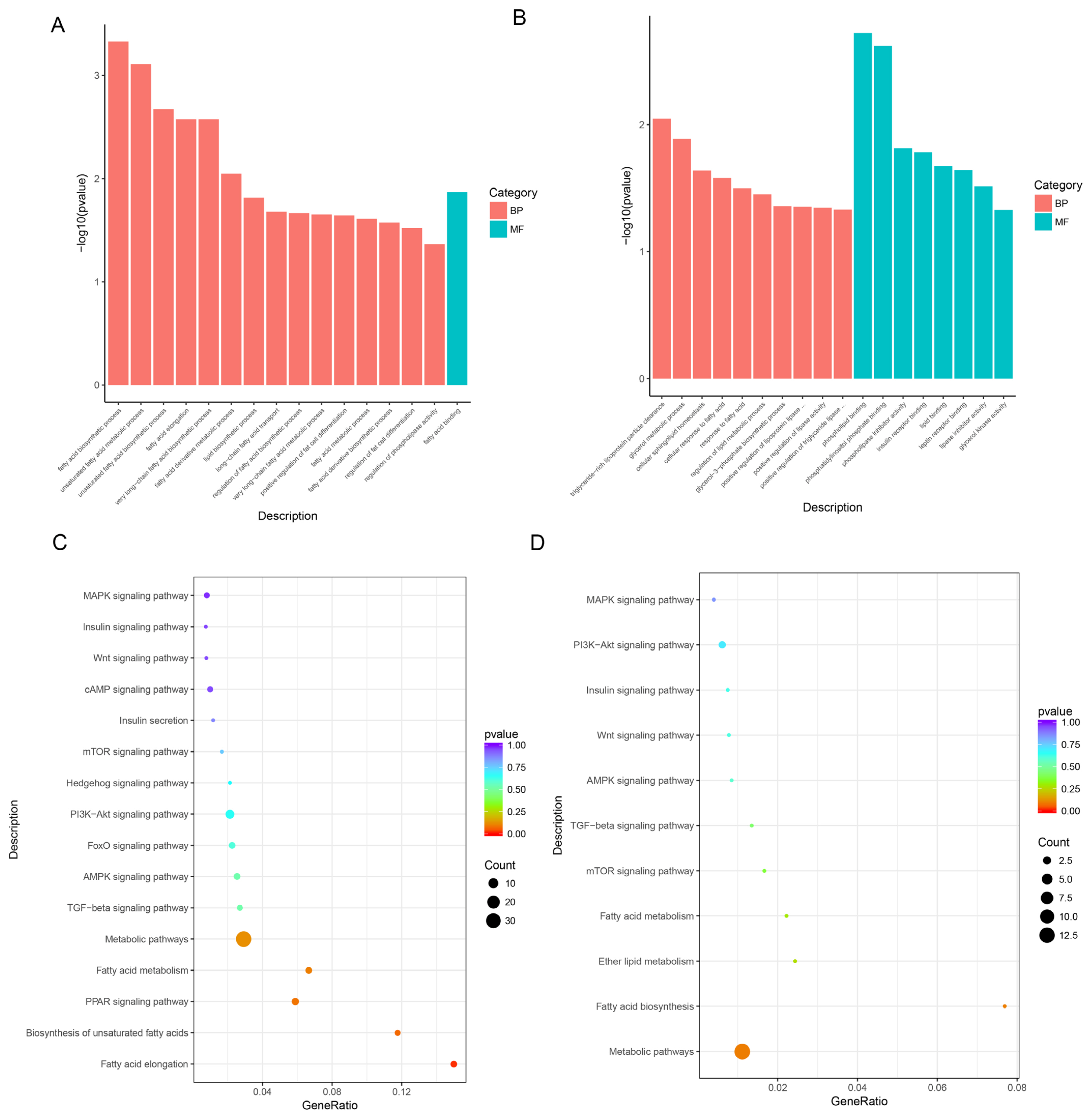
The DE lncRNAs were annotated by GO analysis. As shown in Figure 3, DE lncRNAs were mainly enriched in fatty acid biosynthetic process, unsaturated fatty acid metabolic process, fatty acid metabolic process, and regulation of fat cell differentiation (p<0.05). These genes were also enriched in fatty acid binding molecular functions (Supplementary Table S3). At the same time, the main GO terms of mRNAs related to IMF were significantly enriched in biological processes and molecular functions (p<0.05), including cellular response to fatty acids, cellular sphingolipid homeostasis, insulin receptor binding, and glycerol kinase activity (Supplementary Table S4).
The lncRNA KEGG enrichment analysis demonstrated that 17 DE lncRNAs were enriched in 206 signaling pathways. Among the signaling pathways, the first 15 were listed sorted by p value in Supplementary Table S5. Fatty acid elongation (p = 0.015) and arachidonic acid metabolism (p = 0.019) were the two significantly enriched signaling pathways. In addition, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were also enriched in signaling pathways associated with fat deposition and lipid metabolism, such as biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) signaling pathway, and steroid biosynthesis (Figure 3C). The mRNA KEGG enrichment analysis demonstrated that 180 DE mRNAs were enriched in 114 signaling pathways (the first 15 were listed sorted by p value in Supplementary Table S6). Similar to lncRNAs, the different mRNAs were also enriched in signaling pathways associated with fat deposition and lipid metabolism (Figure 3D).
LncRNAs regulate the expression of target genes (mRNAs) through colocation (in cis) or coexpression (in trans). Intersection analysis of the target genes of DE lncRNAs and the DE mRNAs was performed to elucidate the correlation of lncRNAs and mRNAs. Target gene unions and DE mRNAs of colocation and coexpression were selected for analysis, including two downregulated genes (NEK10 and ZFR) and five up-regulated genes (ERLEC1, RBM47, MYOF, VWA8, and C1orf194). The intersections (full name) of the target genes of DE lncRNAs and mRNAs are shown in Table 2.
To confirm the differences in gene transcription levels between the lowest marbling grade and highest marbling grade samples, we examined the expression of IMF-associated lncRNAs and mRNAs based on the pig quantitative trait locus (QTL) database (https://www.animalgenome.org/cgi-bin/QTLdb/SS/index). In total, 25 DEGs in LD muscle were detected, including five lncRNAs (TCONS_00145693, TCONS_00013374, TCONS_00133808, TCONS_00013376, and TCONS_00014550) and 20 mRNAs (listed in the heatmap in Figure 4M, 4N). The expression of five lncRNAs and mRNAs was confirmed by qRT-PCR. The qRT-PCR analysis showed the expression of lncRNAs (Figure 4Aã4E, TCONS_00013374, TCONS_00133808, TCONS_00014550, TCONS_00013376, and TCONS_00145693) and mRNAs (Figure 4Fã4J, syntaxin binding protein 5 [STXBP5], ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase phosphodiesterase 1 [ENPP1], synemin [SYNM], SR-related CTD associated factor 8 [SCAF8], and spastic paraplegia gene 11 [SPG11]), which were screened based on pig QTL databases (Figure 4). The qRT-PCR results for these genes were consistent with the RNA-seq results.
The Laiwu pig is an excellent breed raised in China with a high IMF content. Several previous studies concerning IMF content have been reported; however, most of these studies were performed to compare the difference between two breeds of pigs [14,20,21] to investigate DEGs associated with IMF deposition. However, in animal production, we found that IMF content varies vastly among individual Laiwu pigs. Among the 29 LD samples tested, the high IMF content could be achieved 13.93%, while the low content was only 2.17%, which was confirmed by pork marbling (Figure 1) and oil red O staining (Figure 2). Our results were similar to the results that a wide range of variation (2.4% to 17.8%) in the IMF trait of Laiwu pig individuals reported in a previous study [12]. Although all types of cells contain the same genome, they have different structures and behaviors due to the cell and tissue specificity of gene expression. All cells in multicellular organisms are derived from a single cell, which differentiates in response to external or internal cell signals and gradually establishes different gene expression patterns to exhibit different functions. Identical twins are not identical, and similarly, clonal microbial cells or Laiwu pigs (our samples in this article) differ in many aspects even when grown simultaneously in a common environment. This phenomenon may be caused by cell-to-cell heterogeneity in gene expression [22]. Cell-to-cell heterogeneity in lipid droplet production results in differences in lipid storage [23,24], which may be responsible for differences in IMF content among individuals of the same breed, even if pigs are under the unified environment. We hypothesize that the significant difference in IMF content among individuals may be regulated by cell-to-cell heterogeneity in candidate gene expression in fat deposition. In the present study, all pigs were selected from the same breed, same sex, and similar weight to allow candidate genes to be more reliable, thereby excluding unreliable factors identified due to different breeds or different feed conditions. To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first attempt to elucidate this phenomenon, which would help to provide new perspectives into the mechanism of IMF accumulation in pigs.
With the development of high-throughput sequencing, an increasing number of studies have indicated that lncRNAs regulate fat deposition processes by affecting epigenetic regulation, transcription, posttranscriptional levels and protein translation processes [7,25,26]. Fat deposition in animals is primarily determined by the proliferation and hypertrophy of adipocytes. Evidence has shown that lncRNA Gm15290 promotes PPARö°-induced fat accumulation and contributes to body weight gain in mice by sponging miR-27b [27]. LncRNA IMFNCR promotes intramuscular adipocyte differentiation in poultry by acting as a ceRNA to be combined with miR-128-3p and miR-27b-3p [6]. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore DE lncRNAs and the mechanisms of IMF deposition.
In GO and KEGG analyses, the DEGs were enriched in the processes of fatty acid elongation and biosynthesis, of which the PPAR, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-protein kinase B (PI3K-Akt), and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathways were significantly highly enriched. These pathways have been demonstrated to be associated with the processes of adipogenesis, preadipocyte differentiation, and transformation of brown and white fat cells [28ã31]. Although the functions of these DE lncRNAs and mRNAs are still unclear, these lncRNAs and mRNAs might regulate fat deposition by these signaling pathways.
To explore the candidate genes related to IMF deposition, intersection analysis of the target genes of DE lncRNAs and mRNAs was performed. Seven genes were obtained, which were both lncRNA target genes and mRNAs (ERLEC1, RBM47, MYOF, VWA8, C1orf194, NEK10, and ZFR). One of the genes is zinc finger RNA binding protein (ZFR), which is an ancient protein in eukaryotic genomes. Snail family transcriptional repressor 2 (SNAI2, also known as SLUG), a C2H2-type zinc finger transcription factor, is expressed in white adipose tissue in humans and regulates adipocyte differentiation by affecting the expression of PPARö° [32]. GATA2 and GATA3 belong to the C2C2-type zinc finger protein subfamily and are negative regulators of the preadipocyte-to-adipocyte transition. Previous studies have confirmed that GATA2 and GATA3 downregulate the expression of adipocyte differentiation markers such as PPARö° and CCAAT enhancer binding protein öÝ (C/EBPöÝ) [33,34]. Although several studies have suggested that the other six genes (ERLEC1, RBM47, MYOF, VWA8, C1orf194, and NEK10) are associated with fat content, there are many studies on the regulation of ZFR in fat deposition. Our sequencing results also provided a new direction to explore the functions of these genes in regulating fat accumulation as each of them may act as the next ZFR in the future.
In addition, 20 protein-coding genes were obtained from the results of DEGs based on the pig QTL database as follows: SCAF8, STXBP5, ENPP1, SPG11, SYNM, TULP3, ERC1, PPHLN1, GNPTAB, DYRK1B, PLD3, MIGA1, NEXN, MIER1, SCFD1, GPHN, ZNF410, YLPM1, NAALADL2, and TASP1 (the full name was shown in Figure 4). Many of these genes have been shown to be associated with fat deposition. The ENPP1 has an important role in adipogenesis processes. The ENPP1 expression in adipose tissue is increased in obese patients with insulin resistance [35], and ENPP1 is also considered both a biomarker and a novel potential therapeutic target to improve adipose tissue function and systemic glucose metabolism. TULP3, an essential regulator of ciliary GPCR (G proteinãcoupled receptors) entry, is critical for adipogenesis. It has been shown that the expression levels of TULP3 correlate with adipogenic potential [36]. In addition, DYRK1B, a member of the DYRK family, mediates the transcriptional activation of PPARö° and C/EBPöÝ in adipogenic differentiation [37]. The number of DEGs was decreased by combining sequencing data with the pig QTL database. The function of the screened differential genes by this method in fat deposition may be valuable.
It is relatively hard for lncRNAs to be applied in livestock production. First, the function of lncRNA target genes is the starting point to study the function of lncRNAs. Gene chips should be constructed to select animals expressing or not expressing specific genes. Second, interference or overexpression of candidate lncRNAs or mRNAs can be used to confirm the functions of these genes, such as lncRNA-siRNA, lncRNA-antisense oligodeoxynucleotides, and overexpression vectors [38]. CRISPR/Cas9 has become a powerful method to alter the structure of genes or the genome of many organisms [39], and it may be used to identify whether these genes function due to the specific sequence or the transcription. Because most of these methods are largely used in cells or small animals, such as mice, the protocol and dosage for pigs, which are relatively large animals compared with mice, need to be confirmed. In the future, additives that affect candidate lncRNAs or mRNAs may be identified, which may be help to improve the IMF content of pork. Therefore, finding a reliable candidate lncRNA or mRNA is a basic and crucial step.
In conclusion, this is the first report on lncRNAs in the LD muscle of half-sibling relationship Laiwu pigs with high and low IMF contents analyzed based on the RNA-seq approach. Seventeen DE lncRNAs and 180 mRNAs were identified, and the target genes of lncRNAs and mRNAs were enriched in the fat accumulation process. In addition, two methods (based on the pig QTL database and correlation analysis of the targets of lncRNAs and mRNAs) were performed to screen the DE lncRNAs and mRNAs from the sequencing data, and several genes screened by these two methods have been demonstrated to be related to fat deposition. Seven lncRNA target genes, namely, ERLEC1, RBM47, MYOF, VWA8, C1orf194, NEK10, and ZFR were identified and validated as associated with the IMF content. Therefore, we hypothesize that these genes may have important roles in the IMF deposition process. In future research, various technical methods will be performed to identify the functions and mechanisms of these DEGs to select pigs with high IMF content. The present study provides a reference for lncRNAs and mRNAs that can be used for biomedical research related to intramuscular fat accumulation in the future. However, this is only the first step in exploring the mechanisms of fat deposition. Further understanding of the molecular mechanisms controlling adipogenesis is crucial to improving pork quality.
Notes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
FUNDING
This study was supported financially by the Agricultural Animal Breeding Project of Shandong Province (No. 2020 LZGC012), Funds of Shandong ãDouble Topsã Program (No. SYL2017YSTD12), Shandong Modern Pig Technology & Industry System Project (No. SDAIT-08-02), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2018BC046, ZR2019MC053).
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Supplementary file is available from: https://doi.org/10.5713/ab.21.0092Supplementary Figure S1
Characteristics of the lncRNAs (A) and mRNAs (B) expression levels.
Supplementary Table S1. Summary of raw reads after quality control and mapping to the reference genome
Supplementary Table S2. The information of the 29 Laiwu pigs
Supplementary Table S3. The GO terms of DE lncRNA enriched in
Supplementary Table S4. The GO terms of DE mRNA enriched in
Supplementary Table S5. The DE lncRNAs KEGG enrichment analysis
Supplementary Table S6. The DE lncRNAs KEGG enrichment analysis
Figureô 1
Laiwu pigs [40] and cross and longitudinal sections of pork with different intramuscular fat contents.

Figureô 2
Intramuscular fat (IMF) content and deposition of samples. oil red O staining was performed to detect lipid accumulation in longissimus dorsi (LD) muscle and liver. ** p<0.01.
Figureô 3
GO terms and KEGG pathways. (A), (C), GO terms and pathways of lncRNAs; (B), (D), GO terms and pathways of mRNAs. GO, gene ontology; KEGG, Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.
Figureô 4
Validation and heatmaps of DE lncRNAs (AãE) and mRNAs (FãK). The DEGs in LD tissues between Laiwu pigs with high and low IMF contents was verified by qRT-PCR. DE, differentially expressed; DEGs, differentially expressed genes; LD, longissimus dorsi; IMF, intramuscular fat; qRT-PCR, quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction; ERC1, ELKS/RAB6-interacting/CAST family member 1; PLD3, phospholipase D family member 3; GNPTAB, N-Acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase subunits öÝ and öý; ZNF410, zinc finger protein 410; NEXN, Nexilin F-actin binding protein; YLPM1, YLP motif containing 1; TULP3, TUB like protein 3; NAALADL2, N-Acetylated öÝ-linked acidic dipeptidase like 2; MIER1, MIER1 transcriptional regulator; TASP1, taspase 1; PPHLN1, periphilin 1; MIGA1, mitoguardin 1; GPHN, gephyrin; DYRK1B, dual specificity tyrosine phosphorylation regulated kinase 1B; SCFD1, sec1 family domain containing 1. * p<0.05; ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.

Tableô 1
Primers for real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis
Tableô 2
Intersection analysis of the target genes of differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs
REFERENCES
1. Fernandez X, Monin G, Talmant A, Mourot J, Lebret B. Influence of intramuscular fat content on the quality of pig meatã1. Composition of the lipid fraction and sensory characteristics of m. Longissimus lumborum. Meat Sci 1999; 53:59ã65.
https://doi.org/10.1016/s0309-1740(99)00037-6


2. Harper GS, Pethick D, Oddy V, Tume R, Barendse W, Hygate L. Biological determinants of intramuscular fat deposition in beef cattle: current mechanistic knowledge and sources of variation. Sydney, Australia: Meat & Livestock Australia; 2001.
3. Guo Y, Huang Y, Hou L, et al. Genome-wide detection of genetic markers associated with growth and fatness in four pig populations using four approaches. Genet Sel Evol 2017; 21:49
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12711-017-0295-4

4. Qiao R, Gao J, Zhang Z, et al. Genome-wide association analyses reveal significant loci and strong candidate genes for growth and fatness traits in two pig populations. Genet Sel Evol 2015; 47:17
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12711-015-0089-5



5. Ropka Molik K, Zukowski K, Eckert R, Gurgul A, Piû°rkowska K, Oczkowicz M. Comprehensive analysis of the whole transcriptomes from two different pig breeds using RNA-Seq method. Anim Genet 2014; 45:674ã84.
https://doi.org/10.1111/age.12184


6. Zhang M, Li F, Sun JW, et al. LncRNA IMFNCR promotes intramuscular adipocyte differentiation by sponging miR-128-3p and miR-27b-3p. Front Genet 2019; 10:42
https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00042



7. Duan L, Min C, Niu Y, et al. Identification of a novel human long non-coding RNA that regulates hepatic lipid metabolism by inhibiting SREBP-1c. Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13:349ã57.
https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.16635



8. Sun Y, Cai R, Wang Y, Zhao R, Qin J, Pang W. A newly identified lncRNA lncIMF4 controls adipogenesis of porcine intramuscular preadipocyte through attenuating autophagy to inhibit lipolysis. Animals 2020; 10:926
https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10060926



9. Wang J, Chen M, Chen J, et al. LncRNA IMFlnc1 promotes porcine intramuscular adipocyte adipogenesis by sponging miR-199a-5p to up-regulate CAV-1. BMC Mol Cell Biol 2020; 21:77
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12860-020-00324-8



10. Kazak L, Rahbani JF, Samborska B, et al. Ablation of adipocyte creatine transport impairs thermogenesis and causes diet-induced obesity. Nat Metab 2019; 3:360ã70.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-019-0035-x

11. Chen X, Ayala I, Shannon C, et al. The diabetes gene and Wnt pathway effector TCF7L2 regulates adipocyte development and function. Diabetes 2018; 67:554ã68.
https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-0318



12. Zhang X, Zhang Y, Wang P, et al. Adipocyte hypoxia-inducible factor 2öÝ suppresses atherosclerosis by promoting adipose ceramide catabolism. Cell Metab 2019; 30:937ã51.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.09.016


13. Chen Q, Zeng Y, Wang H, et al. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of NDUFS4 gene in m. Longissimus dorsi of laiwu pig (sus scrofa). Mol Biol Rep 2013; 2:1599ã608.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2208-5

14. Chen W, Fang G, Wang S, Wang H, Zeng Y. Longissimus lumborum muscle transcriptome analysis of laiwu and yorkshire pigs differing in intramuscular fat content. Genes Genomics 2017; 39:759ã66.

15. Huang Y, Zhou L, Zhang J, Liu X, Huang L. A large-scale comparison of meat quality and intramuscular fatty acid composition among three Chinese indigenous pig breeds. Meat Sci 2020; 168:108182
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2020.108182


16. Vieth B, Parekh S, Ziegenhain C, Enard W, Hellmann I. A systematic evaluation of single cell RNA-seq analysis pipelines. Nat Commun 2019; 10:4667
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12266-7



17. Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Sato Y, Morishima K. KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 2017; 45:D353ã61.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1092


18. Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK, Oshlack A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol 2010; 11:R14
https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14



19. Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 36:suppl_1D480ã4.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm882



20. Cui JX, Zeng QF, Chen W, Zhang H, Zeng YQ. Analysis and preliminary validation of the molecular mechanism of fat deposition in fatty and lean pigs by high-throughput sequencing. Mamm Genome 2019; 30:71ã80.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-019-09795-3



21. Huang W, Zhang X, Li A, Xie L, Miao X. Genome-wide analysis of mRNAs and lncRNAs of intramuscular fat related to lipid metabolism in two pig breeds. Cell Physiol Biochem 2018; 50:2406ã22.
https://doi.org/10.1159/000495101


22. Ansel J, Bottin H, Rodriguez-Beltran C, et al. Cell-to-cell stochastic variation in gene expression is a complex genetic trait. Plos Genet 2008; 4:e1000049
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000049



23. Loo L, Lin H, Singh DK, Lyons KM, Altschuler SJ, Wu LF. Heterogeneity in the physiological states and pharmacological responses of differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Cell Biol 2009; 187:375ã84.
https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200904140



24. Herms A, Bosch M, Ariotti N, et al. Cell-to-cell heterogeneity in lipid droplets suggests a mechanism to reduce lipotoxicity. Curr Biol 2013; 23:1489ã96.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.06.032



25. Cai H, Li M, Jian W, et al. A novel lncRNA BADLNCR1 inhibits bovine adipogenesis by repressing GLRX5 expression. J Cell Mol Med 2020; 24:7175ã86.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15181



26. Zhang S, Kang Z, Cai H, et al. Identification of novel alternative splicing of bovine lncRNA lncFAM200B and its effects on preadipocyte proliferation. J Cell Physiol 2021; 236:601ã11.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29887


27. Liu W, Ma C, Yang B, Yin C, Zhang B, Xiao Y. LncRNA Gm15290 sponges miR-27b to promote PPARö°-induced fat deposition and contribute to body weight gain in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2017; 493:1168ã75.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.09.114


28. Wang S, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, et al. Agrimol B suppresses adipogenesis through modulation of SIRT1-PPAR gamma signal pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016; 477:454ã60.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.078


29. Rachid TL, Silva-Veiga FM, Graus-Nunes F, Bringhenti I, Mandarim-De-Lacerda CA, Souza-Mello V. Differential actions of PPAR-öÝ and PPAR-öý/öÇ on beige adipocyte formation: a study in the subcutaneous white adipose tissue of obese male mice. Plos One 2018; 13:e0191365
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191365



30. Song B, Chi Y, Li X, et al. Inhibition of Notch signaling promotes the adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through autophagy activation and PTEN-PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 2015; 36:1991ã2002.
https://doi.org/10.1159/000430167


31. Yu X, Shen N, Zhang ML, et al. Egr-1 decreases adipocyte insulin sensitivity by tilting PI3K/Akt and MAPK signal balance in mice. EMBO J 2011; 30:3754ã65.
https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.277



32. Perez-Mancera PA, Bermejo-RodrûÙguez C, GonzûÀlez-Herrero I, et al. Adipose tissue mass is modulated by SLUG (SNAI2). Hum Mol Genet 2007; 16:2972ã86.
https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddm278


33. Tong Q, Dalgin G, Xu H, Ting C, Leiden JM, Hotamisligil GS. Function of GATA transcription factors in preadipocyte-adipocyte transition. Science 2000; 290:134ã8.
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5489.134


34. Tong Q, Tsai J, Tan G, Dalgin G, Hotamisligil GS. Interaction between GATA and the C/EBP family of transcription factors is critical in GATA-mediated suppression of adipocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25:706ã15.
https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.25.2.706-715.2005



35. Pan W, Ciociola E, Saraf M, et al. Metabolic consequences of ENPP1 overexpression in adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2011; 301:E901ã11.
https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00087.2011



36. Hilgendorf KI, Johnson CT, Mezger A, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids activate ciliary FFAR4 to control adipogenesis. Cell 2019; 179:1289ã305.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.005



37. Masaki S, Kii I, Sumida Y, et al. Design and synthesis of a potent inhibitor of class 1 DYRK kinases as a suppressor of adipogenesis. Bioorgan Med Chem 2015; 23:4434ã41.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2015.06.018

38. Wang P, Xu J, Wang Y, Cao X. An interferon-independent lncRNA promotes viral replication by modulating cellular metabolism. Science 2017; 358:1051ã5.
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao0409


39. Bortesi L, Zhu C, Zischewski J, et al. Patterns of CRISPR/Cas9 activity in plants, animals and microbes. Plant Biotechnol J 2016; 14:2203ã16.
https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12634



40. China National Commission of Animal Genetic Resources. Animal genetic resources in China: pigs. Beijing, China: Agriculture Press; 2011.






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement
Supplement Print
Print





