 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 33(11); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
This study was conducted to estimate genetic parameters for milk yield traits using daily milk yield records from parlour data generated in an intensively managed commercial dairy farm with Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows in Sri Lanka.
Methods
Genetic parameters were estimated for first and second lactation predicted and realized 305-day milk yield using univariate animal models. Genetic parameters were also estimated for total milk yield for each 30-day intervals of the first lactation using univariate animal models and for daily milk yield using random regression models fitting second-order Legendre polynomials and assuming heterogeneous residual variances. Breeding values for predicted 305-day milk yield were estimated using an animal model.
Results
For the first lactation, the heritability of predicted 305-day milk yield in Jersey cows (0.08±0.03) was higher than that of Jersey-Friesian cows (0.02±0.01). The second lactation heritability estimates were similar to that of first lactation. The repeatability of the daily milk records was 0.28±0.01 and the heritability ranged from 0.002±0.05 to 0.19±0.02 depending on day of milk. Pearson product-moment correlations between the bull estimated breeding values (EBVs) in Australia and bull EBVs in Sri Lanka for 305-day milk yield were 0.39 in Jersey cows and −0.35 in Jersey-Friesian cows.
Conclusion
The heritabilities estimated for milk yield in Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows in Sri Lanka were low, and were associated with low additive genetic variances for the traits. Sire differences in Australia were not expressed in the tropical low-country of Sri Lanka. Therefore, genetic progress achieved by importing genetic material from Australia can be expected to be slow. This emphasizes the need for a within-country evaluation of bulls to produce locally adapted dairy cows.
Over the last 15 years, the quantity of imported milk-products into Sri Lanka has doubled (100,000 metric tonnes in 2016) consuming a substantial part of the country’s export revenues through importation of milk products [1]. To reduce the cost of importation of milk products (particularly milk powder) and to meet the local demand through enhancing the local dairy sector, the national government initiated programs for the importation of temperate dairy cattle to Sri Lanka. However, it is well documented that these breeds, which have been intensely selected for milk production, can have decreased performance for fitness and reproduction traits in their native temperate environments [2]. These problems are exacerbated in tropical production environments where cows are challenged by heat, diseases, inadequate feed and water supply [3]. A possible solution to these problems is to develop a locally adapted dairy breed based on a foundation stock of imported temperate dairy cattle.
A precondition for the efficient implementation of breed ing programs is the availability of reliable phenotypic data and pedigrees, enabling estimation of accurate genetic parameters. In developing countries, this precondition is often not met. However, since dairy production in developing countries is in the midst of slow but ongoing change, from an extensive system managed by smallholders with dairy production embedded in a mixed farm operation to larger, more specialized, intensively managed units with modern milking systems [4], the problem of reliable phenotypic data might be overcome by using information automatically recorded in modern milking parlours. Milk yield, milk flow rate, udder conformation are examples of traits automatically recorded depending on the type of the parlour [5]. These traits represent breeding objective traits or may serve as indicator traits. Compared to conventional test-day records, parlour-collected data offers information on each day (and possibly each session) generating large amounts of data. These data allow the cumulative traits (e.g. 305-day yield) to be calculated by summing up the daily parlour records making sophisticated prediction methods [6] developed for test day records, obsolete. In addition, daily records also allow the application of random regression models, which require a minimum data density along the trajectory to produce reliable parameter estimates. However, parlour records caused a much higher fluctuation in daily milk yield compared with the conventional test-day data [7]. Therefore, the data quality of the automatic milking systems may not be sufficient.
This study investigates the feasibility of using automatically recorded milking data in an intensively managed commercial farm for genetic evaluation of imported Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows in Sri Lanka. Feasibility was assessed by estimating genetic parameters. Genetic parameters for milk yield traits were not estimated in the recent past in Sri Lanka and this is the first study, which utilized daily milk records for genetic evaluation in Sri Lanka. This study presents genetic parameters for 305-day milk yield using univariate animal models and for daily milk yield records using random regression models from data generated in a milking parlour.
Milk yield records were obtained from a single dairy farm in Sri Lanka, which used Jersey and Jersey-Friesian crossbred cows that were imported from Australia as pregnant heifers. The farm is located at 32 meters above sea level (low-country). The local climate is characterized by a distinct wet season, a mean annual temperature of 27 degrees Celsius, an average relative humidity between 70% and 80% and a total annual rainfall from 1,000 to 2,500 mm [8]. Management is characterized by non-grazing and feeding of a total mixed ration produced from cultivated grass and corn, artificial shed cooling, artificial insemination, twice a day milking regime and automatic data recording in a DeLaval milking parlor (Parallel parlour, DeLaval, India).
The first lactation records consisted of 904,437 daily milk records of 2,434 Jersey and Jersey-Friesian crossbred cows, which calved from July 2015 to January 2018. The second lactation records were collected from the same herd and consisted of 456,260 daily milk records of 1,973 Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows. Calving dates for the second lactation ranged from July 2016 to March 2018. Data editing as outlined below resulted in 663,890 and 391,035 daily records from 2,372 and 1,905 cows from first and second lactations, respectively. The data were recorded from July 2015 to March 2018. Overall, data editing excluded 27% of daily milk records from the first lactation and 14% of daily milk records from the second lactation.
Any milk records taken after 350 days postpartum were removed. A higher percentage of records were removed from the first lactation (15%) than the second lactation (0.5%) as records exceeding 350 days postpartum. Then, records identified as valid by the milk recording system were extracted (11% data loss in first and second lactations). This data edit showed that the minimum milk yield identified by the milking system as a valid daily record was 2 kg. Duplicated days in milk for each cow were removed from analysis. Outliers that differed by more than four standard deviations from the mean within each lactation were excluded from the analysis.
The average number of daughters was 61.3 for sires (range 50 to 78) and 12.6 for maternal grandsires (range 5 to 21) with only 1,314 cows having a known maternal grandsire. No maternal grandsires were used as sires. All sires of the imported cows were Jersey bulls and maternal grandsires were either Jersey (for 521 cows) or Friesian (for 793 cows) bulls. Since the dams of imported cows were all unknown, maternal grandsires were included in the pedigree using dummy dams assuming a unique dam for each offspring. The total number of animals in the pedigree was 3,766 (including dummy dams). Only the animals with records and their parents and grandparents identified were used in the pedigree. The pedigree file with all known relationships consisted of the recorded cows plus the previous two generations. The percentage of Jersey and Friesian contribution in crossbred cows was not known.
Altogether four different traits were defined. Two aggregated milk yield traits were defined as predicted 305-day and realized 305-day milk yields. Daily milk yields were used as a longitudinal trait in genetic parameter estimation. In addition, total milk yield for each 30-day intervals across the lactation 1 was used to estimate genetic parameters along the lactation trajectory to provide a comparison with the random regression analysis. Trait definitions for two aggregated milk yield traits are described below.
The multiple trait prediction (MTP) method [6] with the Wood’s model [9] was used to predict the milk yield up to 305 days for each cow using her individual daily milk yield records. Since MTP takes into account the variation of milk yield for each day of milk (t) and the variation of curve parameters within each cow group, 305-day milk yield was predicted for each breed group, separately due to differences in average milk yields between Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows [10].
The following restrictions were made for records to be eli gible for 305-day milk yield prediction. To estimate phenotypic variances for each day in milk across cows, records from at least 300 cows on each day were used. To estimate the curve parameters for each cow, cows with more than 200 daily milk records, with at least one record within the first 20 days in milk and after 300 days in milk were used. For prediction of 305-day yields, only cows with at least 100 daily milk records were used, including the presence of at least one record within the first 30 days and above 100 days in milk. Accordingly, 88% of the daily milk records from cleaned data were used for prediction of 305-day milk yield available for 91% of cows.
For the same cows used to predict 305-day milk yield, observed daily milk yields from day five to a maximum of day 305 were summed up for each cow and realized milk yields were obtained. The R programming language was used for data editing and prediction of 305-day milk yields [11].
Genetic parameters for aggregated 305-day milk yield traits were estimated with a univariate animal model for all cows’ first and second lactation and for each breed group separately. Genetic parameters were also estimated for repeated (daily milk) records applying random regression and repeatability models for all cows’ first lactation, for a dataset, which combined results from all breed groups. Random regression and repeatability models were not applied for cows in second lactation because lactations were still in progress. For comparison with the variance components estimated with random regression, total milk yield for each 30-day interval across the lactation 1 was also fitted in a univariate animal model.
Models included year-season of calving and month of calving as the contemporary group for lactation 1 and 2, respectively. Season was categorized into two classes as dry (from December to April next year) and wet (from May to November) seasons and there were six, year-season effects in total (three years with two seasons). Herd of origin information where they were reared in Australia before importation was not available for these cows. Therefore, all cows were treated as being from the same herd. Cows calved for the first time when they were 578 to 1,493 days of age. Age was not significant and therefore was not included in the model. The minimum size of the contemporary group was maintained as eight to minimize data loss and records from smaller contemporary groups were omitted. For the realized 305-day milk yield trait, lactation length was used as a linear covariate.
The predicted and realized 305-day milk yield in lactation 1 and 2, as well as the total milk yield for each 30-day interval across lactation 1, were fitted in a univariate animal model. Analyses of 305-day milk yields were conducted for each lactation separately. The data on daily yields of the first lactation were divided into ten subsets according to days in milk, namely 5–35, 36–65, up to 276–305 days. Each subset was considered as a different trait and total milk yield for each period was calculated. The univariate animal model fitted was as follows:
Where y = vector of observations for aggregated milk yields in lactation 1, lactation 2, or for 30-day periods within lactation 1, b = vector of fixed effects of year-season (for lactation 1), month of calving (for lactation 2) and lactation length as a covariate (for realized 305-day and 30-day milk intervals), a = vector of random animal effects, e = vector of random residual effects, and X and Z are design matrices which relate records to fixed effects and random animal effects, respectively.
Daily milk records were used to fit the repeatability model for lactation 1.
Where y = vector of daily milk records in lactation 1, b = vector of fixed effects of year-season and breed, a = the vector of random additive genetic effects, pe = vector of random permanent environmental effects and non-additive genetic effects and e = vector of random residual effects. X, Z and W are incidence matrices relating records to the fixed, random animal and permanent environmental effects, respectively.
The variance components for the random effects were de noted as
V a r ( a ) = A σ a 2 , V a r ( pe ) = I σ p e 2 V a r ( e ) = I σ e 2 σ a 2 σ p e 2 σ e 2
A univariate random regression model was fitted using kth order Legendre polynomials for daily milk records in the first lactation. The following model was applied.
where y = vector of daily milk records, b = vector of fixed regression coefficients, X = incidence matrices relating to the fixed effects of year-season, breed and a Legendre polynomial for days in milk, a and pe are vectors of random Legendre polynomial regressions on days in milk for animal additive genetic and permanent environmental coefficients on days in milk, Q and W are corresponding incidence matrices for additive genetic and permanent environmental random effects, respectively, e is the vector of residual effects. Assume that the distribution of the observations conditional on all model terms other than the residual,
and the covariance structure of the random terms in the model (V),
with
where G and P are k×k the (co)variance matrices of the random regression coefficients for additive genetic and permanent environmental effects, A is the additive genetic relationship matrix among animals, ⊗ is the Kronecker product, I is the identity matrix, R is diagonal matrix with elements that depend on days in milk i.e.,
R = d i a g { σ e k 2 }
Variance components based on the univariate animal model were estimated for each breed separately with the BESSiE software [12] using a Bayesian approach. A blocked Gibbs sampler was run for 50,000 cycles, with scaled inverted Wishart distributions assigned as prior processes to the residual and additive genetic co-variance matrices with parameter “ν” set to “x” and “y”, respectively (Sorensen and Gianola [13], pages 576 to 588 for further details). The additive genetic (
σ a 2 σ a 2 / σ p 2 σ p 2 σ a 2 + σ e 2
Variance components for repeatability and random regres sion models were estimated using the WOMBAT software [14]. The most appropriate order of fit for each of the random regression model was selected based on the logarithm of the restricted maximum likelihood function (LogL), Akaike’s information criterion (AIC) [15] and Bayesian information criterion (BIC) [16]. The output of WOMBAT presents the AIC and BIC multiplied by −1/2 which makes them similar scale to LogL so that the greatest value corresponds to the best model.
Estimated breeding values (EBVs) for 305-day predicted milk yield were obtained using an animal model. The sire EBVs based on the Sri Lankan data were regressed on the sire EBVs from Australia to compare the sire EBVs calculated in two countries. Pearson product-moment correlations between the bull EBVs in Australia and bull EBVs in Sri Lanka were derived from 305-day milk yield for Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows, separately.
Jersey-Friesian cows produced higher mean daily milk yield than Jersey cows, especially in the second lactation (Table 1). The number of daily milk records in the second lactation was lower than in the first lactation, especially towards the end of lactation, as most second lactation cows had not completed their lactation at the time of analysis (Figure 1). After initial data edits, the mean and the range of number of daily milk records per cow in first and second lactations were 280 and 1–342 and 205 and 1–337, respectively.
Similar to mean daily milk yield, higher mean predicted 305-day milk yields were observed in Jersey-Friesian cows than Jersey cows. In the second lactation, mean predicted 305-day milk yield was higher than in the first lactation (Table 2). The coefficient of variation (CV) was highest in the realized 305-day milk yield, followed by predicted 305-day milk yield. The highest CV in realized 305-day milk yield was expected due to the variation in days in milk used for the calculation. The minimum and the maximum number of days used for realized 305-day milk yield calculation ranged from 112 to 299 and from 91 to 299, for Jersey and for Jersey-Friesian cows, respectively. Correlations between realized and predicted 305-day milk yield were 0.86 and 0.88, for Jersey and for Jersey-Friesian cows, respectively. The peak milk production was about 18 kg for Jersey-Friesian cows and 17.5 kg for Jersey cows in first lactation and was observed at about 60 days in milk (Figure 2). The peak milk production in second lactation was higher than first lactation in both Jersey (20 kg) and Jersey-Friesian (24 kg) breed groups. However, after around 150 days, daily milk production in second lactation gradually declined below the first lactation for both breed groups (Figure 2).
In this study, heritability estimates for predicted and realized 305-day milk yield traits were low (Table 3). The estimate for Jersey-Friesian cows was very low (0.02±0.01), whereas that for Jersey cows was slightly higher (0.08±0.03) in first lactation. The same trends were observed in the second lactation. In both breed groups, the heritability estimates were similar in both lactations.
The heritability estimates of Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows for predicted and the realized 305-day milk yield were similar (Table 3). Although the phenotypic variance was lower for realized 305-day milk yield compared to the predicted 305-day milk yield, the observed variance (sd2, Table 2) was higher in realized 305-day milk yield compared to predicted 305-day milk yield. This lower phenotypic variance for realized milk yield was due to fitting the days in milk as a covariate in realized 305-day milk yield. Variance components for total milk yield in each 30-day interval as estimated by univariate animal model are given in Table 4, and showed low additive genetic variation resulting in low heritability.
Additive genetic, permanent environment and residual variances estimated using the repeatability model for daily milk yields for both Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows were 0.01, 6.30, and 16.50, respectively. Heritability and repeatability estimates were therefore 0.00±0.004 and 0.276± 0.007, respectively.
Legendre polynomials from order zero (null model) to order 3 for random and permanent environmental effects were evaluated. Random regression models of third order (degree 3) for both additive genetic and permanent environmental across the lactation had significantly higher log-likelihood, −1/2 of AIC and BIC values indicating a better fit of the models. However, with increasing order of Legendre polynomials, fluctuations of curves were observed at the beginning and at the end of lactation (data not shown). Therefore, model with the second order Legendre polynomials for both additive genetic and permanent environmental across the lactation was selected as the best model. The estimated variances along the trajectory for additive genetic, permanent environment, residual and total phenotypic variances estimated using daily milk yields across the first lactation are shown in Figure 3. The shape of the residual variance curve and hence the phenotypic variance along the lactation trajectory shows the heterogeneity of residual variance across the different lactation periods. Similar to the univariate animal model fitted for 305-day milk yield and for each 30-day class along the lactation length, the additive genetic variance observed in the random regression model was very low. In the random regression model, the heritability for daily milk yield ranged from 0.002±0.05 to 0.19±0.02 depending on the stage of lactation (days in milk) (Figure 4). Average heritability across the lactation was 0.05± 0.04 for the random regression model. Heritability was lowest at the peak milk yield and at the end of lactation.
The phenotypic correlations between consecutive days in milk were higher and correlations decreased as the distance between days in milk increased (Table 5). The phenotypic correlations ranged from 0.14±0.02 to 0.71±0.01 with low standard errors. The magnitude of the genetic correlations showed a clear distinction in three phases of lactation namely, 6 to 55 days, 80 days to the days in milk in later lactation and 105 to 255 days in milk. However, no such clear distinction in phenotypic correlations was observed. The genetic correlations were highest between adjacent days in milk between 105 to 280 days with correlations greater than 0.90. Genetic correlations were close to one from 130 to 255 days in milk. Genetic correlations between milk yields at 80 day were positively correlated with days in milk in the later lactation with high standard errors. Yields at 6 to 55 days in milk with consecutive days in milk in the later lactation up to 280 day were negative due to extrapolation of curves at the ends in random regression. The additive genetic variation was close to zero around the peak milk production (Figure 3). Therefore, genetic correlations could not be estimated or yielded high standard errors. The observed genetic correlations between 105 to 280 days in milk indicate that this period can be considered as a single trait.
The variance of bull EBVs for 305-day milk yield in Australia and Sri Lanka were 73,532 kg2 and 414 kg2, respectively. The EBVs calculated for 305-day milk yield in Sri Lanka for Jersey and Jersey-Friesian crossbred cows were regressed on EBVs found for the same Jersey bulls in Australia. The regression equations for Jersey bulls used for Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows were y = 5.229 +0.013x (Adjusted R2 = 8.5%) and y = 4.783+−0.015x (Adjusted R2 = 5.7%), respectively, where y = sire EBVs in Sri Lanka and x = sire EBVs in the Australia. Pearson product-moment correlations between the bull EBVs in Australia and bull EBVs in Sri Lanka for 305-day milk yield were 0.39 in Jersey cows and −0.35 in Jersey-Friesian cows. Therefore, the ranking of sires across the two environments was different as well as difference in EBVs found in Sri Lanka were smaller than Australia.
Since the standard period for comparison of milk production yields or genetic parameters is 305-day, milk yields were predicted to 305-day. Although daily milk records increased the density of trajectorial data considerably in this study, the prediction was still necessary to better accommodate cows with missing daily milk records due to loss of identification tags and partial lactations due to ongoing milking and heavy fluctuations in daily milk yields. Realized 305-day milk yields were then compared with the predicted 305-day milk yield.
The milk production of cows in this study was higher than the milk production from studies earlier reported in Sri Lanka. In Sri Lanka, the temperate breeds and their crossbreds were used to be reared in the hill-country, where there is a comfortable climate for exotic breeds (16°C average annual temperature and >200 mm average annual rainfall). As part of a large project of importation of exotic breeds from Australia to Sri Lanka, Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows were introduced to the low-country farm where the data for this study were collected as a pilot project to assess the suitability of exotic breeds and their crossbreds for production in the low-country of Sri Lanka. Even though the cows in this study were measured in a low-country environment, the first lactation average 305-day milk yield reported in this study was higher than the average milk yield of Jersey cows reported earlier in hill-country of Sri Lanka [17]. In the same study [17], the crossbred cows of exotic breeds (Friesian, Jersey, and Ayrshire) had a similar level of performance to this study. The higher milk production in this study was potentially the result of temperature control through mist in the milking parlour and improved feeding management.
Though the 305-day milk production in this farm has increased in comparison to previous studies in Sri Lanka, the peak milk production and 305-day predicted milk yield observed in this study were substantially lower than the milk yield of Holstein and Jersey cows in the temperate countries [18,19]. In New Zealand, the cows were mostly managed under pasture based management conditions and the average dairy cow milk production (4,259 kg) is similar to Sri Lanka [20]. However, the peak milk production of Holstein-Friesian cows in New Zealand is high (25.5 kg) [21]. In Sri Lanka, lower peak milk production is expected due to heat stress and differences in feed composition and overall management. Hence, there is potential to further upgrade milk production through improved heat regulation and nutritional management with emphasis on economic aspects.
The results of both univariate animal model, as well as random regression models, show that the heritability estimates for milk yield in Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows in Sri Lanka were low. Generally, exotic cattle breeds reared in tropical climates had lower heritability estimates for milk yield than temperate climates [22]. However, in this study the heritability estimates were much lower than what is usually found for milk yield traits in tropical countries. The heritability for 305-day milk production was lower than Danish Jersey heifers imported to Sri Lanka in 1974 (0.22±0.23) [23], Kenyan Holstein-Friesian (0.25±0.04) [22], Jersey cattle in Kenya (0.21) [24] and for Holstein-Friesian cows in Australia (0.32±0.02) [25]. Low heritability estimates similar to our study were reported in Sahiwal cattle in India (0.07) for first lactation [26] and for crossbreds of Sahiwal, Brown Swiss and Ayrshire breeds in Kenya even after accounting for breed proportions (0.09 to 0.13) [27]. Therefore, the low heritability estimates reported in this study have been also observed in some other studies. Low heritabilities can be due to low additive genetic variance or due to high residual variance. In our study we observed both low additive genetic and high residual variances, both reducing the heritability. Possible reasons for low heritability are discussed below.
Comparison of variance components for milk yield traits with literature values has shown that additive genetic variances in our study were low and a major reason for low heritability. For example, an estimate of the additive genetic and phenotypic variances for 305-day milk yield was 360,274 kg and 1,232,113 kg, respectively in Holstein-Friesian cows reared in large scale intensive farms in Kenya as estimated using a repeatability animal model [22]. A low additive genetic variance (36,864 kg) and a phenotypic variance (164,836 kg) similar to our study were reported in Danish Jersey heifers imported and reared in hill-country of Sri Lanka in 1974 [23]. Another study for first lactation 305-day milk yield in Sahiwal cattle in India, also reported a lower additive genetic variance (64,421 kg) and a phenotypic variance (356,368 kg) similar to our study as estimated by the univariate animal model [28]. The main source of information to estimate the additive genetic variance is the variance of progeny means observed for each breed group for predicted 305-day milk yield. The variance of progeny means is
[ ( 1 - t ) / n + t ] σ p 2 σ p 2 = observed variation σ p 2 / n
The low heritability could also be due to low phenotypic variance since heritability increases with increased level of production [29]. In our study, phenotypic variance and the CV were lower than in other studies [22,30]. A similar phenotypic variance (356,368 kg) to our study was observed in Sahiwal cattle in India with a CV of 0.33 [31]. The differences in phenotypic variance in above studies were mainly due to differences in mean milk production, rearing systems and between sire differences. The higher CV of Kenyan Holstein-Friesian cows (0.35) [22] and Sahiwal cattle in India (0.33) compared to our study (0.17 to 0.26) (Table 2) suggests that differences phenotypic variance could be due to differences in rearing system. The cows in this study were imported to Sri Lanka from Australia as pregnant heifers, and accordingly their rearing environment changed drastically not only by the climatic factors (e.g. heat stress) but also due to nutrition and husbandry levels accompanied with transport stress, all of which could have had significant impacts on expression of cows’ genetic potential and thereby reducing the milk production and phenotypic variance.
There remains a possibility that the low heritability for a moderately heritable milk yield trait could also be caused by pedigree errors. The results of a preliminary study which used part of this dataset reported low heritability estimates for milk electrical conductivity (0.12±0.04), milk flowrate (0.13±0.04), and milk yield persistency (0.07±0.02) [32], and these are similar to the heritability for milking speed (0.11) estimated in a study from the United States [33] and lower than an estimate for milk electrical conductivity (0.23) in Italian Brown cattle [34]. Therefore, the heritability estimates for the above mentioned traits other than the milk yield indicate that the pedigree structure used in this study can provide reasonable estimates of heritability. Low heritability for milk yield estimated in this study is a characteristic of milk yield trait, which is largely influenced by reasons explained above. However, the magnitude of pedigree errors could have been traced accurately if genetic markers were used which were not available for this study.
The heritability estimate could be also low due to errors in phenotype recording. One would expect that with automatic milking systems errors in phenotypic recording would be minimal compared with data measured by humans. However, a study based on data collected by voluntary milking systems in Sweden removed 57% of the original data mainly due to incomplete and inconsistent milk recordings, lactations longer than 330 days in milk and missing identification indicating the need for thorough cleaning of raw data recorded automatically by milking systems [35]. In this study, similar data cleaning criteria were implemented and the heritability estimates remained low for the analysed traits. Therefore, data cleaning criteria were minimized to retain more data. Moreover, high daily fluctuation of milk yield was also observed in the cows in this study. Fluctuations and in particular drops in milk production could be due to diseases and sudden changes in the management [7,36]. However, prediction to 305-day milk yield reduced the effect of the fluctuation in daily milk yield and should give better estimates of variance components and heritability compared to observed milk yield. Therefore, errors in phenotypic recording were not the major reason for low heritability estimates in this study.
Other reasons which might reduce the heritability estimate i.e. increased residual variance was described in detail in this paper under the section “suitability of models used to estimate heritability” together with the variation of the residual, permanent environmental and phenotypic variances along the lactation trajectory. Nevertheless, the incorporation of more data from similar production systems in a future study would strengthen the findings of this study.
Other than the change of variance components along the lactation trajectory, random regression models allow to estimate the genetic correlations between different days in milk. Unexpected negative genetic correlation estimates were observed between the beginnings of the lactation with mid-lactation. The additive genetic variance was close to zero at peak milk production and at the end of lactation at around 305th day. Therefore, the negative genetic correlation estimates could also be due to the difficulty in estimating genetic correlations due to low additive genetic variation at the peak and at the end of lactation. High standard errors of correlation estimates between the consecutive days in milk were also observed, especially from 6 to 80 days in milk with later lactation due to low heritability. Similar negative genetic correlation estimates were observed by Bignardi et al [37].
Among the univariate, repeatability and random regression models the heritability and additive genetic and phenotypic variances remained low. The univariate animal models for predicted and realized 305-day milk yield were fitted separately for Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows to visualize the differences in heritability estimates between the two breed groups. The repeatability and random regression models were fitted for both breed groups in a single analysis to enable the modelling of environmental effects with a large data set. These models harbour extra information compared to univariate models.
The repeatability models allow permanent environmental effects to be accounted for repeatability of daily milk records to be estimated. The repeatabilities reported in the literature for milk yield vary from 0.3 [27] to 0.53 [38]. The low repeatability for milk yield reflects a considerable influence of temporary random environmental conditions. Repeatability is important from a management point of view to get similar production from day to day throughout the lactation.
Compared to the repeatability model, random regression models account for the curvilinear nature of lactation and provide more information on the change of variance components along the lactation trajectory. At the beginning of the lactation and towards the end of the lactation, the variance components were increased compared to the mid-lactation. When second order polynomials are fitted, the distribution of predicted animal variances tends to curve at the ends due to artifacts of the Legendre polynomials rather than due to actual increase in variance [39]. This could be due to the presence of fewer records at the beginning and at the end of lactation, which allows more fluctuations of polynomials in the tails. A separate analysis of the total milk yield using the univariate animal model where the milk yield was divided into 10 day periods further confirmed the higher genetic variances observed at the ends of the lactation are due to artifacts of the Legendre polynomials rather than actual increase in variance. A similar trend was observed for additive genetic, permanent environmental effects and residual variances.
Apart from those at the beginning and end of the record ing schedule, the highest additive genetic variance for milk yield was observed at mid-lactation. Though the heritability and additive genetic variance was lower in this study, the trend for additive genetic variance and heritability to peak in mid-lactation was also observed by Druet et al [40], where a maximum heritability of 0.39 was found close to 200 days in milk.
Residual variances were much higher in this study than permanent environmental effects whereas the reverse was reported in most of the other studies [41]. A study by Druet et al [40] reported decreasing residual and permanent environmental variances along the lactation curve in first lactation of French Holsteins. The residual variance could be increased by not accounting for relevant fixed effects or the covariates in the genetic model. For example, herd of origin information is not available for the cows where they were reared in Australia before conception, which was likely to affect the permanent environment of the cows. Due to a lack of such information, herd before conception could not be included in the model, which may have increased the error variance of the model at the beginning of the lactation. The genetic superiority in F1-crossbreds is mostly due to the heterosis and in the model fitting, it was usually captured by the permanent environmental effects [27]. Even though the milk production from Jersey-Friesian cows was higher than Jersey, this could explain why the heritability was low in Jersey-Friesian cows compared to Jersey cows. Moreover, the dam and breed proportions for the Jersey-Friesian cows were not available which may also increase the residual variance. Therefore, this pattern of residual and permanent environmental effects was expected.
Variance of EBV observed in this study was very low due to low additive variance. A study in Australia which used genomic relationships between animals and their phenotypes to estimate genetic variance showed variance in EBVs for 305-day milk yield as 41,910 in Jersey cows and 61,332 in Holstein cows [42]. EBVs for milk yield in Sri Lanka were all close to zero due to the low genetic variation which makes it difficult to identify superior bulls for selection based on the data available. Low EBVs also make it difficult to accurately estimate the extent of genotype by environment interaction and interpretation of it. However, genotype by environment interaction is important in this study to compare the bull performances in Australia and Sri Lanka.
In this study, we did not have data from Australia, but Pear son product-moment correlations between the Sri Lankan bull EBVs and Australian bull EBVs indicated a genotype by environment interaction. The environment provided in Sri Lanka could have reduced the proportion of variation attributed to the additive effects of genes, hence reduced the expression of genetic variance in milk production. Therefore, a very slow genetic progress by importing animals, cows or semen from Australia to the low-country of Sri Lanka could be expected.
Genotype by environment interaction was also reported in hill-country of Sri Lanka where there is a comfortable climate for the exotic cows. Accordingly, a similar study based on cow importation from Denmark to a farm in the hill-country in Sri Lanka in 1974 also found a very low additive genetic correlation between the two environments based on the progeny in both environments (−0.08) [23]. Overall these results demonstrate that the genotype by environment interaction have to be carefully considered in any future importations of exotic cows to Sri Lanka.
Implementation of a breeding programme for dairy cows in Sri Lanka under the intensive system of management requires the recording of pedigree and economically important traits. The price per litre of milk in Sri Lanka is determined by milk fat content and milk solids. Therefore, measuring the individual cow fat and protein yield is also important. The parlour data provide useful information without the need of an extra cost for recording. Therefore, other possible economically important traits, which can be recorded automatically by the parlour, should be incorporated considering the cost of manual recording and the low accuracy of those records. The use of free-roaming bulls in the herd to breed the non-pregnant cows should be avoided at all times since it interferes with the proper pedigree recording. The continued production from imported stock, especially crossbreds depend on the proper selection of bulls for mating and this also emphasizes the need for proper record keeping. Thereby the imported cows and their progeny would serve as foundation stock for within-country evaluation of bulls. Importation of young heifers is preferred over pregnant heifers since transport stress might affect the first lactation milk production. In future, any heifer importations should be on the condition that information describing herd of origin, breed proportions, and complete pedigree including dam and grandparent information, which facilitate the genetic parameter estimation, be available.
Assuming that the imported cows will properly adapt to the Sri Lankan environmental conditions with time, the later lactations of these cows and their daughter performances should be evaluated in a future independent study. Their ability to express genetic potential will help to identify the genetic differences between cows which enable a within-country evaluation of bulls to produce locally adapted dairy cows.
The automatically recorded daily milk records in milking parlours need careful data cleaning and provide a higher data density along the lactation trajectory for each cow. These records were sufficient for a routine genetic evaluation of cows for breeding programmes. Low heritability for 305-day milk yield estimated in this study demonstrate limited potential for genetic improvement of yield based only on data from imported cows in the selected farm and sire differences in Australia were not observed in Sri Lankan data. Therefore, continual phenotype and pedigree recording from the same farm and incorporation of data from other farms with similar production systems is suggested for genetic evaluation to find adequate genetic differences among cows raised in Sri Lanka which enables within-country evaluation of bulls for selection.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank National Livestock Development Board (NLDB), Sri Lanka for supplying the data. The assistance from farm staff especially Roshan Wijethilaka is very much appreciated. The first author received an International Postgraduate Research Award from the University of New England. Authors would like to thank Matt Wolcott and Robert Banks for their constructive comments to improve this manuscript.
Figure 1
Number of daily milk yield records used for prediction of 305-day milk yield and random regression analysis of daily milk yield for Jersey and for Jersey-Friesian cows in lactation 1 and 2.
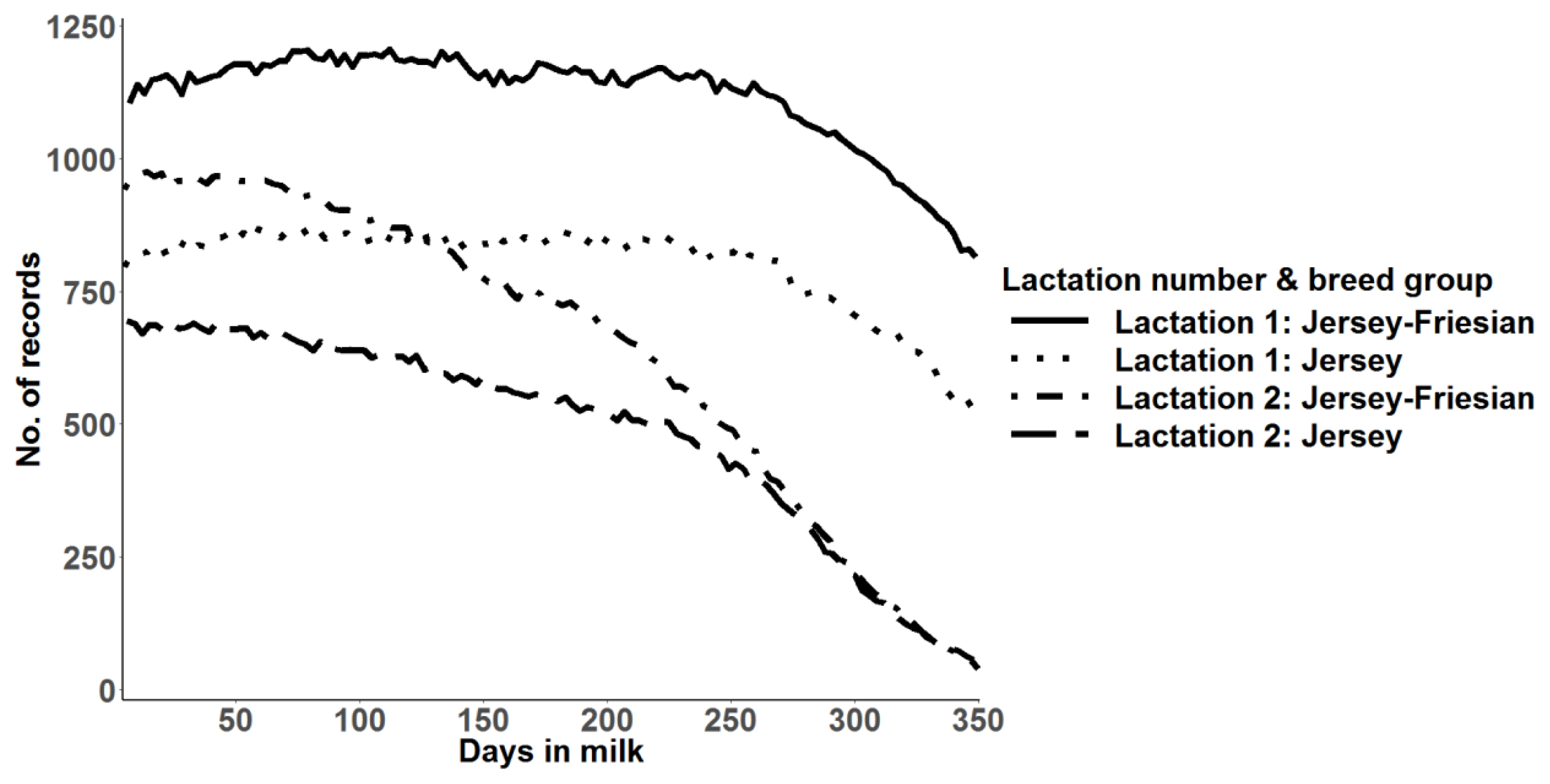
Figure 2
Mean predicted 305-day milk yield with multiple trait prediction for Jersey and Jersey-Friesian cows in lactation 1 and 2.
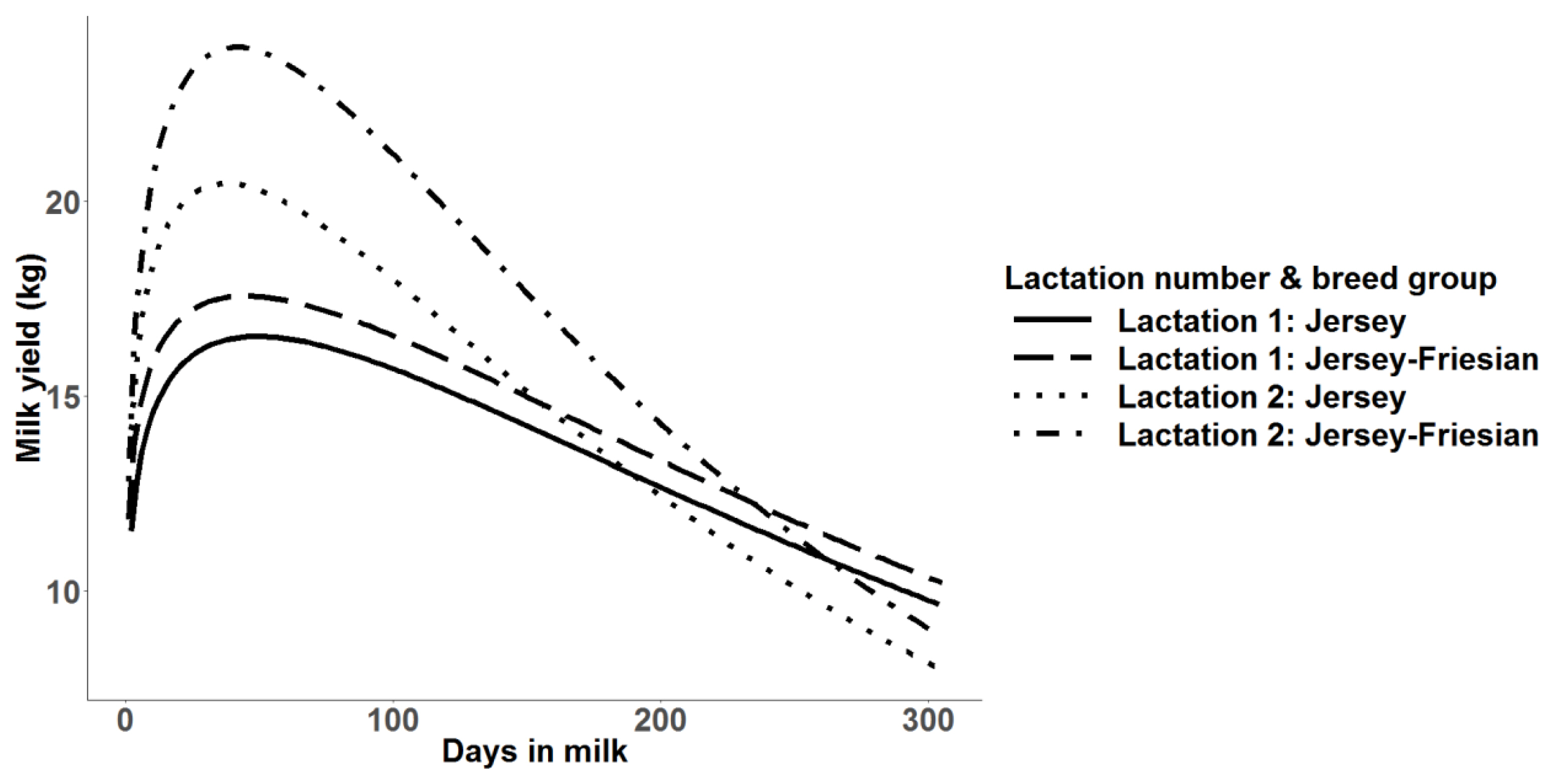
Figure 3
Additive genetic, permanent environment, residual and phenotypic variances for daily milk yields in first lactation from the random regression model with second order Legendre polynomial.
Figure 4
Heritability over days in milk for daily milk yields from the random regression model with second order Legendre polynomial for lactation 1.

Table 1
Descriptive statistics of daily milk yields (kg) from day five to day 350 for lactation 1 and 2
Table 2
Descriptive statistics of predicted 305-day milk yield (kg) and realized 305-day milk yield (kg) from daily milk yields for lactation 1 and 2
Table 3
Heritability estimates with standard errors (h2±se), additive genetic (
σ a 2 σ p 2
Table 4
Heritability estimates with standard errors (h2±se), additive genetic (
σ a 2 σ p 2
Table 5
Estimates of heritability (diagonal), genetic (below diagonal) and phenotypic (above diagonal) correlations between days in milk for first lactation derived from random regression models
REFERENCES
1. Economic and Social Statistics of Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka, Colombo: Central Bank of Sri Lanka; 2018.
2. Ducrocq V, Laloe D, Swaminathan M, Rognon X, Tixier-Boichard M, Zerjal T. Genomics for ruminants in developing countries: from principles to practice. Front Genet 2018; 9:251
https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00251



3. Hoffmann I. Climate change and the characterization, breeding and conservation of animal genetic resources. Anim Genet 2010; 41:Suppl 132–46.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.2010.02043.x


4. Vernooij AG, Houwers HWJ, Zijlstra J. Old friends-new trends: emerging business opportunities in the dairy sector of Sri Lanka. Wageningen The Netherlands: Wageningen UR Livestock Research; 2015.
5. Carlström C, Strandberg E, Johansson K, Pettersson G, Stalhammar H, Philipsson J. Genetic associations of in-line recorded milkability traits and udder conformation with udder health. Acta Agric Scand A Anim Sci 2016; 66:84–91.
https://doi.org/10.1080/09064702.2016.1260154

6. Schaeffer LR, Jamrozik J. Multiple-trait prediction of lactation yields for dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 1996; 79:2044–55.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(96)76578-5


7. Elgersma GG, de Jong G, van der Linde R, Mulder HA. Fluctuations in milk yield are heritable and can be used as a resilience indicator to breed healthy cows. J Dairy Sci 2018; 101:1240–50.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-13270


8. Farm from Ambalangoda Ridiyagama Farm [Internet]. Colombo, Sri Lanka: National Livestock Development Board; c2019. [cited 2019 Jun 25]. Available from: http://www.nldb.gov.lk/RidiyagamaFarm.html
9. Wood PDP. Algebraic model of the lactation curve in cattle. Nature 1967; 216:164–5.
https://doi.org/10.1038/216164a0


10. Sneddona NW, Lopez-Villalobos N, Davisb SR, Hicksona RE, Shallooc L, Garricka DJ. Supply curves for yields of dairy products from first-lactation Holstein Friesian, Jersey and Holstein Friesian-Jersey crossbred cows accounting for seasonality of milk composition and production. In : Proceedings of the New Zealand Society of Animal Production; 2017.
11. R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing [Internet]. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; c2017. [cited 2017 Jan 1]. Available from: https://www.R-project.org/
12. Boerner V, Tier B. BESSiE: a software for linear model BLUP and Bayesian MCMC analysis of large-scale genomic data. Genet Sel Evol 2016; 48:63
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12711-016-0241-x



13. Sorensen D, Gianola D. Likelihood, Bayesian, and MCMC methods in quantitative genetics. New York, USA: Springer Science & Business Media; 2002. p. 576–88.
14. Meyer K. WOMBAT—A tool for mixed model analyses in quantitative genetics by restricted maximum likelihood (REML). J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 2007; 8:815–21.




15. Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. Parzen E, Tanabe K, Kitagawa G, editorsSelected papers of Hirotugu Akaike. New York, USA: Springer; 1974. p. 215–22.

16. Schwarz G. Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Stat 1978; 6:461–4.
https://doi.org/doi:10.1214/aos/1176344136

17. Kollalpitiya KMPMB, Premaratne S, Peiris BL. Reproductive and productive performance of up-country exotic dairy cattle breeds of Sri Lanka. Trop Agric Res 2012; 23:319–26.

18. Smith DL, Smith T, Rude BJ, Ward SH. Short communication: comparison of the effects of heat stress on milk and component yields and somatic cell score in Holstein and Jersey cows. J Dairy Sci 2013; 96:3028–33.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2012-5737


19. Heins BJ, Hansen LB, Seykora AJ. Production of pure Holsteins versus crossbreds of Holstein with Normande, Montbeliarde, and Scandinavian red. J Dairy Sci 2006; 89:2799–804.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(06)72356-6


20. Dairy NZ. More milk per cow, fewer cows: latest dairy stats [Internet]. c2017. [cited 2018 Oct 18]. Available from: https://www.dairynz.co.nz/news/latest-news/more-milk-per-cow-fewer-cows-latest-dairy-stats/
21. Roche JR, Berry DP, Kolver ES. Holstein-Friesian strain and feed effects on milk production, body weight, and body condition score profiles in grazing dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 2006; 89:3532–43.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(06)72393-1


22. Ojango JMK, Pollott GE. Genetics of milk yield and fertility traits in Holstein-Friesian cattle on large-scale Kenyan farms. J Anim Sci 2001; 79:1742–50.
https://doi.org/10.2527/2001.7971742x


23. Buvanendran V, Petersen PH. Genotype-environment interaction in milk production under Sri Lanka and Danish conditions. Acta Agric Scand
https://doi.org/10.1080/00015128009435283

24. Musani SK, Mayer M. Genetic and environmental trends in a large commercial Jersey herd in the Central Rift Valley, Kenya. Trop Anim Health Prod 1997; 29:108–16.



25. Haile-Mariam M, Bowman PJ, Goddard ME. Genetic and environmental relationship among calving interval, survival, persistency of milk yield and somatic cell count in dairy cattle. Livest Prod Sci 2003; 80:189–200.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-6226(02)00188-4

26. Prakash V, Gupta AP, Singh M, Ambhore GS, Singh A, Gandhi RS. Random regression test-day milk yield models as a suitable alternative to the traditional 305-day lactation model for genetic evaluation of Sahiwal cattle. Indian J Anim Sci 2017; 87:340–4.


27. Mackinnon MK, Thorpe W, Baker RL. Sources of genetic variation for milk production in a crossbred herd in the tropics. Anim Sci 1996; 62:5–16.
https://doi.org/10.1017/S1357729800014259

28. Prakash V, Gupta AK, Gupta A, Gandhi RS, Singh A, Chakravarty AK. Random regression model with heterogeneous residual variance reduces polynomial order fitted for permanent environmental effect but does not affect genetic parameters for milk production in Sahiwal cattle. Anim Prod Sci 2016; 57:1022–30.
https://doi.org/10.1071/AN15347

29. Hill WG, Edwards MR, Ahmed MKA, Thompson R. Heritability of milk yield and composition at different levels and variability of production. Anim Sci 1983; 36:59–68.
https://doi.org/10.1017/S0003356100039933

30. Dematawewa CMB, Berger PJ. Genetic and phenotypic parameters for 305-day yield, fertility, and survival in Holsteins. J Dairy Sci 1998; 81:2700–9.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(98)75827-8


31. Singh A, Singh A, Singh M, et al. Estimation of genetic parameters for first lactation monthly test-day milk yields using random regression test day model in Karan fries cattle. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2016; 29:775–81.
https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.15.0643



32. Samaraweera AM, Boerner V, Cyril HW, van der Werf JHJ, Hermesch S. Genetic parameters for milk yield, persistency, conductivity and milking efficiency in first lactation Jersey cows in Sri Lanka. Auckland, New Zealand: Proceedings of the World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production; 2018.
33. Zwald NR, Weigel KA, Chang YM, Welper RD, Clay JS. Genetic evaluation of dairy sires for milking duration using electronically recorded milking times of their daughters. J Dairy Sci 2005; 88:1192–8.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)72785-5


34. Povinelli M, Gallo L, Carnier P, Marcomin D, Zotto RD, Cassandro M. Genetic aspects of milk electrical conductivity in Italian Brown cattle. Ital J Anim Sci 2005; 4:169–71.
https://doi.org/10.4081/ijas.2005.3s.169

35. Carlstrom C, Pettersson G, Johansson K, Strandberg E, Stalhammar H, Philipsson J. Feasibility of using automatic milking system data from commercial herds for genetic analysis of milkability. J Dairy Sci 2013; 96:5324–32.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2012-6221


36. Windig JJ, Calus MPL, Veerkamp RF. Influence of herd environment on health and fertility and their relationship with milk production. J Dairy Sci 2005; 88:335–47.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)72693-X


37. Bignardi AB, El Faro L, Cardoso VL, Machado PF, de Albuquerque LG. Random regression models to estimate test-day milk yield genetic parameters Holstein cows in Southeastern Brazil. Livest Sci 2009; 123:1–7.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2008.09.021

38. Calus MPL. Estimation of genotype × environment interaction for yield, health and fertility in dairy cattle. Wageningen The Netherlands: Wageningen University; 2006.
39. Schaeffer LR. Random regression models. Random regression in animal breeding course notes. Ontario, Canada: University of Guelph; 1997. p. 1–15.
40. Druet T, Jaffrezic F, Boichard D, Ducrocq V. Modeling lactation curves and estimation of genetic parameters for first lactation test-day records of French Holstein cows. J Dairy Sci 2003; 86:2480–90.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(03)73842-9


41. Canaza-Cayo AW, Lopes PS, da Silva MVGB, et al. Genetic parameters for milk yield and lactation persistency using random regression models in Girolando cattle. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2015; 28:1407–18.
https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.14.0620




42. Aliloo H, Pryce JE, Gonzalez-Recio O, Cocks BG, Hayes BJ. Accounting for dominance to improve genomic evaluations of dairy cows for fertility and milk production traits. Genet Sel Evol 2016; 48:8
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12711-016-0186-0









 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





