 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 31(1); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
The aim of the study was to isolate gossypol-degrading bacteria and to assess its potential for gossypol degradation.
Methods
Rumen liquid was collected from fistulated cows grazing the experimental pasture. Approximately 1 mL of the rumen liquid was spread onto basal medium plates containing 2 g/L gossypol as the only source of carbon and was then cultured at 39°C to isolate gossypol-degrading bacteria. The isolated colonies were cultured for 6 h and then their size and shape observed by microscope and scanning electron microscope. The 16S rRNA gene of isolated colonies was sequenced and aligned using National Center for Biotechnology Information-Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. The various fermentation conditions, initial pH, incubation temperature, inoculum level and fermentationperiod were analyzed in cottonseed meal (CSM). The crude protein (CP), total gossypol (TG), and free gossypol (FG) were determined in CSM after fermentation with isolated strain at 39°C for 72 h.
Results
Screening results showed that a single bacterial isolate, named Rumen Bacillus Subtilis (RBS), could use gossypol as a carbon source. The bacterium was identified by 16S rDNA sequencing as being 98% homologous to the sequence of Bacillus subtilis strain GH38. The optimum fermentation conditions were found to be 72 h, 39°C, pH 6.5, moisture 50%, inoculum level 107 cell/g. In the optimum fermentation conditions, the FG and TG content in fermented CSM decreased 78.86% and 49% relative to the control. The content of CP and the essential amino acids of the fermented CSM increased respectively, compared with the control.
China is a major cotton producing country. Cottonseed meal (CSM) is a rich source of protein, containing about 34% to 40% crude protein (CP) and approximately 22.5% high quality protein, as well as about 11% crude fiber, vitamin B, and organic phosphorus. In China, about 6 million metric tons of CSM are produced every year. Among cake and meal feed raw materials, the production is only just below the yield of soybean meal, but only 1.8 million metric tons are used as animal feed. Further use is hampered by the toxic gossypol in the seed [1]. Gossypol is a polyphenol of two naphthalenes, deriving from the plant pigment glands of the cotton genus Malvaceae gossypium. Marchlewski extracted pure gossypol from cottonseed and named it in 1899 [2]. It is a secondary metabolite in cottonseed, found as either bound gossypol (BG) or free gossypol (FG). Animals fed diets containing FG suffer negative effects such as decreased growth and feed conversion, depression of fertility, as well as intestinal and internal organ abnormalities [3–7]. However, BG does not harm animals because it is a combination of FG with protein or saccharide and cannot be absorbed from the digestive tract.
Commonly, cottonseeds are processed into oil and meal, which may contain high concentrations of FG. Thus, it is necessary for CSM to be further processed to reduce FG to permissible levels for use as an animal protein feed resource. Many studies have reported FG detoxification and proposed methods, such as solvent extraction by liquid cyclone and/or acetone [8,9], or chemical treatment with iron sulfate [10,11] or calcium hydroxide [12]. Unfortunately, these methods decreased the protein quality, active vitamin content and palatability of the feed, and increased the use of energy. It is vital to develop a new approach for degradation of FG to improve the nutritional value of CSM.
Microbial fermentation of CSM to improve the nutritional value by degrading FG and improving the protein quality and digestibility has been studied widely [13–15]. Some fungi have been reported to ferment CSM, including Candida, Aspergillus, Rhizopus oryzae, Mucor rouxii, and others [16,17]. The fermentation products for these fungi might be detrimental to livestock and poultry. And thus the safety of fermentation products generally used as animal feeds must be assessed.
Negative effects of CSM on animal health are lower in ruminants than in non-ruminants due to the effects of rumen microbes. The chemical properties of gossypol in CSM were changed by such microorganisms and the toxicity of gossypol was reduced [18]. If the relevant microorganism(s) from rumen are isolated in vitro and then inoculated into CSM to ferment, CSM detoxified by microorganisms could reach safe criteria for feed use. Moreover, the feed could be enhanced in its content of protein, amino acids, coenzymes (secreted by microorganisms), cellulolytic enzymes, amylase, protease and lipolytic enzymes, and some vitamins, without interference from any toxic or harmful substances. Therefore, the objectives of this study were to isolate relevant microorganisms from rumen and investigate the use of gossypol by those microorganisms.
Rumen liquid was collected from fistulated cows grazing the experimental pasture of the Agricultural University of China, Beijing, China, and filtered through a double cheesecloth. Approximately 1 mL of the rumen liquid was spread onto basal medium plates (5 g/L (NH4)2SO4, 1 g/L KH2PO4, 1 g/L NaCl, 0.5 g/L MgSO4·7H2O, 0.1 g/L CaCl2, 0.2 g/L yeast extract, 15 g/L agar) containing 2 g/L gossypol as the only source of carbon and was then cultured at 39°C under aerobic condition. The strains were inoculated on Luria-Bertani (LB) medium (5 g/L yeast extract, 10 g/L tryptone, 5 g/L NaCl, 30 g/L sucrose, and 15 g/L agar) and incubated for several days at 39°C to obtain pure cultures. The isolated strain was maintained at 4°C on LB medium.
To observe the colony characteristics of the isolated strain, the dilution plate method was used to obtain single colonies. The LB medium plates were inoculated with the strain by streaking. The isolated colonies were cultured for 6 h and then observed under the light microscope (Olympus BX50, Hamburg, Germany) for their size and shape. The isolated strain was cultured in LB medium for 2 d at 39°C and the thalli were collected. The thalli were resuspended in 2.5% (v:v) glutaraldehyde solution in 0.1 mol/L phosphate buffer saline (PBS), and fixed for 24 h. The thalli were washed three times with PBS. The thalli were then dehydrated by ethanol concentration gradient (10%, 30%, 50%, 70%, 90%; 10 min each), and dehydrated twice in 100% ethanol at 10 min intervals. For scanning electron microscope (SEM) assay, the thalli were washed with 50%, 70%, 90%, and 100% isoamyl acetate (each 3 min), critical point dried, coated with gold/palladium, and observed and photographed with a scanning electron microscope (model Philips SEMXL-20, Philips, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) [19].
The thalli of the isolated strain were inoculated into liquid LB medium and cultured for 24 h at 39°C with shaking, then harvested from the liquid medium by centrifugation. DNA was extracted using the sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-proteinase K method [20] and purified DNA samples were stored at −20°C. The genomic DNA was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using universal primers F1: 5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′ and R1: 5′-ACGGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′ [21] and the PCR reaction was conducted using the following conditions: 5 min at 94°C, followed by 35 cycles of 30 s at 94°C, 30 s at 56°C, and 90 s at 72°C, and a final extension of 10 min at 72°C. The isolated strain 16S rRNA genes were sequenced by Shanghai Huada, China. The product of 16S rRNA genes of the isolates in the present study were compared against National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database reported sequences with the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) hosted at website of NCBI. A phylogenetic tree was then drawn using the Neighbor joining method [22]. Phylogenetic and molecular evolutionary analyses were conducted at 1000 bootstrap value using Molecular Evolutionary Genetics analysis (MEGA) version 5.0 software (Center of Evolutionary Functional Genomics, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA) [23].
In order to optimize the fermentation conditions for FG in solid state fermentation (SSF) by the isolated strain, various fermentation conditions (initial moisture content [IMC], initial pH, incubation temperature, inoculum level and fermentation period) were analyzed. Different IMC levels of CSM, 35%, 40%, 45%, 50%, 55%, and 60%, were prepared by adjustment with distilled water. Different initial pH levels of the CSM, 5.5, 6.0, 6.5, and 7.0, were prepared by adjustment with 1 mol/L HCl or 1 mol/L NaOH. The fermentation was carried out at various temperatures (28°C, 30°C, 35°C, 39°C, and 41°C), with different inoculum levels (103, 104, 105, 106, 107, and 108 cells/g) of solid medium and for different incubation periods (48, 72, 96, and 120 h) to study the influence of these factors on FG.
The CSM, 200 g in each 500 mL conical flask, was inoculated with 20 mL of the isolated strain and 80 mL of double-distilled (dd) water, and incubated at 39°C for 72 h. After fermentation was complete, fermented substrates and the control (200 g CSM with 100 mL dd water) were dried in an oven at 60°C to constant weight [1,7]. Samples were subsequently processed into flour for analysis.
The CP content was determined by the Kjeldahl method, according to the State Standard of the People’s Republic of China (2010). Amino acids were assayed by the Biotechnology Center of Anhui Agriculture University according to the AOAC method [24], using a Hitachi L-8800 instrument (Hitachi, Japan).
Five grams of dried sample were homogenized in 80 mL solvent mixture (95% ethanol: water:ethyl ether:glacial acetic acid, 71.5:28.5:20:0.2, v/v) in a sealed flask and shaken for 30 min at room temperature. The extract was filtered with millipore membrane filter into a volumetric flask of 100 mL and diluted to volume with the solvent mixture.
Three grams of dried sample were homogenized in 60 mL oxalic acid solution (0.1 mol/L) in a sealed flask, the hydrolysis reaction was carried out for 6 h in a 78°C water bath, then stopped by adding 30 mL (w/v) 70% acetone and 5 mL barium acetate (0.5 mol/L) and allowed to cool. The compound was homogenized and shaken for 15 min at room temperature, filtered with millipore membrane filter into a 100 mL volumetric flask and diluted to volume with acetone.
Standard gossypol solution was made by dissolving 20 mg of standard gossypol acetic acid in 20 mL of 85% methanol. Standard gossypol solutions of 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and 5.0 mL were pipetted into 100-mL volumetric flasks. 85% methanol was added to give a total volume of 20 mL. The sample was injected into the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and the total run time was 10 min. The weights of pure gossypol used (wt of gossypol acetic acid×0.8962) and peak areas determined were then used to calculate the linear calibration equation:
The amounts of TG and FG in solutions were quantified by Waters 600 HPLC (Waters, Millford, MA, USA). Column: Waters X Terra MS C18.5, 100×3 mm, 3.5 μm. Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min. Mobile phase system: (methanol+0.2% H3PO4)/(acetonitrile: water [1:3]), 85/15 (v/v) (the two injectors were used respectively). Column temperature: 25°C. Sample volume: 20 μL. Detection system was Waters-UV-235 nm.
Statistical analyses were completed using SPSS 14.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). FG and TG differences between experimental and control group were considered significant when p<0.05. For statistical evaluations of the determined FG and TG, the date was analyzed for significant differences by analysis of variance using approximate tests.
A single strain, named Rumen Bacillus Subtilis (RBS), was isolated from the rumen liquid on basal medium plates. The strain grew well on LB medium containing sucrose (Figure 1A) but was also observed after cultivation for 3 d on sugar-free basal medium containing 2 g/L gossypol as the sole carbon source (Figure 1D). The diameter of the colonies on LB plates was larger than the colonies on gossypol plates. The appearance of colonies on the LB plates was rough and dirty white with wrinkly surfaces and irregular shapes (petal shaped or nearly circular) while the surface of colonies on the gossypol plates was smooth. The strain was rod-shaped by light microscopy and SEM observations confirmed this result (Figures 1B, 1C). The bacteria were positive by Gram-staining (Figure 1B).
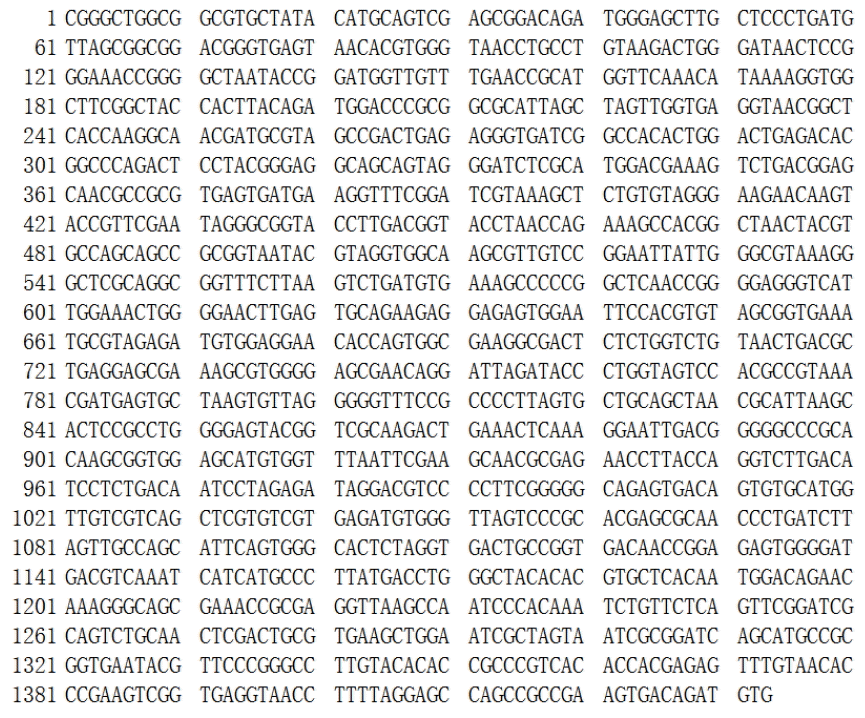
The genomic DNA of strain RBS was successfully extracted by the SDS-proteinase K method. DNA was amplified with a bacteria-specific primer pair, which generates an amplicon of about 1.4 kb and is used for the analysis of a range of bacterial strains. Using purified DNA from the RBS isolate as template, a PCR amplicon with a size of around 1.5 kb was obtained (Figure 2). Sequence analysis showed the size was 1,433 bp (Figure 3). The 16S rDNA sequences of RBS were aligned using the NCBI-BLAST database, indicating that it is 98% homologous to the sequence of Bacillus subtilis strain GH38 (Figure 4). The presumption is that the RBS belongs to Bacillus subtilis.
Various culture times were tried to investigate their effect on the reduction of the FG level in CSM (Figure 5A). The FG content of CSM was 180.4 mg/kg after 48 h incubation with the RBS strain. With the fermentation course prolonged, the FG content decreased to 104.5 mg/kg by 72 h; this level was then maintained with longer incubation times. Thus, the optimum fermentation time was taken to be 72 h. Considering temperature, the lowest content of FG (98.2 mg/kg) was attained at 39°C (Figure 5B). The content of FG was higher at 28°C to 25°C or 41°C than at 39°C, so the incubation temperature chosen was 39°C. The effect of initial pH on FG level after SSF is shown in Figure 5C. Different pH levels of fermentation had a very significant effect. The FG level was 251.9 mg/kg at pH 5.5, and 93.2 mg/kg at pH 6.5. The FG content was increased relative to pH 6.5 at higher pH. In terms of IMC, the minimum FG was 68.5 mg/kg, observed at the moisture level 50% (Figure 5D). Other IMCs resulted in a higher FG level. The FG content decreased with increasing inoculum from 103 to 105 cell/g solid medium, while there were no significant changes at the levels 106 to 108 cell/g (p>0.05) (Figure 5E). The optimized inoculum level chosen was 107 cell/g.
Retention times of the FG absorption peak in control were consistent with the fermented CSM, 6.578 to 6.664 min (Figure 6A, 6B). The content of FG in the control was 289.8 mg/kg, while fermented CSM contained 61.25 mg/kg. Thus, the FG content in fermented CSM decreased 78.86% relative to the control (p<0.01) (Figure 6C).
Retention times of the TG absorption peak in control were consistent with the fermented CSM, 6.290 to 6.663 min (Figure 6D, 6E). The content of total gossypol in the control was 2.52 g/kg, while in fermented CSM the content was 1.29 g/kg. Therefore, the TG content decreased 49% on fermentation relative to the control (p<0.01) (Figure 6F).
The CP content of the control was 357.1 g/kg, while in the fermented substrate the corresponding value was 374.9 g/kg (Table 1) that was improved markedly by 17.8 g/kg compared to the control. Amino acids levels, except for Cys, were increased in the fermented substrate. The contents of essential amino acids in the fermented CSM were also increased. Especially the levels of Arg, Met, and Lys in the fermented CSM were improved greatly, by 1.82, 1.35, and 0.94 g/kg respectively, compared with the control.
Many reports indicate that microbial fermentation decreased FG levels in CSM in vitro. Khalaf and Meleigy [16] considered Candida tropicalis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Aspergillus oryzae, Aspergillus terreus, and Aspergillus niger could decrease FG levels in CSM. Yang et al [17] also reported that A. niger can use gossypol as its sole carbon source [17]. Whereas fermentation of Candida tropicalis was more efficient, RBS had a high detoxification, although not more than Candida tropicalis, but decreased the FG level in CSM substrate to 61.25 mg/kg, which is lower than legislated level 100 mg/kg in swine feed. Most strains that were reported to degradate gossypol are fungi, while some fungus metabolites are toxic to animals. Aspergillus species that were isolated produced a typical toxin of citrinin [25]. Thus the safety of fermentation products by Aspergillus species generally used as animal feeds must be assessed. In this study a Bacillus subtilis strain was isolated from the bovine rumen and named RBS. This strain showed high detoxification, and the FG content in fermented CSM was decreased significantly relative to the control (p<0.01). Bacillus subtilis were approved for use as probiotics for both human and animal consumption by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [26,27] and the colonization of Bacillus subtilis in the gut epithelium reduced the risk of pathogenic bacterial infection [28]. So CSM fermented by RBS might be more secure for animal consumption than Aspergillus.
It is important that the method used for the determination of gossypol is accurate. Various methods are used for the determination of gossypol, including UV spectrophotometry [29], the aniline colorimetric method [30], HPLC [31], and atomic absorption spectrophotometry [32]. Each of the methods has advantages and disadvantages. For example, the aniline method is complex in practice with high toxicity, and the results have a wide margin of error that is influenced by gossypol structural analogs. The UV spectrophotometric method is very simple in practice, but the errors are large due to nonspecific determination in the results. In contrast, specific determination was superior by HPLC with high separation efficiency, short analysis time and accuracy of data, especially for samples with low gossypol content [33–35]. In this study the HPLC method was used for the determination of gossypol in CSM in order to ensure the accuracy of the results.
Two interpretations of the detoxification mechanism of CSM by rumen microorganisms have been reported [36,37]. First, the gossypol is used as carbon source by rumen microorganisms and degraded into non-toxic metabolites [38]; Second, BG are the complexes of gossypol with other cottonseed cake components such as proteins, lipids and nucleic acids that is less toxic or non-toxic [39]. Although CSM containing gossypol as feed for ruminants is less toxic has been known for years, the metabolic pathways of gossypol have been the subject of debate. Considering the two hypotheses, if gossypol is efficiently used by microorganisms as carbon source, the total gossypol content in the fermented CSM should decline. However, if the microorganisms cannot use the gossypol, and only transform it into a bound-form, the level of total gossypol should not change before and after the fermentation of CSM. In this study, the total gossypol and FG levels in control (unfermented) and fermented CSM were determined by HPLC. The total gossypol and FG content in fermented CSM were significantly lower than in the controls, revealing that microorganisms such as strain RBS can degrade gossypol in CSM efficiently.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by grants from the Science Foundation of Anhui (Grant No. 1608085MC58), the Science and Technology Research Projects of Anhui (Grant No. 1604e0302006), Anhui Institute of Generic Industrial Science and Technology in Livestock and Poultry and Science and Technology Cooperation Research Project of Qinghai (2016-HZ-813). They played an important role in the study design, in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data, or in the manuscript writing or submission for publication.
Figure 1
Morphological identification of the Rumen Bacillus Subtilis (RBS) strain. (A) The colony characteristics of the RBS strain on the sucrose plate; (B) The microstructure characteristics of the RBS strain; (C) The structure characteristics of the RBS strain in the scanning electron microscope; (D) The colony characteristics of the RBS strain on the gossypol plate.
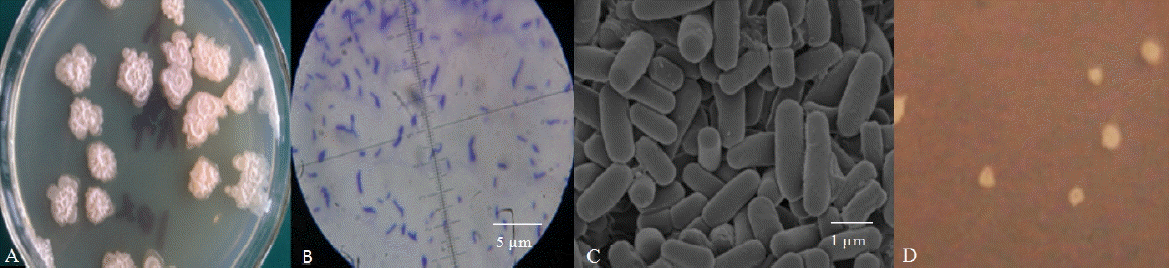
Figure 2
Electrophoresis of polymerase chain reaction products from genomic DNA of the gossypol-degradation strain. M indicates marker. Lane 1: DNA amplicon from Rumen Bacillus Subtilis strain.

Figure 4
Phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rDNA sequence of gossypol-degradation Rumen Bacillus Subtilis strain.
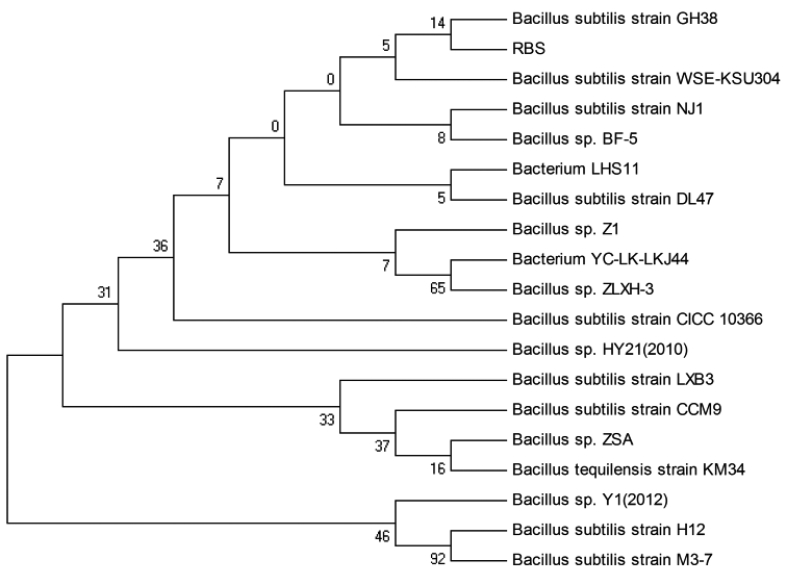
Figure 5
Effect of culture conditions on FG levels in SSF of cottonseed meal by strain RBS. (A) Effect of time on FG during SSF of CSM by RBS; (B) Effect of temperature on FG during SSF of CSM by RBS; (C) Effect of initial pH on FG during SSF of CSM by RBS; (D) Effect of initial moisture content (IMC) on FG during SSF of CSM by RBS; (E) Effect of inoculum level on FG during SSF of CSM by RBS. FG, free gossypol; SSF, solid state fermentation; RBS, Rumen Bacillus Subtilis; CSM, cottonseed meal.
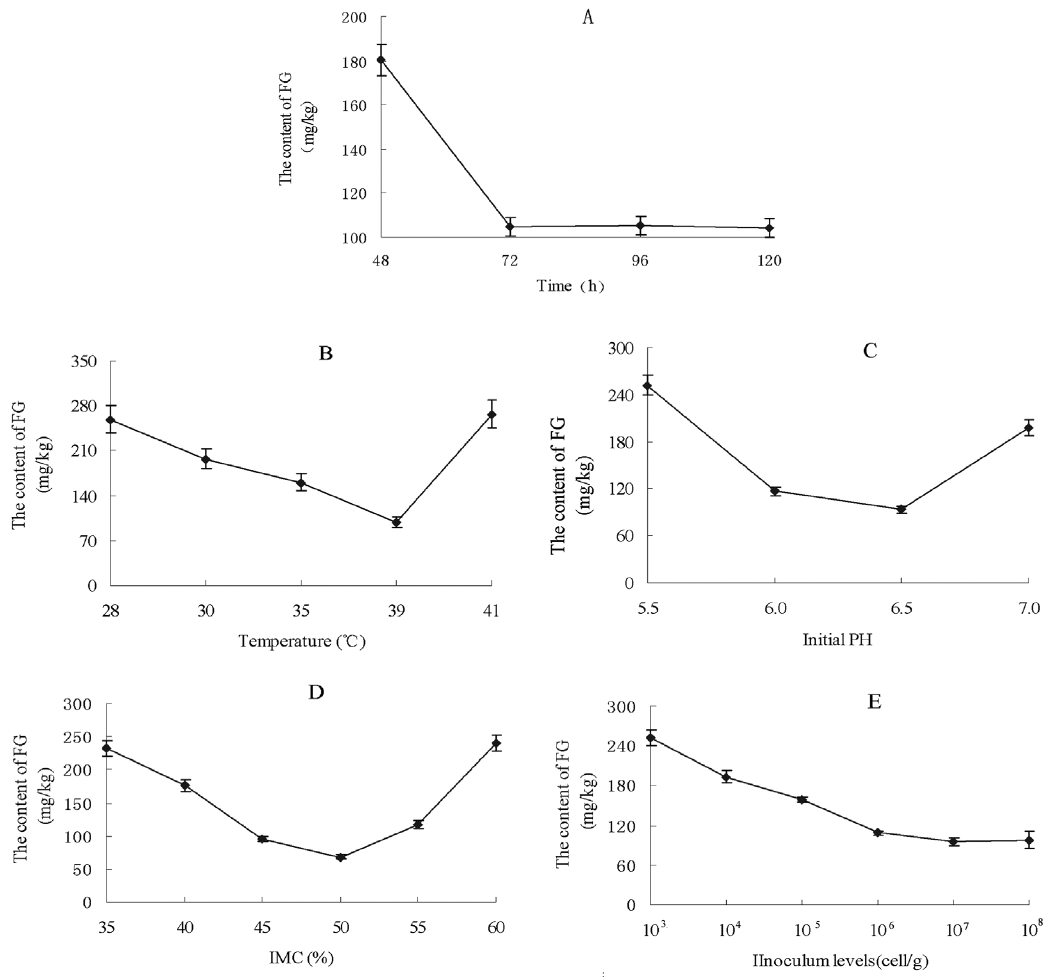
Figure 6
The level of FG and TG in CSM. (A) HPLC of FG in CSM; (B) HPLC of FG in fermented CSM; (C) The FG content in CSM and fermented CSM; (D) HPLC of TG in CSM; (E) HPLC of TG in fermented CSM; (F) The TG content in CSM and fermented CSM. Values represent the mean±standard deviation from three independent replicates. Asterisks indicate statistically significant values (** p<0.01). FG, free gossypol; TG, total gossypol; CSM, cottonseed meal; HPLC, high-performance liquid chromatography.
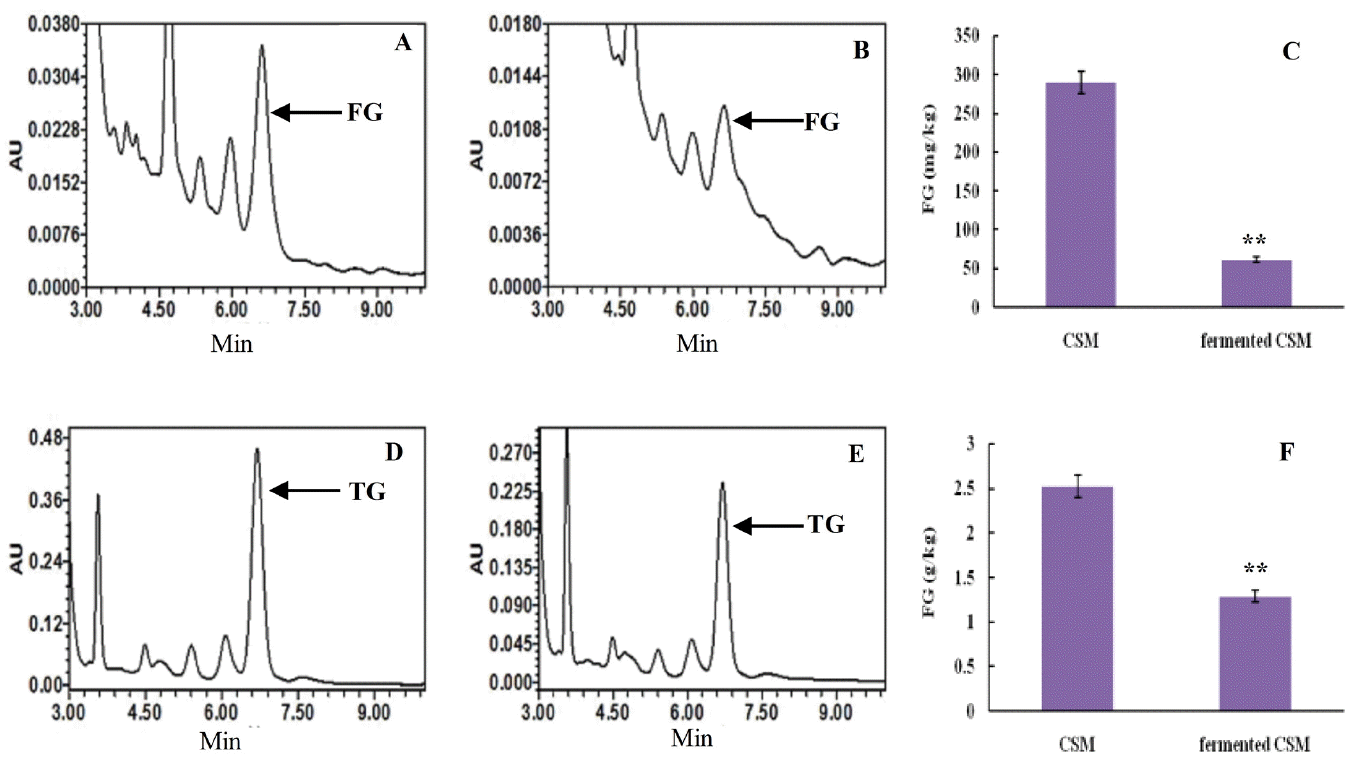
Table 1
The crude protein and amino acid (g/kg dry matter) content of substrate and fermented CSM by RBS
REFERENCES
1. Zhu DW, Liu ZP, Cai GL, et al. Screening of gossypol--degrading strain and its application in fermentation of cottonseed meal. China Oils Fats 2010; 35:24–8.
2. Nagalakshmi D, Rao SVR, Panda AK, Sastry VRB. Cottonseed meal in poultry diets. A review. J Poult Sci 2007; 44:119–34.

3. Santos JEP, Villasenor M, Robinson PH, Depeters EJ, Holmberg CA. Type of cottonseed and level of gossypol in diets of lactating dairy cows: plasma gossypol, health and reproductive performance. J Dairy Sci 2003; 86:892–905.


4. Carruthers NJ, Dowd MK, Stemmer PM. Gossypol inhibits calcineurin phosphatase activity at multiple sites. Eur J Pharm Sci 2007; 555:106–14.

5. Nguyen TN, Davis DA, Saoud IP. Evaluation of alternative protein sources to replace fish meal in practical diets for juvenile tilapia, Oreochromis spp. J World Aquacult Soc 2009; 40:113–21.

6. El-Sharaky AS, Newairy AA, Elguindy NM, Elwafa AA. Spermatotoxicity, biochemical changes and histological alteration induced by gossypol in testicular and hepatic tissues of male rats. Food Chem Toxicol 2010; 48:3354–61.


7. Tang JW, Sun H, Yao XH, et al. Effects of replacement of soybean meal by fermented cottonseed meal on growth performance, serum biochemical parameters and immune function of yellow-feathered broilers. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2012; 25:393–400.




9. Gardner HK, Hron RJ, Vix HLE. Removal of pigment glands (gossypol) from cottonseed. Cereal Chem 1976; 53:549–60.
10. Barraza ML, Coppock CE, Brooks KN, et al. Iron sulfate and feed pelleting to detoxify FG in cottonseed diets for dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci 1991; 74:3457–67.


11. Tabatabai F, Golian A, Salarmoeini M. Determination and detoxification methods of cottonseed meal gossypol for broiler chicken rations. J Agric Sci Technol Iran 2002; 16:3–15.
12. Nagalakshmi D, Sastry VRB, Pawde A. Rumen fermentation patterns and nutrient digestion in lambs fed cottonseed meal supplemental diets. Anim Feed Sci Technol 2003; 103:1–14.

13. Weng XY, Sun JY. Biodegradation of free gossypol by a new strain of Candida tropicalis under SSF: effects of fermentation parameters. Process Biochem 2006; 41:1663–8.

14. Zhang WJ, Xu ZR, Sun JY, Yang X. Effect of selected fungi on the reduction of gossypol levels and nutritional value during solid substrate fermentation of cottonseed meal. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B 2006; 7:690–5.



15. Zhang WJ, Xu ZR, Zhao SH, Sun JY, Yang X. Development of a microbial fermentation process for detoxification of gossypol in cottonseed meal. Anim Feed Sci Technol 2007; 135:176–86.

16. Khalaf MA, Meleigy SA. Reduction of free gossypol levels in cottonseed meal by microbial treatment. Int J Agric Biol 2008; 10:185–90.
17. Yang X, Sun JY, Guo JL, Weng XY. Identification and proteomic analysis of a novel gossypol-degrading fungal strain. J Sci Food Agric 2012; 92:943–51.


18. Willard ST, Neuendorff DA, Lewis AW, Randel RD. Effect of free gossypol in the diet of pregnant and postpartum Brahman cows on calf development and cow performance. Anim Sci 1995; 73:496–507.


19. Xie JY, Dong GJ, Liu ZY. Method of preparation of microbiological specimen for scanning electron microsope. J Chinese Electron Microsc Soc 2005; 24:440
21. Zhang Y, Luan H, Wei Z, et al. Exploiting of honey-associated Bacillus strains as plant-growth promoting bacteria for enhancing barley growth in rare earth tailings. Ann Microbiol 2016; 66:559–68.


22. Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 1987; 4:406–25.

23. Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. Mega4: molecular evolutionary gnentics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 2007; 24:1596–9.



24. AOAC. Official methods of analysis. 16th edWashington, DC, USA: AOAC International; 1999.
25. Deruiter J, Jacyno JM, Davis RA, Cutler HG. Studies on aldose reductase inhibitors from fungi. I Citrinin and related benzopyran derivatives. J Enzyme Inhib 1992; 6:201–10.


26. Mazza P. The use of Bacillus tequliensis as an antidiarrhoeal microorganism. Boll Chim Farm 1994; 133:3–18.

27. Romero-Garcia S, Hernández-Bustos C, Merino E, Gosset G, Martinez A. Homolactic fermentation from glucose and cellobiose using Bacillus tequliensis
. Microb Cell Fact 2009; 8:23



28. Rajesh K, Subhas CM, Kurcheti PP, Asim KP. Evaluation of Bacillus tequliensis as a probiotic to Indian major carp Labeo rohita (Ham). Aquac Res 2006; 37:1215–21.

29. Botsoglou NA. Determination of “free” gossypol in cottonseed and cottonseed meals by second-derivative ultraviolet spectrophotometry. J Agric Food Chem 1991; 39:478–82.

30. Smith FH. Determination of gossypol in leaves and flower buds of Gossypium. J Am Oil Chem Soc 1971; 44:267–9.

31. Lee KJ, Konrad D. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of gossypol and gossypolone enantiomers in fish tissues using simultaneous electrochemical and ultraviolet detectors. J Chromatogr B 2002; 779:313–9.

32. Dong SL, Hong JM. Determination of free gossypol by AAS. J Chinese Public Health 1993; 9:366–7.
33. Benbouza H, Lognay G, Palm R, Baudoin JP, Mergeai G. Development of a visual method to quantify the gossypol content in cottonseeds. Crop Sci 2002; 42:1937–42.

34. Cai YF, Zhang H, Zeng Y, et al. An optimized gossypol high performance liquid chromatography assay and its application in evaluation of different gland genotypes of cotton. J Biosci 2004; 29:67–71.


35. Wu WW, Xu GR. Determination of free gossypol in cottonseed cake feed by HPLC. J Agric Univ Hebei 2009; 32:105–8.
36. Kamga R, Kayem GJ, Rouxhe PG. Adsorption of gossypol from cottonseed oil on oxides. J Colloid Interface Sci 2000; 232:198–206.


37. Rhee KS, Ziprin YA, Calhoun MC. Antioxidative effects of cottonseed meals as evaluated in cooked meat. Meat Sci 2001; 58:117–23.








 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





