 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 32(8); 2019 Special Issue > Article |
|
Abstract
Goat population world-wide is increasing, and the dairy goat sector is developing accordingly. Although the new technology applied to the goat industry is being introduced slowly because the weight of traditional subsector in the dairy sector, considerable advances have been made in the last decade. Present review focuses on the emerging topics in the dairy goat sector. Research and development of traditional and new dairy goat products are reviewed, including the new research in the use of goat milk in infant formula. The research in alternatives to brine, production of skimmed goat cheeses and the use of different modified atmosphere packaging are also addressed. Special attention is given to antibiotic residues and their determination in goat milk. Functional foods for human benefits are a trending topic. Health properties recently discovered in dairy goat products are included in the paper, with special attention to the antioxidant activity. The dual-purpose use of goats by humankind is affecting the way of how new technology is being incorporated in the dairy goat sector and will certainly affect the future development of dairy goat products.
The earliest evidences for cheese making date about 7,500 years ago [1]. Archaeological sieve fragments were found in Kuyavia, Poland, showing lipids residues from cow milk. It is acknowledged that goat was one of the earliest domesticated animals for milk production and human benefits (8,000 B.C.) [2]. It is argued that the first cheeses were made from goat and sheep milk. The importance of goat milk changed as cow milk was introduced into human diets, and consequently its economic significance/impact decreased progressively in the world. Goat milk differs from cow milk in its higher digestibility, diverse alkalinity, higher buffering capacity and confident therapeutic use in human nutrition. Goat milk has smaller fat globules; distinct protein’s polymorphism, with significantly lower as1- and higher as2-casein, thus higher tolerability than cow milk; when acidified, shows better digestibility than cow milk. Goat milk has more short- and medium-chain fatty acids, giving a special ability to provide energy mostly for growing children. To date goat milk accounts for less than 1.6% of the dairy production worldwide [3].
Most of goat milk is consumed fresh, especially in those regions where goat is reared for family consumption, e.g., in Asia, Africa and South America [4]. Thus, the official statistics related to goat milk and dairy production are scarce and likely underestimated, as is their importance for human nutrition.
In 2017 dairy goats were estimated at 217.7 million heads (i.e., 21% of the total goat population), mostly distributed in Asia (52%) and Africa (39%), with the remainder in Europe, Americas, and Oceania [3]. Goat milk world production accounted 18.66 million tons, where India is the top producer in the world, with more than 6.16 million tons of goat milk, followed by Bangladesh, Sudan, Pakistan, France, Greece, Turkey, and Spain respectively.
Breed, breeding program (i.e. seasonal or year-round), production system, feeding system, organization of the production chain, research and development activity are main factors affecting goat milk production and quality.
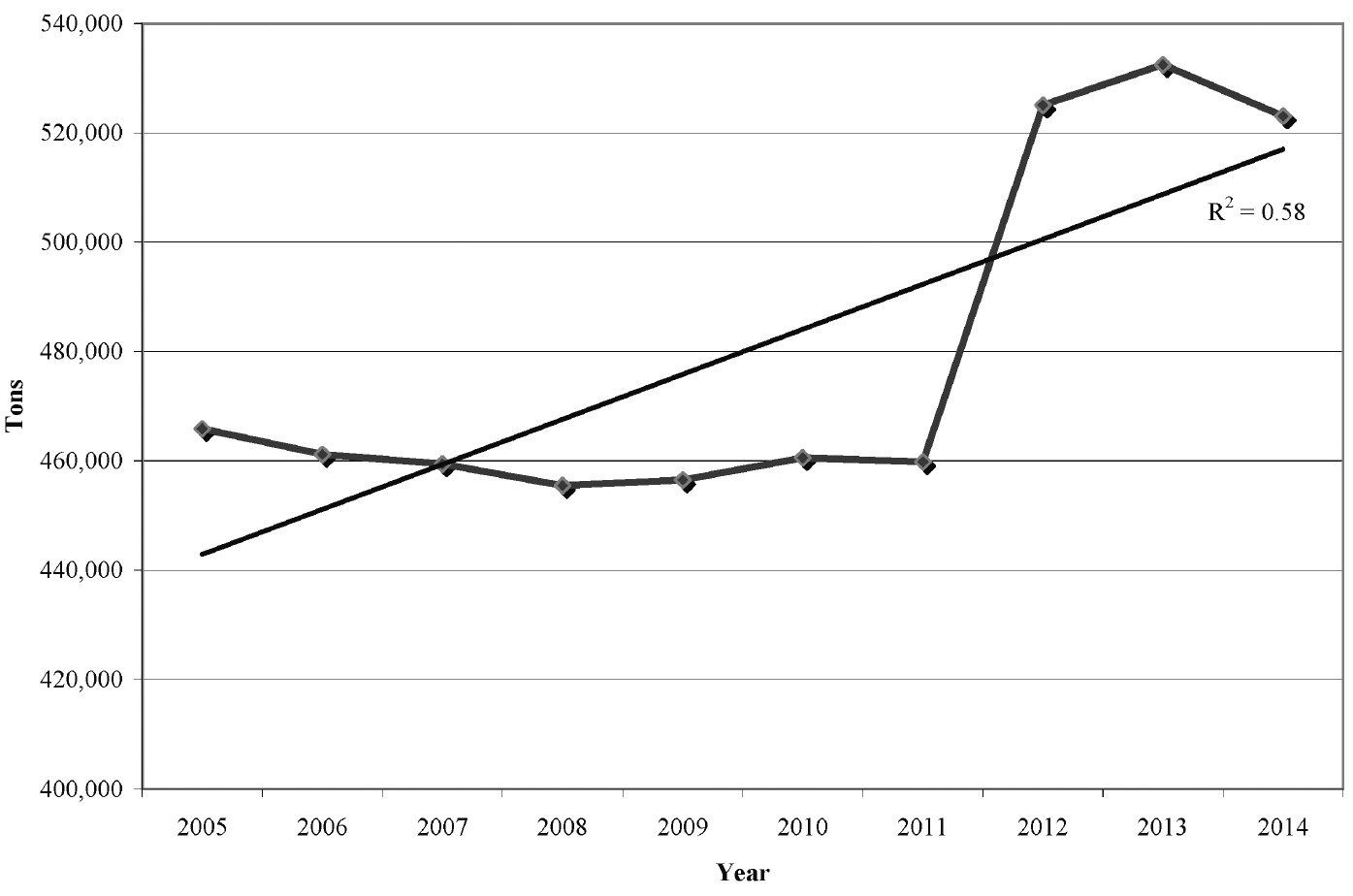
Goat dairy products around the world consist of yogurt, fermented milk, curd and cheese, ice cream, made of pure goat milk or mixed with other types of milk (i.e., sheep, cow). According to latest FAOSTAT database [3], in 2014 the world production of goat cheeses counted totally 523,000 tons, showing a rapid increase from 2011 to 2013 (Figure 1), just over 15%, in comparison to world cow dairy production in the same period (5.4%).
Despite a large proportion of goat milk in the world was produced in Asia (10.55 million tons, i.e. 56% in 2014, and 57% in 2017), the highest production of goat cheese came from Africa, in particular from South Sudan (110,750 tons). Europe produced 35% of world goat cheese with only 15% of goat heads. This may be explained with the differences in production system, extensive vs. more intensive, and the destination of milk, drinking milk rather than cheese (Figure 2).
The world areas top producers of goat milk cheese were Eastern Africa (i.e. South Sudan), and Western Europe (87,407 tons, from France, Germany, and Austria), followed by Northern Africa (85,105 tons, from Sudan, Morocco, and Tunisia) and Southern Europe (81,854 tons, from Greece, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Albania, and Malta).
Goat milk production systems vary considerably by region. In Asia, Africa and South America, the majority of goat rearing is carried out by small enterprises, farmstead and/or family operations, which have not access to modern pasteurization facilities. Raw milk is processed or sold locally to dairies that process daily, thus eliminating the risks of bacterial contaminations and spoilage during storage and transportation. In fact, these operation scales are so small that often official statistics of goat milk and dairy products are not kept in many countries. The production system is extensive, mostly with grazing and rarely with feed supplementation. In other regions, such as North America, goat milk production is increasing slowly but steadily. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, as of the beginning of 2017 there were 373,000 registered dairy goats in the United States, with the largest numbers in Wisconsin (44,000 heads) and California (41,000 heads). Similarly, dairy goat operations in the U.S. are mainly of small and farmstead scales. Industrial scale goat farms and milk processing plants have been established in recently years due to an increased interest and demand among consumers.
The present review aims to present the recent advances in dairy goat production, with a multidisciplinary approach.
Accordingly to Gellynck and Kühne [5], traditional dairy products can be defined those, with or without label, that meet four criteria: i) the key production steps of a traditional cheese product must be performed in a certain area, which can be national, regional or local; ii) the traditional cheese must be authentic in its recipe (ingredients), origin of raw material, and/or production process; iii) the traditional cheese must be commercially available for at least 50 years; and iv) it must be part of the gastronomic heritage.
Goat cheese is a universe itself, where each type of cheese has its own “character”, a restricted trait among the cheeses. Traditional goat cheeses are characterized by diversity of appearance, typical sensory profile, different process and tools, and ripening degree, such as fresh vs ripened lactic cheese, fresh or ripened curd, moulded, spreadable, cooked or uncooked, natural caves, etc.; some of them are linked to specific breeds of goats, such as the Italian Fatulì cheese, produced only with milk from Bionda dell’Adamello goat breed (PAT - Traditional Agri-Foodstuffs, Italian Quality Label).
Generally, goats are the only domesticated animals that can feed with restricted vegetation in harsh environments where steep gradients, damp climate, thin limestone based or rocky soil represent difficult condition for agricultural activities by human.
Few studies gather specifically the traditional goat dairy products worldwide. The “Atlas of goat products” [6] is the only worldwide collection giving information on origin, type, area and technique of production, scale of production, uses and demand trend on dairy goat products. This inventory reports 170 goat dairy products, among which 150 cheeses, and drinking milk, yogurt, ice cream, salted whey from 23 countries in 4 continents. It is surely not an exhaustive list (Table 1). An update is encouraged to include the products not yet inventoried, the estimation of production and the latest recognition labels applied.
Broadly the traditional dairy goat products are linked to the “environment”. Similar to wine production, they are the result of the “terroir”: mankind as for savoir faire, cultural heritage, and environment, such as soil, water availability, location, climate, vegetable and animal biodiversity.
The dairy products by natural starters in milk are commonly located in very dry and warm climate areas such as desert regions. Goat breeding in these areas has been the main occupation of numerous people since ancient times, and goat’s milk and cheese have always been a fundamental part of their economy, diet and cultural heritage. The products may be consumed fresh or dry. Examples are J’ben from Morocco, Djamid/Jameed, and Labaneh from the Middle East. The small scale of production supplies the market locally but diffusely (Table 1). In Turkey [7], the traditional goat dairy products are destined to local and regional market, such as Erzincan, Izmir Brined, and Cimi Tulum cheeses (tulum means wrapped in goatskin), Karin Kaymagi, Ezine, Carra or Testi, Sepet, Kefir, Hellim cheese (the equivalent of Halloumi from Cyprus), and Ayran cheese.
The cheeses from enzymatic coagulation, with animal or vegetal rennet, represent the most of the world production, both farmstead and industrial. The farmstead scale is linked to the low amount of production and kind of process, both labelled and non-labelled cheeses. Few traditional cheeses are produced at an industrial scale, with one exception of Greek Feta protected designation of origin (PDO) cheese.
El Galiou et al [8] carried out a chemical and microbiological survey on 28 fresh raw goat’s milk cheeses from different small domestic producers in Northern Morocco. This study compared three manufacturing processes: calf rennet, with and without cooling milk after milking, and vegetable rennet without cooling milk after milking. The variability in pH values (3.8 to 4.0) and dry matter contents (24.9 to 31.2 g/100 g), together with the free fatty acids and microbiota composition, revealed a large variability of milk quality and lack of standardization in the manufacturing process.
Martinez et al [9] conducted a review in which the description of 32 Spanish goat cheeses, their manufacture processes, their organoleptic characteristics and the studies carried out on them were reported (Table 2). Raynal-Ljutovac et al [10] presented an up-date on the French market for goat milk cheeses. It is suggested that the particular technology of lactic cheeses and the slow coagulation at room temperature are perfectly suited with habits of women herding little flock of goats in late 19th century. These processes became so famous abroad that they are synonymous with French type cheese.
In Europe, the traditional products are protected and valorised by the recognition with labelling system, where the production is regulated by severe disciplinary. The labels are namely the PDO and the protected geographical indication (PGI): PDO cheese is produced and processed and prepared in its area of production; PGI is produced or processed or prepared in its area of production, and both benefit from a long-lasting good reputation. As of April 2019 European Union had 216 PDO cheeses and 59 PGI cheeses [11]. Among them, 41 were from goat milk (Table 3).
It was found [12] that the PDO labelling created a quantifiable added-value, in comparison to other cheeses, roughly +50% when sold at the market and +20% on farm. The PDO label system is best fitted with the small scale production of traditional goat cheeses and helps the distribution of the value along the whole production chain, and to increase the power of producers’ supply in the market.
Due to the increased popularity, many cheeses originally made with pure goat milk are made with cow milk or a mix of goat, sheep and cow, such as Añejo Enchilado cheese produced in Mexico, Caprino cheese in Italy, and Halloumi cheese in Cyprus. Sometimes the rennet originally used (from kid and lamb) has been replaced by liquid calf rennet, and consequently mild flavour cheeses are produced, which are preferred by today’s consumers. For example, the Norwegian brown whey cheese Brunost is less consumed, while the popularity of rennet- and acid-coagulated cheeses has increased [13]. The Turkish Gokceada cheese in the past was made with a home-made kid rennet, however, commercial calf rennet is commonly used today [14].
The dairy production in South America is the result of the adaptation of imported technologies to local customs and environment. The widespread small and farmstead scale productions of Queso blanco, Queso fresco, Requeson, and Quesillo in Venezuela, Peru and Bolivia, respectively, indicate that traditional products are critically important to local economies; moreover they are characterized by the women labour. On the other hand, Queijo Minas Frescal produced in Brazil is an exception to the role, as it is produced by specialized industries.
The traditional cheeses are appreciated for their original shape, sensory profile, and the occasion of maintaining gastronomic and rural tradition. Darfyieh and Arichi cheeses from Lebanon may be considered among the most original cheeses: they are produced from milk and whey, respectively, and then put in alternate layers into a goat skin to ripen. The production is ancient, linked to the Baladi goat breed. The Sudanese white Gibna Bayda cheese is produced by women, like many other cheeses, and is representative of many traditional cheeses in Africa: no standard processing methods, resulting in high variability in nutritional composition, microbial proliferation of natural lactic acid bacteria (LAB), and sensory characteristics [15].
The world dairy production claims several traditional milk derived products: yogurt (naturally probiotic) and not -enzymatic coagulation curds. Tamime et al [16] reviewed the panorama of goat fermented milk, where most products are traditionally made locally in different countries in the Middle East and in other regions, and some are produced at industrial scale. The fermented milk and yogurt change name by country and region, and the quality is affected by the local strains of LAB (traditional and adjunct, including probiotic organisms), yeasts and moulds (or combination of these) employed. Among the products, they described Caprine yoghurt, the Italian Gioddu, the Chinese Tarag, caprine probiotic yoghurt, kefir, the concentrated yogurt Labneh, the salted yoghurt Tuzlu and Shankleesh, dried fermented milks such as Kurut, Keş, Kiş.
Pandya and Ghodke [17] reviewed several studies on cream, butter such as Turkish “Yayik” butter, more appreciated than sheep or cow milk butter, chhana and paneer, very popular in India and nearby countries. Chhana is a heat and acid coagulated Indian milk product, generally processed by women. It is obtained from adding sour whey from previous day to hot milk (70°C). The coagulum is filtered through fine cloth, pressed and used immediately. Paneer is a variation of chhana, a soft uncured cheese, more similar to Cottage or Queso blanco. Paneer is traditionally produced with cow milk, little from goat milk.
Cheese and yogurt are predominant products of goat milk, however, there are other economically viable products derived from goat milk as well. For this review we will focus on recent advances in ice cream, fermented beverages and infant formula.
The addition of fortification substrates to ice cream made from goat milk was addressed by Chaves et al [18]. The substrates evaluated were chia mucilage and bean gum, which both impacted moisture and viscosity. Adding polydextrose (as a prebiotics) and Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei and Bifidobacterium longum + Bifidobacterium bifidum in a combined culture (as probiotic cultures) to goat ice cream yielded very interesting results extending the shelf life of the product [19]. Relatedly, viability of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium BB-12, [20] in goat ice cream was increased (increasing the value as a probiotic) by addition of Carob extract and whey powder, with best results when the substances were included at 1%.
Fermented goat milk products containing Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 and Propionibacterium jensenii 702 were made by Ranadheera et al [21], with no negative effects on the sensory properties. Collagen hydrolysate, cheese whey, and acai pulp (Euterpe oleracea) have been successfully incorporated in fermented goat milk beverages to extend the viability of probiotics [22]. SHIME is a unique scientifically validated dynamic model of the complete gastrointestinal tract for study of physicochemical, enzymatic, and microbial parameters in the gastrointestinal tract in a controlled in vitro setting. Using SHIME, [23] was able to keep Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Streptococcus thermophilus viable during their passage through the intestinal tract, which had a positive effect on gut microbiota metabolism using a grape probiotic fermented beverage made with goat milk. Use of inulin and oligofructose as prebiotics in goat milk fermented beverages including Bifidobacterium lactis has had favourable effects enhancing probiotic viability and sensory characteristics [24].
After the approval of the use of goat milk or derivates in infant formulas (Directive 2013/46/EU), research in this area has been conducted. With simulation of infant digestive conditions, similar results were observed for cow and goat milk, although production of bioactive peptides differed [25]. In reference to the presence of oligosaccharides in goat milk versus cow colostrum, [26] have showed that oligosaccharides from goat milk were determined as more potential ingredients of infant formulae based on potency of adherence inhibition, safety, and the availability of the starting material. Furthermore, [27] compared in vitro proteolysis of human, cow, and goat milk, and observed more similarities between human and goat milk than human and cow milk.
The adoption of new technology in the dairy goat sector is usually slower than that in the dairy cattle sector, largely because of the lesser world economic importance and relatively lower input production systems of the dairy goat industry world-wide.
Presently diets low in salt and fat are viewed as having positive effects on human nutrition and health. This is in part relevant to the making of some types of goat cheese because of brine usage. Relatedly, Miloradovic et al [28] attempted to reduce the NaCl level of a white brined cheese from 6% to 3% but noted a marked decrease in consumer acceptability, apparently because of an altered texture profile and an increased cohesiveness. Further studies in this area are needed to solve such consumer acceptability issues. Regarding the level of fat, goat cheese made with skimmed milk has posed some negative characteristics for consumers [29]. New technologies, such as supercritical fluid extraction, hold promise to decrease the level of fat after cheese is produced [30].
Considerable scientific attention is being given to microbiome and microbiota, including the dairy goat sector. Using cheese as a probiotic carrier has been proposed by Meira et al [31]. These authors incorporated Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Bb-12 and Lactobacillus acidophilus La-05 into goat Ricotta with little change in physical-chemical characteristics, mainly derived from a lower concentration of lactose due to a higher transformation to lactic acid. It was reported that Ricotta serviced as a carrier of the probiotic, providing protection for survival of the stressful conditions imposed by the human gastrointestinal tract.
Biotechnology is now being applied in practical settings, an example of which is widespread use of substances extracted from bacteria, yeast and fungus. However, use of such products in the dairy goat sector is not common. Listeria monocytogenes is a problem in raw milk cheeses around the world, and its control is key factor. The use of bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances have been proposed to control the growth of Listeria monocytogenes in goat cheese [32]. This research group used Enterococcus durans E204 as a source of bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances that successfully inhibit the Listeria monocytogenes growth in Jben goat cheese (a traditional Moroccan fresh cheese).
Storing cheese frozen as a means of conservation has long been a common practice in the cheese industry and new knowledge has emerged in the last decade [33,34]. Although the length of time of cheeses in freezers has always been a concern, Park [34] did not observe any major negative effects of freezing goat milk Monterey Jack cheese at −20°C for 5 years on consumer acceptance. Conversely, Andic et al [33] reported negative effects of freezing Motal cheese on organoleptic quality (i.e., free fatty acids released).
There has been some research attention to packaging of dairy foods in the last 10 years. Technological characteristics of foils for packaging of cheese during ripening have been recently determined [35]. Foils differing in permeability to CO2 and O2 have influence on appearance and physical characteristics of cheese that consequently affect the final quality of products. Relatedly, use of different atmospheres during the packaging was addressed by [28]. To replace the O2 in the atmosphere surrounding the cheese has an impact on the ripening process. It was determined that replacing the normal atmosphere with a modified one, e.g., 60% CO2 and 40% N2, reduced the growth of psychrotrophic bacteria and yeasts/moulds, although no differences were observed in proteolysis or cheese colour. Arvanitoyannis et al [36] found different results with other gas levels of 40% CO2, 55% N2, and 5% O2; 60% CO2 and 40% N2; and 50% CO2 and 50% N2. Vacuum packaging has been widely used in the last 40 years; it has been reported that this type of packaging has little or no effects after ripening of Urda whey cheese [37]. Future research is needed to identify optimal combinations of gas levels for specific types of cheese and the use of biodegradable plastic materials.
Antimicrobial resistance is a growing global health concern in both human and animals. An increasing number of studies has shown that antimicrobial usage in humans [38] and animals [39] is the main driver of the development of antimicrobial resistance, although an environmental role has been recently proposed as well [40]. Antibiotic residues in animal foods are caused by antimicrobial usages in animal treatments and feed additives. Obviously, this area is of importance to the dairy goat sector and has consequently received considerable research attention.
Screening tests are commonly used in detecting antibiotic residues in milk. For detecting oxytetracycline residues in goat milk, Charm Rosa and SNAP tests have performed satisfactorily [41]. Betastar Combo, SNAP Betalactam, SNAP Tetracycline, and Twinsensor tests have been successfully used in goat milk [42]. Brilliant black reduction test AiM, Delvotest MCS, Eclipse 100, and Copan Milk tests have been also used in goat milk for detection of residues of non-beta-lactam and beta-lactam antibiotics, with concerns expressed by the authors about their sensitivity for non-beta-lactam and no concerns for beta-lactam [43,44]. Also the successful use of electronic nose (a metal oxide semiconductor gas-sensing device) have been proposed for Penicillin G residues detection [45].
The presence of antibiotic residues in cheese has been evaluated recently [46]. Goat milk was added with European Union maximum residue limits of amoxicillin, benzylpenicillin, cloxacillin, erythromycin, ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin, and oxytetracycline to manufacture ripened Spanish Tronchon cheese. It was reported that high concentrations of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin residues were observed in the cheeses after 60 d of maturation. Therefore, special attention must be implemented to guarantee the safety of cheese in regard to antibiotic residues. A different approach using whey as an indicator was used by Giraldo et al [47]. Results were similar to those of Quintanilla et al [46], where different antibiotics varying in retention behaviour in curd.
The off-label use of some drugs in the goat sector is common because of the small number of products labelled for use with goats. Off-label use of macrolides in dairy goats was addressed by Quintanilla et al [48]. There were no residues of erythromycin, tylosin or spiramycin after the mandatory 7 days of withdrawal. In regard to use of antibiotics in reproductive management practices, no residual antibiotics were found in milk when doxycycline, oxytetracycline, and sulfathiazole-framycetin were used at recommended doses in intravaginal sponges [49].
The presence of antibiotic residues in milk did not markedly impact the manufacturing process of dairy goat products, including yogurt [50] and cheese [46], but different results could be observed in relation to the antibiotic type.
Microbial inhibitor tests are widely used in laboratories for screening antimicrobials in milk because they are easy to use and inexpensive [51]. However, some substances present in milk can interfere with the test. No interference of antiparasitic drugs such as albendazole has been observed [51]. On the contrary, ivermectin residues in goat milk after parasite treatment altered the microbial inhibitor test [52]. The doses of the antiparasitic drug play an important role, with [53] observing that high doses interfere with the most microbial inhibitor tests including BRT MRL, Delvotest SP-NT MSC, and Eclipse 100. Residues of detergents used in the cleaning process of the milking machine can have impact on microbial inhibitor test results, depending on the chemical nature of detergent [54]. The presence of colostrum in milk samples interferes with normal use of microbial inhibitor tests due to the relatively high protein concentration [55]. Therefore, these authors conclude that microbial inhibitor tests are not suitable to detect antibiotic residues in colostrum.
Bioactive compounds in food associated with proteins, lipids and polysaccharides are one of the most recent research fields, together with studies on their metabolism to assess their contributions to human health [56]. Scientific evidences stimulated a new consumers approach towards foods: the awareness that food may be more than basic nutrition but a step towards well-being. Research evidence and consumer awareness have elevated the functional food market in the entire world.
The main trait of goat milk that has contributed to its increasing interest by the consumers is its lower allergenic properties due to the lower level of α-s1-CN and its higher digestibility, linked to the higher proportion of short and medium chain fatty acids than cow milk [57]. In regions dominated by the consumption of cow milk, goat milk is known to be an alternative, especially in case of poor digestibility or intolerance to cow milk. However, one of the main limits by the consumer, besides the cultural heritage, is goat milk’s sensory profile.
While health properties [58,59] and utilization of particular bioactive compounds for childhood nutrition [60] of goat milk are increasingly studied, studies on goat milk dairy products are relatively scarce.
Goats grazing in pastoral systems, by eating large amounts of natural browsing plants, are almost unknown carriers of health promoting compounds. Goat dairy products supply in different way and measure the milk nutritional compounds and other new molecules: fatty acids, organic acids, exopolysaccharides (EPS) [61], vitamins, bioactive peptides and lipids, and enzymes.
Hereby, the recent advances on healthy contribution of goat dairy products are reviewed.
World goat rearing is characterized mostly by grazing system, where animals feed pasture resources with low or no supplementation. Several studies found how the feeding system and the botanical composition of the pasture affect the nutritional profile of cheese in terms of fatty acid profile and content. Recently, Sant’Ana et al [62] evaluated the fatty acid profiles and sensory profiles of goat milk and Coalho cheese. Their study compared goats grazing Caatinga plants on native semiarid pasture (PS) (Brazil) or being raised in Confinement System (CS). Both cheese and milk from PS had slightly higher polyunsaturated fatty acids and saturated fatty acids ratio (PUFA/SFA) and a markedly lower atherogenic index and n−6/n−3 ratio, which are favourably considered for the potential impact on consumer’s health. The decrease in short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) in PS, in comparison to CS, was mostly due to the decrease of medium chain FA C12:0 and C14:0, both considered hypercholesterolaemic FA, resulting in the decreased atherogenic index (C12:0, from 3.26 to 2.59, and C14:0 from 10.86 to 9.05 in CS and PS, respectively). Furthermore, they found a reduction of short-chain saturated FA C6:0, C8:0 and C10:0, considered negative for the healthy profile of cheese. Trans-FA C18:2c9t11 (i.e., conjugated linoleic acid or CLA) was significantly lower in PS cheese (0.33% vs 0.38% total FA), whereas C18:3n−3 was significantly higher (0.23% vs 0.10% total FA), contributing to favourably decrease the ratio n−6/n−3.
In a semi-extensive system, goat flocks are fed forage and concentrate supplementation, mostly in certain lactation periods and physiological stages. Claps et al [63] reported significant differences in cheeses from Mediterranean red goats fed 8 Mediterranean forage species, 4 legumes and 4 grasses given in pureness, on fatty acid profile. Cheeses made with milk from goats fed T. incarnatum, Triticosecale and H. vulgare showed the highest content in CLA, while cheeses from goats fed Vicia sativa displayed the lowest CLA content but the highest content of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), probably due to the higher level of tannic polyphenols in forage, which was able to interact with lipolysis and PUFA bio-hydrogenation. The highest health-promoting index was observed in cheeses from goats fed H. vulgare and A. sativa.
The lipid components of cheese, such as CLA, PUFA and polar lipids, may exert anti-inflammatory activities [64]. Traditional Greek Ladotiri and Kefalotiri cheeses were studied for their lipid fractions, in particular those able to inhibit platelet activating factors (PAF, a potent thrombotic phospholipid mediator of atherosclerosis). Cheeses showed inhibitory properties against PAF-induced platelet aggregation, and sphingomyelin, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine lipid derivatives as the most biologically active compounds. The anti-inflammatory activities increase during lipolysis (during yogurt and cheese manufacture processes). Megalemou et al [65] found the most vigorous PAF inhibitors in yogurt from sheep and goat milk, in comparison to those from cow milk. The studies showed that native pastures as well as farm-grown forages can be considered effective low-cost feed to improve goat milk fatty acid composition without affecting yield, a pathway toward the sustainable intensification of goat production.
In an attempt to improve health properties of dairy goat products, trials were carried out to study the effect of vegetable oils and fatty acid supplementation on goat cheese nutritional profile. De Medeiros et al [66] experimented diets containing 4% vegetable oils (faveleira, sesame, or castor oils), taking also into account the sensory profile. The diets containing faveleira and sesame oils positively affected the fatty acid profile, increasing the unsaturated fatty acid (USFA) content, 35.73% and 35.08%, respectively, to levels considered beneficial to human health.
The studies on functional properties of bioactive compounds are applied mostly in vitro and in animal model, while still few studies concern human trial. Santurino et al [56] enriched naturally goats cheese by feeding Murciano-Granadina goats with extruded linseed with good consistency of retention of the bioactive ingredients in order to be applied in human clinical trials among overweight and obese subjects engaged in cardiovascular risk prevention study. Diet, besides increasing milk yield, significantly favoured the increase of CLA (2.32% vs 1.47% of total fatty acid methyl esters and 5-fold higher omega-3 (4.05% vs 0.49%), thus reducing 7-fold the ratio omega-6/omega-3, with beneficial effect for human health. ALA increased (0.64 g/100 g vs 0.13 g/100 g cheese), allowing the claim for “source of omega-3”, according to EU Regulation.
Few studies reported on the presence of angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitor peptides in goat cheese and yogurt. These enzymes, produced by hydrolysis of milk proteins by LAB, showed antihypertensive activity. In commercial Kefir made with goat milk, two peptides, with sequences PYVRYL and LVYPFTGPIPN, resistant to a simulated digestion were found with potent ACE inhibitor activities [67]. In one Spanish pure goat cheese and in Cabrales cheese [68], the peptide DKIHP (fragment β-CN f[47–51]) showed the highest ACE inhibitor activity, with the lowest half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value as 113.1 μM.
Few studies were concerned the antioxidant molecules and capacity in goat dairy products. Several compounds exert antioxidant activity, protecting lipids and other molecules against the oxidation or the production of free radicals, which have been regarded as dangerous forerunner of cardiovascular diseases (CVD).
Sepe et al [69] fed Siriana goats with fresh Avena sativa in pureness to study the occurrence of phenolic compounds in milk, cheese and whey. They found a variety of phenolic compounds carried from milk to Caciotta cheese: 15 simple phenols, 5 benzoic acid derivatives and 5 unclassified phenolic compounds. Notwithstanding the presence in milk, cinnamic acid derivatives, hippuric acid, riboflavin, and indole derivatives were not found in cheese. One of the indole derivatives found in milk was recovered in cheese. These preliminary results allowed proposing a method to analyse phenolic compounds in cheese and to observe that a variety of phenolic compounds are carried from milk to whey and cheese, boosting the knowledge on the healthy benefits from goat dairy products.
In a more recent study [70], feeding system (free-range vs confinement), heat treatment (raw vs pasteurized) and season (dry vs rainy) were the variables on the antioxidant capacity and total phenolic content (TPC) in goat cheeses. Cheeses from goats grazing five hours in thorny deciduous forest land, dominated by shrubs, and supplemented (concentrate, hay, and silage), showed significantly higher antioxidant capacity compared with cheeses from confined feeding system. The same occurred for TPC, and in particular during dry season and from unpasteurized milk (363.21 mg gallic acid equivalent/L milk).
Recently, the interest for non-bovine healthy dairy products involved the research and dairy industry, conjugating the benefit traits of goat milk to the health properties of probiotic LAB. Besides the protective and technological properties, LAB produce or increase specific bioactive compounds in food.
Feta, probably the most famous traditional Greek cheese, made with blend of sheep and goat milk (up to 70:30 ratio), was produced with Lb. plantarum T571 strain, with the aim to investigate the probiotic performance as a co-starter [71]. Surviving Lb. plantarum was counted in probiotic Feta in levels required for claiming a probiotic effect (≥6 log colony-forming unit/g) during the storage at 4°C and ripened for 9 months, compared to the usual period by the industry (6 months). Moreover, the probiotic Feta was evaluated with similar or better scores of sensory attributes (i.e. acidity, sweetness, rancidity and hardness). Even though the consumer approach is predictable to complete the holistic evaluation, the authors considered the Lb. plantarum strain T571 as a promising candidate to develop functional Feta cheese.
Several studies [72] demonstrated that goat milk is a successful carrier for probiotic LAB, in cheese, yogurt, fermented milk, milk beverage, ice-cream and other products, since these dairy products can facilitate probiotic viability and high surviving level during storage. Dairy goat products exhibit a high potential in heightening the functional properties of probiotics such as gastrointestinal tolerance and adhesion to intestinal epithelium. On the other hand, certain LAB strains cause concerns in the sensory profile of dairy products, as they are capable of producing volatile aromatic compounds that contribute to an elevated sensory profile, sometimes too “goaty” for the consumer.
A recent analysis [73] highlighted the critical role of autochthonous LAB from in the protective, technological and functional properties of dairy goat products. In particular, EPS from LAB such as Lb. plantarum, under regular consumption, are associated with antimutagenic property, while antigastritis, antiulcer, and antitumor effects are associated with EPS from another LAB. Moreover, autochthonous strains of L. coryniformis are good producers of cobalamin (vitamin B12) while Lactococcus lactis is a good source of riboflavin (vitamin B2) and folate.
The large variability, in physical-chemical and microbiological quality, in those environments where the hygienic conditions of milking and cheese-making may lead to high bacterial load, is ascribable to lack of standardization in the manufacturing process. Moreover, the need for improving milk quality and/or using heat-treated milk to produce the cheese is common, besides the implementation of strategies to enhance the chemical and microbiological quality of traditional products [8].
The dairy goat industry has gathered the desire of the consumer, in slow but steady growth, for products alternative to cow’s milk. Innovative goat dairy products are therefore increasing, with ingredients that can satisfy the taste of today’s consumer [24], such as inulin in beverage, or with technologies that respect the original ingredient in traditional cheeses [74].
The dairy industry has also beheld the chance to produce functional dairy products from goat milk, which may potentially benefit human health and contribute to attenuate issues related to CVD, obesity and diabetes. One of the most emergent challenges for the dairy industry is to counteract the image of milk by-products as cholesterol enemy. In this way, one of the perspectives is linked to the cholesterol-lowering properties exerted by some LAB [75]. Seven strains of LAB, used in goat yogurt and cheese process with raw milk, were found to be able to decrease the cholesterol first in broth and then in cheeses during ripening. It was reported that the cholesterol-lowering property was more significant in cheeses ripened for 60 days than 30 days, with the exception of Lb. plantarum VS166 and VS513. Further studies on autochthonous LAB and their strains may lead to novel functional dairy goat products or improved traditional products.
One of the greatest challenges for humankind is to combat the climate change, which prompts us to develop sustainable strategies to adapt to the changes in water availability, temperature, soil system, vegetable and animal biodiversity, both preserving the environment and satisfying the increasing food demand. Goat is, in many ways, the most adaptable species that allows sustainable breeding and production, especially in those harsh environments characterized by scarce resources. Moreover, goats emit less methane than other domestic ruminants, contributing to the mitigation of climate changes [76]. In this sense, there is a reasonable perspective that goat rearing and dairy production will continue to grow and develop in the future, provided that sustainable strategies mentioned above are developed.
Furthermore, given the growth of market demand for goat products, the system must be equipped with advanced, fast and yet accurate methods to detect adulteration of fraudulent blends of goat’s milk from other milks. Advances in electronic nose have made it a rapid, accurate and not invasive tool to detect adulterations with high sensitivity and specificity. Several studies have validated its accuracy and cost-effectiveness of this method, using a large database library [77]. This approach has also shown encouraging potential in other applications, such as discrimination of watered milks, differentiation of diet supplementation, identification of cheese ripening age/stage, in the near future.
Recent issues that characterize the demand by the postmodern consumer concern “all-natural product”, less processed and preservative-free options, all favouring the growing of the demand for organic products. The world trend for organic foods is increasing: the global organic retail sales in 2017 counted 92.08 Billion € (about 103.81 Billion $), having grown about 2.7-fold in the last decade [78]. The global organic cheese market is expected to increase 14% by 2023 [79], with Europe and China to be key future markets, whereas India and Brazil to be emerging contributors to this growth. The organic food, that implies prohibition for artificial additives and genetically modified organisms, is perceived as a healthier alternative to products from intensive system. Given the pastoral system that characterizes the goat breeding and production in most regions worldwide, organic goat production may be economically important in those regions where intensive system is dominant. Perspective is a small but steady growth.
The seasonality, which characterizes goat milk production, in certain states may be considered a limit, i.e. for industrial scale, while in artisan and farmstead scale it is considered a plus value, a factor that gives uniqueness to regional and traditional products. In fact, season means diversity of natural feedstuff (for botanical and chemical composition), climatic conditions and milk composition.
Breed in some regions is the key factor for sustainability and quality production. The native breeds, in fact, have the resilience, more than other breeds, to adapt themselves to the climatic change and to use the local resources more efficiently. One of the strengths of the native breeds lays in this nature. Only a few goat dairy products are linked to a native breed, as seen previously, but these cases could represent winning examples of biodiversity enhancement, worthy of being extended to other products. Furthermore, the label system attesting the origin (PDO and PGI) [12,73,80] has shown to be also a mean for supporting and safeguarding the maintenance of such rural identity, through the perpetuation of cheese making techniques. This label scheme, moreover, mostly for small and farmstead scale, clearly favours the quality instead the quantity growth, the preservation of local employment in rural far-flung areas and highlights a product in consumer’s eyes.
Many factors affect the quality of dairy products, i.e. feeding, breed, process (rennet, tools, technology, ripening), autochthonous LAB (that have the further property to differentiate the sensory profile), production system (environment and persons). Hence, one strategy to promote the increase of the demand for traditional products would be the multidisciplinary approach, in order to communicate their benefits and cultural heritage. One of the approaches may be the measurement of life cycle assessment, but still few studies concern goat dairy production system.
Finally, one of the most recent challenges is giving an economic measure to the ecosystem services performed by shepherds and breeders cheese-makers. This incentive system would represent a concrete recognition towards those intangible services they carry out in favour of safeguarding the biodiversity, maintaining the environment and cultural heritage.
This article, after an overview on the worldwide traditional and new goat dairy production, presented the recent advances under different points of view: technology, packaging, residual antibiotics, and health benefits.
Dairy goats, once reared as the little cows for poor people or in harsh environments, are still one of the most efficient animals in bio-valorising the feed resources, mostly in difficult regions where goats cannot be replaced by other species, able to give quality meat, milk and hair/skin. It is affirmed particularly today, when the intensification of cow milk production signs the crisis of milk in many regions, and human population shows increasing level of intolerance and allergy towards cow milk. Additionally, when climatic changes sound the alarm asking humankind for new and more respectful approaches to the Nature, dairy goats represent a more viable and sustainable production system.
The research is giving answers to the popular belief about the health properties of goat’s milk products, common in many regions of the world. Nevertheless, further efforts are needed to highlight the results, together with further clinical studies on their potential effects on consumer health. In the future starting today, supplementary research in sustainably feeding goats, improving milk and by-products’ quality, eco-friendly and smartly exploiting milk whey, will be strategic for the development of the dairy goat production chain.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Authors sincerely thank Prof. Steve Zeng for his encouraging support in writing this paper.
Figure 2
Fresh goat milk production (a) (latest official data available year 2017) and cheese production (b) (latest official data available year 2014) (%) per world region [3]. The variation in milk production between 2014 and 2017 was 1 to 2 points percentage. Thus the comparison between fresh milk production 2017 and cheese production 2014 is considered.

Table 1
Main traditional goat cheeses and dairy products by regions of Africa, Middle East, Americas and Asia
| Region | Country | Name | Milk (breed)/other dairy prod. | Scale of production | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Africa | Algeria | Djben/Jben/Gibneh | Raw goat, sheep, cow | Small | [7] |
| Egypt | Dhani | Raw goat | Small | [7] | |
| Karish | Raw goat, camel | Small/Bedouins | [7] | ||
| Mish | Raw goat, cow, camel | Small, home | [7] | ||
| Morocco | J’ben | Raw goat | Small | [7] | |
| Sudan | Gibna Bayda | Raw goat | Farmstead | [18] | |
|
|
|||||
| Middle East | Djamid/Jameed | Raw goat, sheep | Small | [7] | |
| Labaneh | Goat, cow, sheep/conc. yogurt | Small/Bedouins | [7] | ||
| Lebanon | Darfyieh | Raw goat/cheese in goat skin | Small | [7] | |
| Arichi | Whey cheese/in goat skin | Small | [7] | ||
| Turkey | Tulum (Erzincan, Izmir Brined and Cimi) | Raw goat | Nom.& transhumance s. | [8] | |
| Ayran | Raw goat | Nom.& transhumance s. | [8] | ||
| Carra or Testi | Raw goat | Nom.& transhumance s. | [8] | ||
| Ezine | Raw goat | Nom.& transhumance s. | [8] | ||
| Hellim | Raw goat | Nom.& transhumance s. | [8] | ||
| Karin Kaymagi | Raw goat | Nom.& transhumance s. | [8] | ||
| Kefir | Raw goat | Small, Industrial | [8] | ||
| Kurut, Keş, Kiş | Goat/dried fermented milk | Small | [19] | ||
| Sepet | Goat | Small | [8] | ||
| Tuzlu and Shankleesh | Goat/dried salted yogurts | Small | [19] | ||
| Yayik | Goat/butter | Small | [21] | ||
|
|
|||||
| Americas | Argentina | Quesillo | Raw goat (Criolla) | Small | [7] |
| Bolivia | Quesillo | Raw goat | Small | [7] | |
| Brazil | Minas frescal | Raw goat | Industrial (’70) | [7] | |
| Doce de leite | Goat/processed dessert | Small | [7] | ||
| Mexico | Fresco [Queso] | Raw goat | Small | [7] | |
| Fresco de Aro | Raw goat | Small | [7] | ||
| Ranchero de cabra de Queretaro | Raw goat | Small | [7] | ||
| Ranchero molido | Raw goat | Small | [7] | ||
| Peru | Quesillo | Raw goat | Small | [7] | |
| Queso Fresco | Raw goat | Small | [7] | ||
| Venezuela | Queso Blanco | Raw goat (Baladi) | Small | [7] | |
| Natilla | Goat and cow/condensed | Small | [7] | ||
|
|
|||||
| Asia | India | Dahi | Raw goat/yogurt | Small | [20] |
| China | Tarag | Goat/yogurt | Small | [19] | |
Table 2
Spanish goat milk cheeses, by region and origin of the milk (adapted from [11])
Table 3
| Country | EU label1) | Cheese name | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyprus | PDO | Halloumi/Hellim (Ap.) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| France | PDO | Banon | Chabichou Du Poitou | Charolais | Chevrotin | Crottin De Chavignol | Mâconnais | Pélardon |
| Picodon | Pouligny-Saint-Pierre | Rocamadour | Sainte-Maure De Touraine | Selles-Sur-Cher | Valençay | Brousse Du Rove (Ap.) | ||
| PGI | Tomme Des Pyrénées | |||||||
| None | Boxe Cheese From Poitou | Cabecou D’autan | Cabecou Perigord | Calenzana (whey cheese) | La Feuille Du Limousine | Mothais Sur Feille | ||
|
|
||||||||
| Germany | PDO | Altenburger Ziegenkäse | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Greece | PDO | Anevato | Batzos | Feta | Formaella Arachovas Parnassou | Galotyri | Kalathaki Limnou | Kasseri |
| Katiki Domokou | Kefalograviera | Ladotyri Mytilinis | Metsovone | San Michali | Sfela | Xygalo Siteias/Xigalo Siteias | ||
| Xynomyzithra Kritis | Arseniko Naxou (Ap.) | |||||||
| PGI | Krasotiri Ko - Tiri Tis Possias (Ap.) | |||||||
| None | Anthotiros | Armirotiri | Chlorotiri | Galomyzithra | Kathoura | Kefalotiri | Kopanisti | |
| Manoura | Manouromizithra | Mizithra | Telemes | Xynotiri | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Italy | PDO | Formaggella del Luinese | Robiola di Roccaverano | Valle D’Aosta Fromadzo | ||||
| PGI | Canestrato Di Moliterno | |||||||
| None | Agrino Orobie | Blue | Cachat | Cacioricotta | Canestrato D’aspromonte | Caprino della Carnia | Caprino della Val Vigezzo | |
| Caprino Semicotto | Caprino Valsesiano | Casieddu | Caso Conzato | Caso Peruto | Cevrin Di Coazze | Crotonese | ||
| Fatulì | Felciata | Formaggio morbido della Valle D’Aosta | Jama | Juncata | Musulupu | Nicastrese | ||
| Robiola del Bec | Tomino di Talucco | Vecjo di Cjavre | Ricotta (whey cheese) | Scuete (whey c.) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Norway | None | Ekte geitost (whey c.) | Gudbrandsdalsost | Kvit geitost (whey c.) | Snoefrisk | |||
|
|
||||||||
| Poland | None | Blekitna kraina | Czarnuszka | Ser podpuszczkowy wedzony | Ser twarogowy swiezy | Ser zolty | Blekitna kraina | Ser twardy wedzony |
|
|
||||||||
| Portugal | PDO | Queijo de Cabra Transmontano/Transmontano Velho | Queijo Rabaçal | Queijo Amarelo da Beira Baixa/Queijo Picante da Beira Baixa | ||||
| PGI | Queijo mestiço de Tolosa | |||||||
| None | Algarve | |||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Sweden | None | Vit geitost | Mesost (whey c.) | |||||
|
|
||||||||
| Switzerland | None | Ziegenkäse | ||||||
REFERENCES
1. Salque M, Bogucki PI, Pyzel J, et al. Earliest evidence for cheese making in the sixth millennium BC in northern Europe. Nature 2013; 493:522–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11698



2. Hatziminaoglou Y, Boyazoglu J. The goat in ancient civilisations: from the Fertile Crescent to the Aegean Sea. Small Rumin Res 2004; 51:123–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2003.08.006

3. FAOSTAT [Internet]. Rome, Italy: FAO; c2018. [cited 2019 April]. Available from: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/
4. Escareno L, Salinas-Gonzalez H, Wurzinger M, Iniguez L, Solkner J, Meza-Herrera C. Dairy goat production systems. Trop Anim Health Prod 2012; 45:17–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-012-0246-6



5. Gellynck X, Kühne B. Horizontal and vertical networks for innovation in the traditional food sector. Int J Food System Dynamics 2010; 2:123–32. https://doi.org/10.18461/ijfsd.v1i2.124

6. Rubino R, Morand-Fehr P, Sepe L. Atlas of goat products: a wide international inventory of whatever things the goat can give us. Caseus. 2004. p. 381
7. Hayaloglu AA, Karagul-Yuceer Y. Utilization and characterization of small ruminants’ milk and milk products in Turkey: current status and new perspectives. Small Rumin Res 2011; 101:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2011.09.027

8. El Galiou O, Zantar S, Bakkali M, Laglaoui A, Centeno JA, Carballo J. Chemical and microbiological characteristics of traditional homemade fresh goat cheeses from Northern Morocco. Small Rumin Res 2015; 129:108–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2015.06.005

9. Martinez S, Franco I, Carballo J. Spanish goat and sheep milk cheeses. Small Rumin Res 2011; 101:41–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2011.09.024

10. Raynal-Ljutovac K, Le Pape M, Gaborit P, Barrucand P. French goat milk cheeses: an overview on their nutritional and sensorial characteristics and their impacts on consumers’ acceptance. Small Rumin Res 2011; 101:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2011.09.026

11. European Commission. Agriculture and food. DOOR (database) [Internet]. [cited 2019 April]. http://ec.europa.eu/agriculture/quality/door/list.html?locale=en
12. Giraud G. Economics of goat and ewe milk cheeses with protected designation of origin in Europe. Proceedings in System Dynamics and Innovation in Food Networks. 2016. p. 381–3. https://doi.org/10.18461/pfsd.2016.1641

13. Skeie SB. Quality aspects of goat milk for cheese production in Norway: a review. Small Rumin Res 2014; 122:10–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2014.07.012

14. Hayaloglu AA, Yasar K, Tolu C, Sahingil D. Characterizing volatile compounds and proteolysis in Gokceada artisanal goat cheese. Small Rumin Res 2013; 113:187–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2013.01.001

15. Hamid OIA, El Owni OAO. Processing and properties of Sudanese white cheese (Gibna Bayda) in small-scale cheese units in South and West Darfur states (Sudan). Livest Res Rural Dev. 2008. 20:Article #16. https://www.lrrd.org/lrrd20/8/hame20116.htm
16. Tamime AY, Wszolek M, Bozanic R, Ozer B. Popular ovine and caprine fermented milks. Small Rumin Res 2011; 101:2–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2011.09.021

17. Pandya AJ, Ghodke KM. Goat and sheep milk products other than cheeses and yoghurt. Small Rumin Res 2007; 68:193–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2006.09.007

18. Chaves MA, Piati J, Malacarne LT, et al. Extraction and application of chia mucilage (Salvia hispanica L.) and locust bean gum (Ceratonia siliqua L.) in goat milk frozen dessert. J Food Sci Technol 2018; 55:4148–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3344-2




19. Acu M, Kinik O, Yerlikaya O. Functional properties of probiotic ice cream produced from goat’s milk. Carpath J Food Sci Technol 2017; 9:86–100.
20. Guler-Akin MB, Goncu B, Akin MS. Some properties of probiotic yoghurt ice cream supplemented with carob extract and whey powder. Adv Microbiol 2016; 6:1010–20. https://doi.org/10.4236/aim.2016.614095

21. Ranadheera CS, Evans CA, Adams M, Baines SK. Co-culturing of probiotics influences the microbial and physico-chemical properties but not sensory quality of fermented dairy drink made from goats’ milk. Small Rumin Res 2016; 136:104–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2016.01.016

22. Rigoto JD, Ribeiro THS, Stevanato N, Sampaio AR, Ruiz SP, Bolanho BC. Effect of acai pulp, cheese whey, and hydrolysate collagen on the characteristics of dairy beverages containing probiotic bacteria. J Food Process Eng 2019; 42:e12953https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.12953

23. Freire FC, Adorno MAT, Sakamoto IK, et al. Impact of multi-functional fermented goat milk beverage on gut microbiota in a dynamic colon model. Food Res Int 2017; 99:315–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.05.028


24. da Silveira EO, Neto JHL, da Silva LA, Raposo AES, Magnani M, Cardarelli HR. The effects of inulin combined with oligofructose and goat cheese whey on the physicochemical properties and sensory acceptance of a probiotic chocolate goat dairy beverage. LWT-Food Sci Technol 2015; 62:445–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.09.056

25. Hodgkinson AJ, Wallace OAM, Smolenski G, Prosser CG. Gastric digestion of cow and goat milk: Peptides derived from simulated conditions of infant digestion. Food Chem 2019; 276:619–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.10.065


26. Urakami H, Saeki M, Watanabe Y, et al. Isolation and assessment of acidic and neutral oligosaccharides from goat milk and bovine colostrum for use as ingredients of infant formulae. Int Dairy J 2018; 83:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2018.03.004

27. Maathuis A, Havenaar R, He T, Bellmann S. Protein digestion and quality of goat and cow milk infant formula and human milk under simulated infant conditions. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2017; 65:661–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000001740



28. Miloradovic Z, Smigic N, Djekic I, et al. The influence of NaCl concentration of brine and different packaging on goat white brined cheese characteristics. Int Dairy J 2018; 79:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2017.11.010

29. Sanchez-Macias D, Fresno M, Moreno-Indias I, et al. Physicochemical analysis of full-fat, reduced-fat, and low-fat artisan-style goat cheese. J Dairy Sci 2010; 93:3950–6. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2010-3193


30. Sanchez-Macias D, Laubscher A, Castro N, Argueello A, Jimenez-Flores R. Effects of supercritical fluid extraction pressure on chemical composition, microbial population, polar lipid profile, and microstructure of goat cheese. J Dairy Sci 2013; 96:1325–34. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2012-5473


31. Meira QGS, Magnani M, de Medeiros FC, et al. Effects of added Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium lactis probiotics on the quality characteristics of goat ricotta and their survival under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Res Int 2015; 76:828–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.08.002


32. Khay E, Idaomar M, El Moussaoui N, Abrini J. Application of a bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance producing Enterococcus durans E204 strain, isolated from camel milk, to control Listeria monocytogenes CECT 4032 in goat jben
. Ann Microbiol 2014; 64:313–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0666-1


33. Andic S, Tuncturk Y, Javidipour I. Effects of frozen storage and vacuum packaging on free fatty acid and volatile composition of Turkish Motal cheese. Food Sci Technol Int 2011; 17:375–94. https://doi.org/10.1177/1082013210382485


34. Park YW. Effect of 5 years long-term frozen storage on sensory quality of Monterey Jack caprine milk cheese. Small Rumin Res 2013; 109:136–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2012.08.002

35. Darnay L, Nemeth A, Koncz K, et al. Effect of different O2/CO2 permeable foils on aging of semi-hard goat cheese. Int Dairy J 2019; 90:114–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2018.11.010

36. Arvanitoyannis IS, Kargaki GK, Hadjichristodoulou C. Effect of three MAP compositions on the physical and microbiological properties of a low fat Greek cheese known as “Anthotyros”. Anaerobe 2011; 17:295–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2011.04.007


37. Pappa EC, Samelis J, Kondyli E, Pappas AC. Characterisation of Urda whey cheese: Evolution of main biochemical and microbiological parameters during ripening and vacuum packaged cold storage. Int Dairy J 2016; 58:54–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2015.12.016

38. Costelloe C, Metcalfe C, Lovering A, Mant D, Hay AD. Effect of antibiotic prescribing in primary care on antimicrobial resistance in individual patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br Med J 2010; 340:c2096https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.c2096

39. Simoneit C, Burow E, Tenhagen BA, Kasbohrer A. Oral administration of antimicrobials increase antimicrobial resistance in E-coli from chicken - a systematic review. Prev Vet Med 2015; 118:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed.2014.11.010


40. Chamosa LS, Alvarez VE, Nardelli M, Quiroga MP, Cassini MH, Centron D. Lateral Antimicrobial Resistance Genetic Transfer is active in the open environment. Sci Rep 2017; 7:513https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00600-2




41. Attaie R, Bsharat M, Mora-Gutierrez A. Applicability of screening tests for oxytetracycline in the milk of three breeds of goats. J Food Prot 2016; 79:1013–20. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-15-200


42. Beltran MC, Borras M, Nagel O, Althaus RL, Molina MP. Validation of receptor-binding assays to detect antibiotics in goat’s milk. J Food Prot 2014; 77:308–13. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-13-253


43. Sierra D, Contreras A, Sanchez A, et al. Detection limits of non-beta-lactam antibiotics in goat’s milk by microbiological residues screening tests. J Dairy Sci 2009; 92:4200–6. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2009-2101


44. Sierra D, Sanchez A, Contreras A, et al. Detection limits of four antimicrobial residue screening tests for beta-lactams in goat’s milk. J Dairy Sci 2009; 92:3585–91. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2008-1981


45. Ding W, Zhang Y, Kou LP, Jurick WM. Electronic nose application for the determination of Penicillin g in Saanen goat milk with Fisher discriminate and multilayer perceptron neural network analyses. J Food Process Preserv 2015; 39:927–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.12305

46. Quintanilla P, Beltran MC, Molina A, Escriche I, Molina MP. Characteristics of ripened Tronchon cheese from raw goat milk containing legally admissible amounts of antibiotics. J Dairy Sci 2019; 102:2941–53. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2018-15532


47. Giraldo J, Althaus RL, Beltran MC, Molina MP. Antimicrobial activity in cheese whey as an indicator of antibiotic drug transfer from goat milk. Int Dairy J 2017; 69:40–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2017.02.003

48. Quintanilla P, Beltran MC, Penis B, Rodriguez M, Molina MP. Antibiotic residues in milk and cheeses after the off-label use of macrolides in dairy goats. Small Rumin Res 2018; 167:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2018.08.008

49. Romero T, Balado J, Althaus RL, Beltran MC, Molina MP. Short communication: Drug residues in goat milk after prophylactic use of antibiotics in intravaginal sponges for estrus synchronization. J Dairy Sci 2016; 99:141–5. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2015-10200


50. Beltran MC, Morari-Pirlog A, Quintanilla P, Escriche I, Molina MP. Influence of enrofloxacin on the coagulation time and the quality parameters of goat’s milk yoghurt. Int J Dairy Technol 2018; 71:105–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0307.12388

51. Romero T, Althaus R, Moya VJ, Beltran MD, Reybroeck W, Molina MP. Albendazole residues in goat’s milk: Interferences in microbial inhibitor tests used to detect antibiotics in milk. J Food Drug Anal 2017; 25:302–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2016.08.007


52. Romero T, Moya VJ, Fernandez N, Althaus R, Reybroeck W, Molina MP. Interferences on microbial inhibitor tests related to ivermectin treatment in lactating dairy goats. J Dairy Res 2016; 83:341–4. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022029916000443


53. Romero T, Beltran MC, Reybroeck W, Molina MP. Effect in vitro of antiparasitic drugs on microbial inhibitor test responses for screening antibiotic residues in goat’s milk. J Food Prot 2015; 78:1756–9. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-15-020


54. Romero T, Beltran MC, Althaus RL, Molina MP. Interference of non-specific detergents in microbial inhibitor test results for screening antibiotics in goat’s milk. J Appl Anim Res 2017; 45:159–63. https://doi.org/10.1080/09712119.2015.1129341

55. Romero T, Beltran MC, Perez-Baena I, Rodriguez M, Molina MP. Effect of the presence of colostrum on microbial screening methods for antibiotic detection in goats’ milk. Small Rumin Res 2014; 121:376–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2014.07.007

56. Santurino C, Calvo M, Gómez-Candela C, Fontecha J. Characterization of naturally goat cheese enriched in conjugated linoleic acid and omega-3 fatty acids for human clinical trial in overweight and obese subjects. Pharma Nutr 2017; 5:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phanu.2016.12.001

57. Almaas H, Cases AL, Devold TG, et al.
In vitro digestion of bovine and caprine milk by human gastric and duodenal enzymes. Int Dairy J 2006; 16:961–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2005.10.029

58. Claps S, Di Napoli MA, Caputo AR, Rufrano D, Sepe L, Di Trana A. Factor affecting the 3′ sialyllactose, 6′ sialyllactose and disialyllactose content in caprine colostrum and milk: Breed and parity. Small Rumin Res 2016; 134:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2015.11.002

59. Giorgio D, Di Trana A, Claps S. Oligosaccharides, polyamines and sphingolipids in ruminant milk. Small Rumin Res 2018; 160:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2018.01.006

60. Hodgkinson AJ, Wallace OAM, Boggs I, Broadhurst M, Prosser CG. Gastric digestion of cow and goat milk: Impact of infant and young child in vitro digestion conditions. Food Chem 2018; 245:275–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.028


61. Caggianiello G, Kleerebezem M, Spano G. Exopolysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria: from health-promoting benefits to stress tolerance mechanisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2016; 100:3877–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7471-2



62. Sant’Ana AMS, Bessa RJB, Alves SP, et al. Fatty acid, volatile and sensory profiles of milk and cheese from goats raised on native semiarid pasture or in confinement. Int Dairy J 2019; 91:147–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2018.09.008

63. Claps S, Rossi R, Di Trana A, Di Napoli M, Giorgio D, Sepe L. Bioactive compounds in goat milk and cheese: the role of feeding system and breedKukovics S, editorGoat science. IntechOpen; 2018. 978-1-78923-202-8https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.70083
64. Lordan R, Zabetakis I. The anti-inflammatory properties of dairy lipids. J Dairy Sci 2017; 100:4197–212. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2016-12224


65. Megalemou K, Sioriki E, Lordan R, Dermiki M, Nasopoulou C, Zabetakis I. Evaluation of sensory and in vitro anti-thrombotic properties of traditional Greek yogurts derived from different types of milk. Heliyon 2017; 3:e00227https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2016.e00227



66. de Medeiros EJL, Queiroga R, de Medeiros AN, et al. Sensory profile and physicochemical parameters of cheese from dairy goats fed vegetable oils in the semiarid region of Brazil. Small Rumin Res 2013; 113:211–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2013.02.006

67. Quiros A, Hernandez-Ledesma B, Ramos M, Amigo L, Recio I. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of peptides derived from caprine Kefir. J Dairy Sci 2005; 88:3480–7. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)73032-0


68. Gomez-Ruiz JA, Taborda G, Amigo L, Recio I, Ramos M. Identification of ACE-inhibitory peptides in different Spanish cheeses by tandem mass spectrometry. Eur Food Res Tech 2006; 223:595–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-005-0238-0


69. Sepe L, Cornu A, Graulet B, Claps S, Rufrano D. Phenolic content of forage, milk, whey and cheese from goats fed Avena sativa. In : 10-th International Meeting on Mountain cheese; 2011; Dronero (CN), Italy. p. 31–2. 978-88-902754-5-6
70. Chavez-Servin JL, Andrade-Montemayor HM, Vazquez CV, et al. Effects of feeding system, heat treatment and season on phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity in goat milk, whey and cheese. Small Rumin Res 2018; 160:54–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2018.01.011

71. Papadopoulou OS, Argyri AA, Varzakis EE, Tassou CC, Chorianopoulos NG. Greek functional Feta cheese: Enhancing quality and safety using a Lactobacillus plantarum strain with probiotic potential. Food Microbiol 2018; 74:21–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2018.02.005


72. Ranadheera CS, Naumovski N, Ajlouni S. Non-bovine milk products as emerging probiotic carriers: recent developments and innovations. Curr Opin Food Sci 2018; 22:109–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2018.02.010

73. de Souza JV, Dias FS. Protective, technological, and functional properties of select autochthonous lactic acid bacteria from goat dairy products. Curr Opin Food Sci 2017; 13:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2017.01.003

74. Fresno M, Alvarez S, Diaz E, Virto M, de Renobales M. Short communication: Sensory profile of raw goat milk cheeses made with artisan kid rennet pastes from commercial-weight animals: Alternative to farmhouse goat cheeses. J Dairy Sci 2014; 97:6111–5. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2014-8238


75. Albano C, Morandi S, Silvetti T, Casiraghi MC, Manini F, Brasca M. Lactic acid bacteria with cholesterol-lowering properties for dairy applications: In vitro and in situ activity. J Dairy Sci 2018; 101:10807–18. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2018-15096


76. Darcan NK, Silanikove N. The advantages of goats for future adaptation to climate change: a conceptual overview. Small Rumin Res 2018; 163:34–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrurnres.2017.04.013

77. Costa C, Taiti C, Strano MC, et al. Multivariate approaches to electronic nose and PTR-TOF-MS technologies in agro-food products. Electronic Noses and Tongues in Food Science Academic Press; 2016. p. 73–82.
78. Statistics F. European and global organic farming statistics [Internet]. c2019. [cited 2019 April]. Available from: https://statistics.fibl.org/world.html
79. Global Organic Dairy Market Report 2019 [Internet]. OMSCo - The Organic Dairy People; c2019. [cited 2019 April]. Available from: https://www.omsco.co.uk/news/reports/
80. Eriksson C, Bull J. Place-making with goats and microbes: the more-than-human geographies of local cheese in Jamtland, Sweden. J Rural Stud 2017; 50:209–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2017.01.010

- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles
-
Research advances in reproduction for dairy goats2019 August;32(8)
Recent advances in breeding and genetics for dairy goats2019 August;32(8)
Current status, challenges and prospects for dairy goat production in the Americas2019 August;32(8)
Current status of global dairy goat production: an overview2019 August;32(8)
Recent advances in the feeding and nutrition of dairy goats2019 August;32(8)






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print




