 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 36(2); 2023 Special Issue > Article |
|
Abstract
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract of ruminants contains diverse microbes that ferment various feeds ingested by animals to produce various fermentation products, such as volatile fatty acids. Fermentation products can affect animal performance, health, and well-being. Within the GI microbes, the ruminal microbes are highly diverse, greatly contribute to fermentation, and are the most important in ruminant nutrition. Although traditional cultivation methods provided knowledge of the metabolism of GI microbes, most of the GI microbes could not be cultured on standard culture media. By contrast, amplicon sequencing of 16S rRNA genes can be used to detect unculturable microbes. Using this approach, ruminant nutritionists and microbiologists have conducted a plethora of nutritional studies, many including dietary interventions, to improve fermentation efficiency and nutrient utilization, which has greatly expanded knowledge of the GI microbiota. This review addresses the GI content sampling method, 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing, and bioinformatics analysis and then discusses recent studies on the various factors, such as diet, breed, gender, animal performance, and heat stress, that influence the GI microbiota and thereby ruminant nutrition.
The gastrointestinal (GI) microbes play an important role in the digestion, performance, and health of ruminants. Within the GI microbes, the ruminal microbes are the most important in ruminant nutrition because they can digest and convert various feeds containing cellulose, hemicellulose, starch, protein, and lipid to volatile fatty acids (VFAs) and microbial proteins [1,2]. The small intestine plays an important role in post-ruminal digestion, and the microbial biomass and diversity in the small intestine are low due to the short transit time [3]. There are only a few studies on the microbiota in the small intestine of ruminants [4], but the results have shown that the microbiota composition in the small intestine differs from that in the rumen and large intestine [5]. Like the ruminal microbes, the microbes in the large intestine can also ferment nutrients escaping the small intestine and produce VFAs, major end-products important for maintaining gut health. Many ruminant nutritionists and microbiologists have focused their research efforts on identifying strategies for maintaining optimal GI fermentation and improving nutrient utilization efficiency [1,6].
Initially, GI microbes, particularly ruminal microbes, were assessed using culture-dependent methods, which contributed to understanding the functions and metabolisms of GI microbes. However, it became evident that only a small portion of the GI microbes could be isolated using this approach on the standard culture media used in the laboratory [2]. By contrast, because the 16S rRNA gene can serve as a phylogenetic marker to analyze microbial taxa, 16S rRNA gene sequencing can be used to identify unculturable GI microbes in ruminants [6]. As traditional methods, clone library construction and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) analysis of 16S rRNA gene amplicons, followed by Sanger sequencing, can reveal the composition of the GI microbiota [2,7]. However, because of the low depth of microbial diversity analyzed by these methods, minor taxa cannot be detected using these two methods. Since amplicon sequencing of 16S rRNA genes was developed, many nutritional studies have assessed the microbial diversity of the GI microbiota in great depth [6].
The objective of this review is to discuss the association between the GI microbiota composition and various factors, such as diet, breed, gender, feed efficiency, marbling score, and heat stress, using 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing to improve the understanding of ruminant nutrition. In addition, some research challenges for nutrition studies of ruminants are discussed.
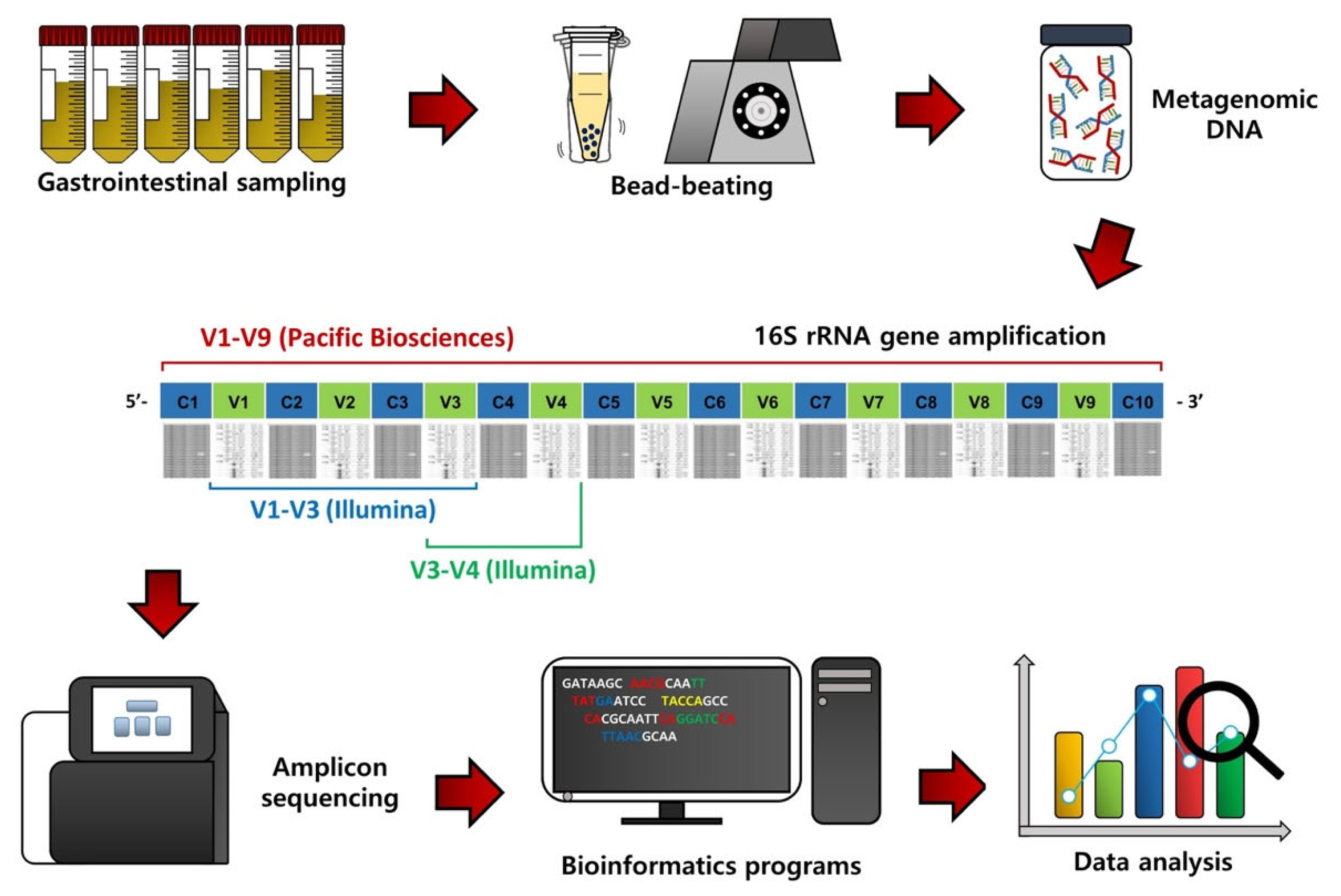
To assess the GI microbiota in ruminants, the first procedure is GI content sampling and metagenomic DNA extraction (Figure 1). Contents of the rumen can be collected via a ruminal cannula or the stomach tube method [8,9], while fecal samples can be collected by rectal grab using a clean glove [10]. Contents of other segments of the GI tract, such as the duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, and colon, can be collected from animals after sacrifice [5]. The bacterial metagenomic DNA can be extracted from the collected samples, usually using the bead-beating method, which can improve DNA yield [11].
From the extracted metagenomic DNA, 16S rRNA gene amplicons can be obtained using universal primers and subsequentially sequenced using a next-generation sequencing system (Figure 1) [6]. Initially, the 454 Genome Sequencer FLX system (Roche, Branford, CT, USA) was used for 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing, but this sequencer is no longer used due to low sequence reads and the high cost. Instead, most microbiota studies use the Illumina MiSeq/HiSeq sequencing platform (San Diego, CA, USA) because of high sequence reads and the low cost compared to the 454 Genome Sequencer FLX system. The Pacific Biosciences sequencing system (Menlo Park, CA, USA) is also used to sequence nearly full-length 16S rRNA gene amplicons because it can provide more accurate phylogenetic resolution, but the cost is still high.
Bioinformatics and data analyses are conducted on the resulting sequence data to assess the GI microbiota in ruminants (Figure 1). The QIIME software package is one of the most popular bioinformatics programs for sequence processing, such as sequence assembling, demultiplexing, denoising with quality filtering, and chimeric sequence detection [12]. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) or amplicon sequencing variants can be classified based on the pre-trained reference databases, such as Greengenes and Silva, using the na├»ve Bayesian taxonomic classifier [13]. Alpha diversity, such as species richness, evenness, phylogenetic diversity, ShannonŌĆÖs index, and SimpsonŌĆÖs index, can be used to evaluate microbiota diversity, while beta diversity based on principal coordinates analysis can be assessed to compare microbiota dissimilarities among treatment groups. In addition, from the 16S rRNA gene sequence data, functional features can be predicted using the Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States (PICRUSt) method [14].
Ruminal microbiota digest and ferment various feeds that are subsequently utilized by the host and thus have a crucial role in ruminant nutrition. Many studies have used traditional 16S rRNA gene-based methods, such as clone library construction [15], quantitative real-time PCR [16], and phylogenetic microarray [6], to evaluate various factors, such as diet, breed, gender, age, and geographic region [2], affecting the ruminal microbiota composition of various ruminant breeds. However, these traditional methods with low sequence reads cannot detect minor ruminal microbiota because of the low depth of percentage coverage of the microbial diversity. Since 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing producing high sequence reads was first used for microbiota studies, various factors affecting the ruminal microbiota composition have been assessed at an improved resolution of the microbial diversity in many nutritional studies.
In ruminant nutrition, collecting samples of the rumen contents from ruminants allows an analysis of the rumen microbiota, digestibility, and fermentation parameters. For rumen content sampling, rumen cannulation has been used as the standard method in many studies [17]. However, its disadvantage is the need for a surgical procedure for cannulation, and the number of rumen-cannulated ruminants that can be used in an experiment is limited. As an alternative method, the stomach tube method is attractive because it enables multiple collections of the rumen contents from many ruminants. Therefore, the stomach tube method is advantageous for increasing the statistical power of the analysis [9].
Although previous studies used the traditional DGGE method to compare the ruminal microbiota between the cannulation and stomach tube method, the coverage depth of the rumen microbial diversity analyzed in these studies was limited [8,18,19]. Next-generation sequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicons was used to assess the feasibility of the stomach tube method as an alternative to standard cannulation procedures. The cannulation and stomach tube methods gave similar results for the ruminal microbiota composition of Holstein and Jersey cattle [20]. Our recent study also indicated that the ruminal microbiota collected from Korean native Hanwoo cattle was not affected by the two different sampling methods [9]. In this context, 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing of the ruminal microbiota helped identify whether the stomach tube was a feasible alternative to the standard cannulation method in the field of ruminant nutrition.
Traditional 16S rRNA gene-based techniques, such as clone library construction and DGGE, have been used to assess how the rumen microbiota composition is affected by dietary changes in ruminants (e.g., [15]). However, these traditional methods detected only dominant microbes and represented only a small portion of the ruminal microbial communities [2]. Therefore, results produced by traditional methods may be biased.
High-resolution characterization of the microbial diversity using 16S rRNA gene amplicon analysis has been conducted to explore the effects of dietary changes on the composition of the ruminal microbiota. Some in vitro rumen fermentation studies evaluated the effects of different levels of additives on the ruminal microbiota composition (e.g., [21,22]) (Table 1). For example, Petri et al [21] evaluated the effects of different combinations of alkaloids, minerals, vitamins, prebiotics, and tannins on rumen microbiota, and these combinations increased the phylum Bacteroidetes and decreased the genus Pyramidobacter. Zhang et al [22] showed that a diet supplemented with grape seed procyanidin increased the abundance of Methanomassiliicoccus and decreased the abundance of Methanobrevibacter in the rumen. Other in vitro studies assessed the effects of different levels of feed ingredients on the ruminal microbiota composition (e.g., [23]). For example, when analyzing the effects of different levels of bakery by-products as a feed ingredient on rumen microbiota, Humer et al [23] found that the inclusion of bakery by-products increased the genera Prevotella, Roseburia, and Megasphaera (Table 1). Cui et al [24] assessed whether the ruminal microbiota composition was affected by different levels of energy and protein in the diet with the same ingredients (Table 1). In this study, the family Prevotellaceae and the genus Butyrivibrio were increased by the low energy level diet. In this context, 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing will remain a useful tool in future nutritional studies for assessing the effect of dietary interventions on the ruminal microbiota.
Host breed is another factor affecting the ruminal microbiota composition of ruminants. Recent studies showed that the ruminal microbiota composition analyzed by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing was different between Holstein and Jersey cattle breeds fed the same diet [17,20] and was associated with different methane emissions from the rumen [17]. Differences have also been observed in the ruminal microbiota composition among Angus, Charolais, and Kinsella composite hybrid breeds (Table 1) [25]. Similarly, our recent study demonstrated that the overall microbiota composition of the rumen differed between Korean native brown Hanwoo and Jeju black cattle fed the same diet at the same farm [26]. Particularly, cellulolytic Ruminococcus was greater in brown Hanwoo cattle than in Jeju black cattle (Table 1). Host genetics can affect heritable rumen microbial features, and different breeds may shape distinct ruminal microbiota due to genetic influence [27]. Therefore, selective breeding may be one strategy to manipulate the ruminal microbiota composition [25].
A recent study of the ruminal microbiota composition in 709 beef cattle identified gender as one of the factors affecting the ruminal microbiota composition (Table 1) [27]. Another study showed that the ruminal microbiota composition differed between different genders of Tibetan goats (Table 1) [28]. Gut microbiota in humans was changed after male castration [29], indicating that different sex hormones could lead to microbial differences between genders [30]. In addition, body mass index (BMI) has been reported to be associated with the gut microbiota in humans [30]. The BMI was significantly associated with the gut microbiota in females, whereas it was not associated with the gut microbiota in males [31]. As shown in humans, BMI may differentially influence the ruminal microbiota between different genders.
Feed accounts for the largest portion of total cost in the beef industry, so improving feed efficiency is important to increase profitability in animal production. Although some studies evaluated the association between feed efficiency and the ruminal microbiota using the traditional DGGE method [32,33], the use of 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing has improved the depth of percentage coverage of microbial diversity for assessing and comparing the ruminal microbiota between high- and low-feed efficiency groups in beef cattle (Table 1) [34]. The results showed that the phylum Firmicutes and the families Lachnospiraceae and Veillonellaceae were more abundant in the high-efficiency group than in the low-efficiency group. At the genus level, Acidaminococcus was more abundant in the high-efficiency group than in the low-efficiency group, whereas Anaerovibrio was more abundant in the low-efficiency group than in the high-efficiency group. In addition, some OTUs assigned to the genus Prevotella were more abundant in the high-efficiency group than in the low-efficiency group. Since this study, many studies on the association between feed efficiency and the ruminal microbiota have been conducted in cattle [25,27,35] and sheep [36,37]. Li et al [25] indicated that the phylum Firmicutes was more abundant in the high-efficiency group than in the low-efficiency group, while the genera Succiniclasticum, Moryella, and Blautia were more abundant in the high-efficiency group than in the low-efficiency group in Charolais cattle (Table 1). Conversely, in Kinsella composite hybrid cattle, the genera Butyrivibrio and Desulfovibrio were more abundant in the high-efficiency group than in the low-efficiency group, whereas Shuttleworthia, Desulfobulbus, and Mitsuokella were more abundant in the low-efficiency group than in the high-efficiency group. Li et al [27] showed that the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes was positively correlated with feed efficiency in beef cattle (Table 1). Paz et al [35] reported that OTUs assigned to the families Prevotellaceae, Spirochaetaceae, Paraprevotellaceae, Veillonellaceae, and Lachnospiraceae were more abundant in the high-efficiency groups than in the low-efficiency group, while Prevotellaceae OTUs were more or less abundant in the high-efficiency group than in the low-efficiency group in steers (Table 1). In heifers, one OTU assigned to the family Victivallaceae was more abundant in the high-efficiency group than in the low-efficiency group, whereas OTUs assigned to the families Prevotellaceae and Fibrobacteraceae were less abundant in the high-efficiency group than in the low-efficiency group. Our recent study assessed the association between feed efficiency and the ruminal microbiota in Hanwoo cattle [38]. Taxa abundant in high-efficiency ruminants may serve as potential biomarkers of high-feed efficiency and provide strategies to improve feed efficiency through the manipulation of the ruminal microbiota.
In the beef industry, increasing the marbling content is important to increase economic benefits. Our recent study assessed the association between the marbling score and the ruminal microbiota in Hanwoo cattle with a genetically high-marbling content [39]. In this study, Hanwoo steers belonging to either a high-marbling score group or a low-marbling score group were selected for comparison. Results showed that the overall ruminal microbiota composition differed between these two extreme groups, and the lipid metabolism pathways were enriched in the high-marbling score group in functional prediction. Taxa identified in high-marbled cattle (Table 1) may be targeted to increase marbling content through the manipulation of the ruminal microbiota.
16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing has provided valuable insight into the impact of heat stress on the ruminal microbiota composition of cattle. Correia Sales et al [40] indicated differences in the ruminal microbiota composition between thermoneutral (24┬░C) and heat-stressed groups (34┬░C) of Nellore cattle; in particular, heat stress decreased the relative abundance of fibrolytic bacteria. In another study, lactate-producing bacteria decreased, and acetate-producing bacteria increased in Holstein dairy cattle exposed to heat stress (34┬░C) compared to the thermoneutral (24┬░C) group [41]. Our recent study assessed the ruminal microbiota composition in Hanwoo cattle exposed to acute heat stress in climate-controlled chambers [42]. The results showed that after the environmental temperature of 15┬░C was raised to 35┬░C at 60% humidity, the fibrolytic bacteria decreased, whereas the lactate-producing bacteria increased (Table 1). In cattle exposed to heat stress, increased lactate production reduces the ruminal pH and, subsequently, the abundance of fibrolytic bacteria, which are sensitive to low pH [43]. These 16S rRNA gene amplicon analyses may contribute to developing new feeding strategies to improve the adaptability of ruminants and maintain a normal ruminal microbiota composition under heat stress [44].
While most of the microbiota studies published to date have focused on the rumen or feces of ruminants, some studies have assessed the microbiota in the small and large intestine of ruminants. Myer et al [45] showed that the jejunal microbiota composition was associated with feed efficiency in beef cattle; specifically, OTUs assigned to Butyrivibrio were more abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group (Table 1). Liu et al [4] collected samples of the duodenal, jejunal, and ileal contents to evaluate the association between feed efficiency and the small intestine microbiota in Angus cattle (Table 1). In this study, the families Lachnospiraceae, Ruminococcaceae, and Christensenellaceae were more abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group in the duodenum [4]. The family Lachnospiraceae was more abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group in the jejunum, while the families Ruminococcaceae and Christensenellaceae were more abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group in the ileum [4]. Other researchers investigated the association between the microbiota of the large intestine (e.g., cecum and colon) with feed efficiency in cattle [46,47]. Freetly et al [5] assessed the ruminal, duodenal, jejunal, ileal, cecal, and colonic microbiota to investigate their associations with animal performance in beef cattle (Table 1). In the duodenum, OTUs assigned to Lachnospiraceae, Ureibacillus, Bacillus, and Prevotella were more abundant in the inefficient group than in the efficient group, while the reverse held true for one OTU assigned to Lachnospiraceae [5]. In the jejunum, OTUs assigned to Butyrivibrio, Dialister, Desulfovibrio, Agrobacterium, and Ochrobactrum were more abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group, whereas OTUs assigned to Mogibacterium, Shuttleworthia, Lactobacillus, Corynebacterium, and Atopobium were less abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group [5]. In the ileum, OTUs assigned to Bulleidia and Saccharopolyspora were more abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group, while one OTU assigned to Bacillus was less abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group [5]. In the cecum, OTUs assigned to the genera Dorea, Coprococcus, Butyrivibrio, Lachnospira, Sutterella, and Anaeroplasma were more abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group, while OTUs assigned to the families Lachnospiraceae, Ruminococcaceae, and Erysipelotrichaceae were more or less abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group [5]. In the colon, OTUs assigned to the order Clostridiales were more abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group, whereas OTUs assigned to the genera Coprococcus and Pirellulaceae were less abundant in the efficient group than in the inefficient group [5]. Wang et al [48] evaluated the ruminal, duodenal, jejunal, ileal, cecal, colonic, and rectal microbiota and identified microbial differences across the GI tract in crossbred cattle. In this study, Actinobacteria and Patescibacteria were dominant in the small intestine, while Ruminococcaceae, Rikenellaceae, and Bacteroidaceae were dominant in the large intestine [48]. Although intestinal microbes are less diverse than ruminal microbes, these studies have identified possible intestinal microbiota that can serve as potential biomarkers to represent high-feed efficiency, and their manipulation may be used as strategies to improve feed efficiency in ruminants.
The fecal microbiota in ruminants can affect animal health and food safety. Various factors affect both the fecal microbiota composition and the ruminal microbiota composition; however, the overall fecal microbiota composition differs from the ruminal microbiota composition [49]. Recent studies of the changes in the fecal microbiota due to various factors, such as diet, gender, feed efficiency, and pathogen prevalence, using 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing, have improved the understanding in the field of ruminant nutrition.
Previous studies indicated that fecal microbiota composition differed among cattle fed different levels of dried distillers grains plus solubles (DDGS) [50] and cattle fed different levels of wet distillers grains diets (DG) [51]. Callaway et al [50] indicated that Acinetobacter was lower in the 0% DDGS group than in the 25% and 50% DDGS groups in cattle (Table 1). Rice et al [51] showed that Clostridium, Ruminococcus, Oscillibacter, Hydrogenoanaerobacterium, Pseudoflavonifractor, Ethanoligenens, Selenomonas, and Desulfonispora were more abundant in the 15% DG group than in the 5% DG group, whereas Parabacteroides and Barnesiella were less abundant in the 15% DG group than in the 5% DG group in cattle (Table 1). Kim et al [52] showed that the fecal microbiota composition of 426 beef cattle was affected by feeding different levels of concentrates. In this study, Oscillibacter, Roseburia, Faecalibacterium, Coprococcus, Blautia, Lactobacillus, Subdoligranulum, Anaerovibrio, Prevotella, and Bacteroides were more abundant in the concentrate-based diet group than in the forage-based diet group, whereas Sporacetigenium, Anaerovorax, Propionibacterium, and Akkermansia were more abundant in the forage-based diet group than in the concentrate-based diet group (Table 1). Our recent study also indicated that diet greatly affected the fecal microbiota in Hanwoo cattle [53]. In this study, Romboutsia, Paeniclostridium, and Turicibacter were differentially more abundant in Hanwoo cattle fed the late fattening total mixed ration (TMR) diet, while Akkermansia, Bacteroides, and Monoglobus were differentially more abundant in the Hanwoo cattle fed TMR plus oat hay. Diet is a major factor affecting the fecal microbiota composition, and an appropriate diet is necessary to maintain gut health in ruminants.
To date, little study has been conducted to compare the fecal microbiota between different genders of ruminants. Our recent study compared the fecal microbiota composition between Hanwoo steers and heifers fed the same diet at the same farm [53]. In this study, Marvinbryantia, Coprococcus, Alistipes, and Ruminococcus were differentially abundant between Hanwoo steers and heifers under the same dietary condition (Table 1) [53]. The results showed that gender influenced the fecal microbiota composition of Hanwoo cattle. Different sex hormones could lead to microbial differences between genders because bile acid profiles affecting gut microbiota can be shifted by sex hormones [27]. Consideration of the diet├Śgender interaction may be useful for maintaining gut health in ruminants.
Similar to findings for the rumen, there is a possible link between feed efficiency and the fecal microbiota in cattle. Some studies indicated that the fecal microbiota composition differed between high- and low-feed efficiency cattle [54,55]. Lourenco et al [54] compared fecal microbiota between efficient and inefficient Angus steers during the feedlot-finishing stage. Their results showed that Ruminococcaceae and Clostridiaceae were decreased in inefficient Angus steers, whereas Peptostreptococcaceae and Turicibacteraceae were increased in efficient Angus steers during the feedlot-finishing stage (Table 1). Welch et al [55] showed that Ruminococcaceae, Rikenellaceae, and Christensenellaceae were more abundant in efficient Angus steers than inefficient Angus steers (Table 1). Our recent study also noticed differences between high- and low-feed efficiency groups of Hanwoo cattle; specifically, Paeniclostridium and Romboutsia were less abundant in efficient Hanwoo steers than in inefficient Hanwoo steers [56]. Differentially abundant taxa between the two extreme groups may be used as potential biomarkers of high-feed efficiency in cattle. Manipulation of the fecal microbiota composition may be a strategy to improve feed efficiency in ruminants.
Pathogenic Escherichia coli (E. coli) O157:H7 is commonly found in cattle feces and can infect humans through contaminated food [57]. Although most cattle shed low numbers of E. coli O157:H7 in their feces, some supershedder cattle produce a great number of E. coli O157:H7 in their feces. Kim et al [10] indicated that the fecal microbiota composition was different between high and low E. coli O157:H7 prevalence and enumeration groups of beef cattle, suggesting that manipulation of the fecal microbiota composition may be a strategy to reduce E. coli O157:H7 shedding. The addition of corn wet distillers grains with solubles to the diet of cattle increased E. coli O157:H7 in the bovine feces [58], whereas the addition of soybean meal decreased E. coli O157:H7 in the bovine feces [59]. These studies indicate that dietary interventions can be used as strategies to reduce E. coli O157:H7 prevalence and enumeration in cattle feces.
In recent nutritional studies, 16S rRNA gene amplicon analysis has been increasingly used to expand the knowledge of the GI microbiota, particularly the ruminal microbiota, and the influencing factors, such as diet, additives, breed, gender, feed efficiency, methane production, and heat stress, in ruminants. The GI microbiota that are differentially abundant in high-efficiency ruminants may be used as potential biomarkers for improving animal productivity. Some heat-stress-resistant microbes may be beneficial as probiotics in ruminant nutrition to enhance the performance or health of cattle under heat stress [44]. Microbial metabolism can be reconstructed from metagenomic data, and new culture media may be devised to isolate and cultivate novel GI microbes [60]. The use of these novel GI microbes may contribute to enhancing the performance of ruminants. In addition, the GI microbiota in ruminants needs to be considered as a heritable phenotype in future studies [61]. The GI microbiota, particularly the ruminal microbiota, may be incorporated into breeding programs to maximize the number of high-performance ruminants. In order to account for the influence of host species and the geographic region, continuous efforts to assess the GI microbiota in domestic ruminants are needed to improve animal performance or health in future studies.
Notes
Figure┬Ā1
Flowchart outlining 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing, bioinformatic procedures, and data analysis of gastrointestinal content samples of ruminants.
Table┬Ā1
Summary of factors affecting gastrointestinal microbiota in ruminants
| Factor | Region | Animal | Findings regarding microbial differences | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diet | Rumen | In vitro inoculation of rumen fluid collected from Holstein cows | ŌåæBacteroidetes and ŌåōPyramidobacter by the addition of different combinations of alkaloids, minerals, vitamins, prebiotics, and tannins | [21] |
| Rumen | In vitro inoculation of rumen fluid collected from Holstein cows | ŌåæMethanomassiliicoccus and ŌåōMethanobrevibacter by addition of grape seed procyanidin | [22] | |
| Rumen | In vitro inoculation of rumen fluid collected from Holstein cows | ŌåæPrevotella, Roseburia and Megasphaera by the inclusion of bakery by-products as a feed ingredient | [23] | |
| Rumen | Lambs | ŌåæPrevotellaceae and Butyrivibrio by diet with a low energy level | [24] | |
| Feces | Beef cattle | ŌåōAcinetobacter in the 0% dried distillers grains plus solubles (DDGS) group than in the 25% and 50% DDGS groups | [50] | |
| Feces | Beef cattle |
ŌåæClostridium, Ruminococcus, Oscillibacter, Hydrogenoanaerobacterium, Pseudoflavonifractor, Ethanoligenens, Selenomonas and Desulfonispora in the 15% wet distillers grains (DG) group than in the 5% DG group ŌåōParabacteroides and Barnesiella in the 15% DG group than in the 5% DG group |
[51] | |
| Feces | Beef cattle |
ŌåæOscillibacter, Roseburia, Faecalibacterium, Coprococcus, Blautia, Lactobacillus, Subdoligranulum, Anaerovibrio, Prevotella and Bacteroides in the concentrate-based diet group ŌåæSporacetigenium, Anaerovorax, Propionibacterium and Akkermansia were more abundant in the forage-based diet group |
[52] | |
| Breed | Rumen | Brown Hanwoo cattle and Jeju black cattle | ŌåæRuminococcus in brown Hanwoo cattle than in Jeju black cattle | [26] |
| Rumen | Angus, Charolais, and Kinsella composite hybrid cattle |
ŌåæBacteroidetes and Synergistetes in Charolais cattle than in the other breeds ŌåæSpirochaetes, Fibrobacteres, Verrucomicrobia, Lentisphaerae, Tenericutes and Chloroflexi in Kinsella composite hybrid than in the other breeds |
[25] | |
| Gender | Rumen | Angus, Charolais, and Kinsella composite hybrid cattle |
ŌåæArchaea and ŌåōBacteria in bulls than in steers and heifers ŌåōArchaea and ŌåæBacteria in steers than in bulls and heifers |
[27] |
| Rumen | Tibetan goats | ŌåæFibrobacter, Ruminococcus_1 and Pyramidobacter in female Tibetan goats than in male Tibetan goats | [28] | |
| Feces | Hanwoo cattle |
ŌåæMarvinbryantia and Coprococcus in heifers than in steers ŌåæAlistipes and Ruminococcus in steers than in heifers |
[53] | |
| Marbling | Rumen | Hanwoo cattle |
ŌåæOscillospira and Paludibacter in the high-marbling score group ŌåæOlsenella in the low-marbling score group |
[39] |
| Heat stress | Rumen | Hanwoo cattle |
ŌåæPrevotellaceae, Lactobacillaceae and Succinivibrionaceae in response to short-term heat stress ŌåōRuminococcaceae, Desulfovibrionaceae, Anaerolineaceae, and Pirellulaceae in response to short-term heat stress |
[42] |
| Feed efficiency | Rumen | Steers |
ŌåæFirmicutes, Lachnospiraceae, Veillonellaceae and Acidaminococcus in the high-efficient group ŌåæAnaerovibrio in the low efficient group ŌåæOperational taxonomic units (OTUs) assigned to Prevotella in the high efficient group |
[34] |
| Rumen | Angus, Charolais, and Kinsella composite hybrid cattle |
ŌåæFirmicutes, Succiniclasticum, Moryella and Blautia in the high efficient group in Charolais cattle ŌåæButyrivibrio and Desulfovibrio in the high efficient group in Kinsella composite hybrid cattle ŌåæShuttleworthia, Desulfobulbus and Mitsuokella in the low efficient group in Kinsella composite hybrid cattle |
[25] | |
| Rumen | Angus, Charolais, and Kinsella composite hybrid cattle | ŌåæRatio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes in the high efficient group | [27] | |
| Rumen | Beef cattle |
ŌåæOTUs assigned to Prevotellaceae, Spirochaetaceae, Paraprevotellaceae, Veillonellaceae and Lachnospiraceae in the high efficient group in steers ŌåæOne OTU assigned to Victivallaceae in the high efficient group in heifers ŌåōPrevotellaceae and Fibrobacteraceae in the high efficient group in heifers |
[35] | |
| Small intestine | Steers | ŌåæOTUs assigned to Butyrivibrio in the high efficient group in the jejunum | [45] | |
| Small intestine | Angus heifers |
ŌåæLachnospiraceae, Ruminococcaceae and Christensenellaceae in the high efficient group in the duodenum ŌåæLachnospiraceae in the high efficient group in the jejunum ŌåæRuminococcaceae and Christensenellaceae in the high efficient group in the ileum |
[4] | |
| Small intestine | Angus and crossbred steers |
ŌåæOTUs assigned to Lachnospiraceae, Ureibacillus, Bacillus and Prevotella in the low efficient group in the duodenum ŌåæOne OTU assigned to Lachnospiraceae in the high efficient group in the duodenum ŌåæOTUs assigned to Butyrivibrio, Dialister, Desulfovibrio, Agrobacterium and Ochrobactrum in the high efficient group in the jejunum ŌåōOTUs assigned to Mogibacterium, Shuttleworthia, Lactobacillus, Corynebacterium and Atopobium in the high efficient group in the jejunum ŌåæOTUs assigned to Bulleidia and Saccharopolyspora in the high efficient group than in the inefficient group in the ileum ŌåōOne OTU assigned to Bacillus in the high efficient group in the ileum |
[5] | |
| Large intestine | Angus and crossbred steers |
ŌåæOTUs assigned to Dorea, Coprococcus, Butyrivibrio, Lachnospira, Sutterella and Anaeroplasma in the high efficient group in the cecum ŌåæOTUs assigned to Clostridiales in the high-efficient group in the colon ŌåōOTUs assigned to Coprococcus and Pirellulaceae in the high efficient group in the colon |
[5] | |
| Feces | Angus steers |
ŌåōRuminococcaceae and Clostridiaceae in inefficient steers ŌåæPeptostreptococcaceae and Turicibacteraceae in efficient steers |
[54] | |
| Feces | Angus steers | ŌåæRuminococcaceae, Rikenellaceae and Christensenellaceae in efficient steers | [55] |
REFERENCES
1. Firkins JL, Yu Z. Ruminant nutrition symposium: How to use data on the rumen microbiome to improve our understanding of ruminant nutrition. J Anim Sci 2015; 93:1450ŌĆō70.
https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2014-8754


2. Kim M, Morrison M, Yu Z. Status of the phylogenetic diversity census of ruminal microbiomes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2011; 76:49ŌĆō63.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.01029.x


3. Kastl AJ, Terry NA, Wu GD, Albenberg LG. The structure and function of the human small intestinal microbiota: current understanding and future directions. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020; 9:33ŌĆō45.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.07.006



4. Liu Y, Liu C, Wu H, Meng Q, Zhou Z. Small intestine microbiome and metabolome of high and low residual feed intake angus heifers. Front Microbiol 2022; 13:862151
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.862151



5. Freetly HC, Dickey A, Lindholm-Perry AK, et al. Digestive tract microbiota of beef cattle that differed in feed efficiency. J Anim Sci. 2020. 98:skaa008
https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skaa008



6. Kim M, Park T, Yu Z. Metagenomic investigation of gastrointestinal microbiome in cattle. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2017; 30:1515ŌĆō28.
https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.17.0544



7. Kim M, Wells JE. A meta-analysis of bacterial diversity in the feces of cattle. Curr Microbiol 2016; 72:145ŌĆō51.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0931-6


8. Laflin SL, Gnad DP. Rumen cannulation: Procedure and use of a cannulated bovine. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract 2008; 24:335ŌĆō40.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvfa.2008.02.007


9. Song J, Choi H, Jeong JY, et al. Effects of sampling techniques and sites on rumen microbiome and fermentation parameters in Hanwoo steers. J Microbiol Biotechnol 2018; 28:1700ŌĆō5.
https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1803.03002


10. Kim M, Kuehn LA, Bono JL, et al. The impact of the bovine faecal microbiome on Escherichia coli O157:H7 prevalence and enumeration in naturally infected cattle. J Appl Microbiol 2017; 123:1027ŌĆō42.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13545


11. Yu ZT, Morrison M. Improved extraction of PCR-quality community DNA from digesta and fecal samples. Biotechniques 2004; 36:808ŌĆō12.
https://doi.org/10.2144/04365st04


12. Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 2019; 37:852ŌĆō7.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9



13. Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 2007; 73:5261ŌĆō7.
https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00062-07



14. Douglas GM, Maffei VJ, Zaneveld JR, et al. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat Biotechnol 2020; 38:685ŌĆō8.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-0548-6



15. Kim M, Morrison M, Yu Z. Phylogenetic diversity of bacterial communities in bovine rumen as affected by diets and microenvironments. Folia Microbiol 2011; 56:453
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-011-0066-5

16. Kim M, Yu Z. Quantitative comparisons of select cultured and uncultured microbial populations in the rumen of cattle fed different diets. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 2012; 3:28
https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-1891-3-28



17. Islam M, Kim SH, Ramos SC, et al. Holstein and Jersey steers differ in rumen microbiota and enteric methane emissions even fed the same total mixed ration. Front Microbiol 2021; 12:601061
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.601061



18. Ramos-Morales E, Arco-Perez A, Martin-Garcia AI, Y├Ī├▒ez-Ruiz DR, Frutos P, Herv├Īs G. Use of stomach tubing as an alternative to rumen cannulation to study ruminal fermentation and microbiota in sheep and goats. Anim Feed Sci Technol 2014; 198:57ŌĆō66.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2014.09.016

19. Terre M, Castells L, Fabregas F, Bach A. Short communication: Comparison of pH, volatile fatty acids, and microbiome of rumen samples from preweaned calves obtained via cannula or stomach tube. J Dairy Sci 2013; 96:5290ŌĆō4.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2012-5921


20. Paz HA, Anderson CL, Muller MJ, Kononoff PJ, Fernando SC. Rumen bacterial community composition in holstein and jersey cows is different under same dietary condition and is not affected by sampling method. Front Microbiol 2016; 7:1206
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01206



21. Petri RM, Mickdam E, Klevenhusen F, Beyer B, Zebeli Q. Effects of the supplementation of plant-based formulations on microbial fermentation and predicted metabolic function in vitro. Anaerobe 2019; 57:19ŌĆō27.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2019.03.001


22. Zhang H, Tong J, Wang Z, Xiong B, Jiang L. Illumina MiSeq sequencing reveals the effects of grape seed procyanidin on rumen archaeal communities in vitro. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2020; 33:61ŌĆō8.
https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.19.0226


23. Humer E, Aditya S, Kaltenegger A, Klevenhusen F, Petri RM, Zebeli Q. Graded substitution of grains with bakery by-products modulates ruminal fermentation, nutrient degradation, and microbial community composition in vitro. J Dairy Sci 2018; 101:3085ŌĆō98.
https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-14051


24. Cui K, Qi M, Wang S, Diao Q, Zhang N. Dietary energy and protein levels influenced the growth performance, ruminal morphology and fermentation and microbial diversity of lambs. Sci Rep 2019; 9:16612
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53279-y



25. Li F, Hitch TCA, Chen Y, Creevey CJ, Guan LL. Comparative metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analyses reveal the breed effect on the rumen microbiome and its associations with feed efficiency in beef cattle. Microbiome 2019; 7:6
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-019-0618-5



26. Kim M, Park JK, Lee HG, Song J. Differences in rumen microbiomes of Korean Native Hanwoo and Jeju Black cattle under the same dietary condition. In : 47th Annual Meeting & International Symposium of Korean Society for Microbiology and Biotechnology; 2020 September 23ŌĆō25; e-Conference
27. Li F, Li C, Chen Y, et al. Host genetics influence the rumen microbiota and heritable rumen microbial features associate with feed efficiency in cattle. Microbiome 2019; 7:92
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-019-0699-1



28. Guo X, Sha Y, Lv W, et al. Sex differences in rumen fermentation and microbiota of Tibetan goat. Microb Cell Fact 2022; 21:55
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-022-01783-8



29. Yurkovetskiy L, Burrows M, Khan AA, et al. Gender bias in autoimmunity is influenced by microbiota. Immunity 2013; 39:400ŌĆō12.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.08.013


30. Kim YS, Unno T, Kim BY, Park MS. Sex differences in gut microbiota. World J Mens Health 2020; 38:48ŌĆō60.
https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.190009


31. Dominianni C, Sinha R, Goedert JJ, et al. Sex, body mass index, and dietary fiber intake influence the human gut microbiome. PLoS One 2015; 10:e0124599
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124599



32. Guan LL, Nkrumah JD, Basarab JA, Moore SS. Linkage of microbial ecology to phenotype: correlation of rumen microbial ecology to cattleŌĆÖs feed efficiency. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2008; 288:85ŌĆō91.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01343.x


33. Hernandez-Sanabria E, Guan LL, Goonewardene LA, et al. Correlation of particular bacterial PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis patterns with bovine ruminal fermentation parameters and feed efficiency traits. Appl Environ Microbiol 2010; 76:6338ŌĆō50.
https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01052-10



34. Myer PR, Smith TP, Wells JE, Kuehn LA, Freetly HC. Rumen microbiome from steers differing in feed efficiency. PLoS One 2015; 10:e0129174
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129174



35. Paz HA, Hales KE, Wells JE, et al. Rumen bacterial community structure impacts feed efficiency in beef cattle. J Anim Sci 2018; 96:1045ŌĆō58.
https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skx081



36. McLoughlin S, Spillane C, Claffey N, et al. Rumen microbiome composition is altered in sheep divergent in feed efficiency. Front Microbiol 2020; 11:1981
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01981



37. Zhang YK, Zhang XX, Li FD, et al. Characterization of the rumen microbiota and its relationship with residual feed intake in sheep. Animal 2021; 15:100161
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.animal.2020.100161


38. Park CJ, Lee HS, Yoon S, et al. Evaluation of rumen microbiome of early fattening Hanwoo steers with different feed efficiencies. In : The 19th AAAP Animal Science Congress; 2022 August 23ŌĆō26; Jeju, Korea.
39. Kim M, Park T, Jeong JY, Baek Y, Lee HJ. Association between rumen microbiota and marbling score in Korean native beef cattle. Animals-Basel 2020; 10:712
https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10040712



40. Correia Sales GF, Carvalho BF, Schwan RF, et al. Heat stress influence the microbiota and organic acids concentration in beef cattle rumen. J Therm Biol 2021; 97:102897
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtherbio.2021.102897


41. Zhao S, Min L, Zheng N, Wang J. Effect of heat stress on bacterial composition and metabolism in the rumen of lactating dairy cows. Animals (Basel) 2019; 9:925
https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110925



42. Baek YC, Choi H, Jeong JY, et al. The impact of short-term acute heat stress on the rumen microbiome of Hanwoo steers. J Anim Sci Technol 2020; 62:208ŌĆō17.
https://doi.org/10.5187/jast.2020.62.2.208



43. Kim SH, Ramos SC, Valencia RA, Cho YI, Lee SS. Heat Stress: effects on rumen microbes and host physiology, and strategies to alleviate the negative impacts on lactating dairy cows. Front Microbiol 2022; 13:804562
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.804562



44. Park T, Ma L, Gao ST, Bu DP, Yu ZT. Heat stress impacts the multi-domain ruminal microbiota and some of the functional features independent of its effect on feed intake in lactating dairy cows. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 2022; 13:71
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-022-00717-z



45. Myer PR, Wells JE, Smith TP, Kuehn LA, Freetly HC. Microbial community profiles of the jejunum from steers differing in feed efficiency. J Anim Sci 2016; 94:327ŌĆō38.
https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2015-9839


46. Myer PR, Wells JE, Smith TP, Kuehn LA, Freetly HC. Cecum microbial communities from steers differing in feed efficiency. J Anim Sci 2015; 93:5327ŌĆō40.
https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2015-9415


47. Myer PR, Wells JE, Smith TP, Kuehn LA, Freetly HC. Microbial community profiles of the colon from steers differing in feed efficiency. Springerplus 2015; 4:454
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-015-1201-6



48. Wang K, Zhang H, Hu L, et al. Characterization of the microbial communities along the gastrointestinal tract in crossbred cattle. Animals (Basel) 2022; 12:825
https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12070825



49. Durso L, Wells JE, Kim MS. Diversity of microbiomes in beef cattle. Nelson KE, editorEncyclopedia of metagenomics. New York, NY, USA: Springer; 2014. 1ŌĆō11.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6418-1_730-4

50. Callaway TR, Dowd SE, Edrington TS, et al. Evaluation of bacterial diversity in the rumen and feces of cattle fed different levels of dried distillers grains plus solubles using bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing. J Anim Sci 2010; 88:3977ŌĆō83.
https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2010-2900


51. Rice WC, Galyean ML, Cox SB, Dowd SE, Cole NA. Influence of wet distillers grains diets on beef cattle fecal bacterial community structure. BMC Microbiol 2012; 12:25
https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-25



52. Kim M, Kim J, Kuehn LA, et al. Investigation of bacterial diversity in the feces of cattle fed different diets. J Anim Sci 2014; 92:683ŌĆō94.
https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2013-6841


53. Sim S, Lee H, Yoon S, Seon H, Park C, Kim M. The impact of different diets and genders on fecal microbiota in Hanwoo cattle. J Anim Sci Technol 2022; 64:897ŌĆō910.
https://doi.org/10.5187/jast.2022.e71



54. Lourenco JM, Welch CB, Krause TR, et al. Fecal microbiome differences in angus steers with differing feed efficiencies during the feedlot-finishing phase. Microorganisms 2022; 10:1128
https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061128



55. Welch CB, Lourenco JM, Krause TR, et al. Evaluation of the fecal bacterial communities of angus steers with divergent feed efficiencies across the lifespan from weaning to slaughter. Front Vet Sci 2021; 8:597405
https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2021.597405



56. Seon HS, Lee HS, Yoon S, et al. Assessment of fecal microbiome of late fattening Hanwoo steers with different feed efficiencies. In : The 19th AAAP Animal Science Congress; 2022 August 23ŌĆō26; Jeju, Korea.
57. Wells JE, Kim M, Bono JL, Kuehn LA, Benson AK. Meat science and muscle biology symposium: Escherichia coli O157:H7, diet, and fecal microbiome in beef cattle. J Anim Sci 2014; 92:1345ŌĆō55.
https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2013-7282


58. Berry ED, Wells JE, Varel VH, Hales KE, Kalchayanand N. Persistence of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and total Escherichia coli in feces and feedlot surface manure from cattle fed diets with and without corn or sorghum wet distillers grains with solubles. J Food Protect 2017; 80:1317ŌĆō27.
https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028x.Jfp-17-018

59. Wells JE, Berry ED, Kim M, Shackelford SD, Hales KE. Evaluation of commercial beta-agonists, dietary protein, and shade on fecal shedding of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from feedlot cattle. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2017; 14:649ŌĆō55.
https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2017.2313


60. Pope PB, Smith W, Denman SE, et al. Isolation of Succinivibrionaceae implicated in low methane emissions from Tammar wallabies. Science 2011; 333:646ŌĆō8.
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1205760


61. Myer PR. Bovine genome-microbiome interactions: metagenomic frontier for the selection of efficient productivity in cattle systems. mSystems 2019; 4:e00103ŌĆō19.
https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00103-19









 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





