 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 35(11); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
Conclusion
Notes
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Figure 1
Figure 3
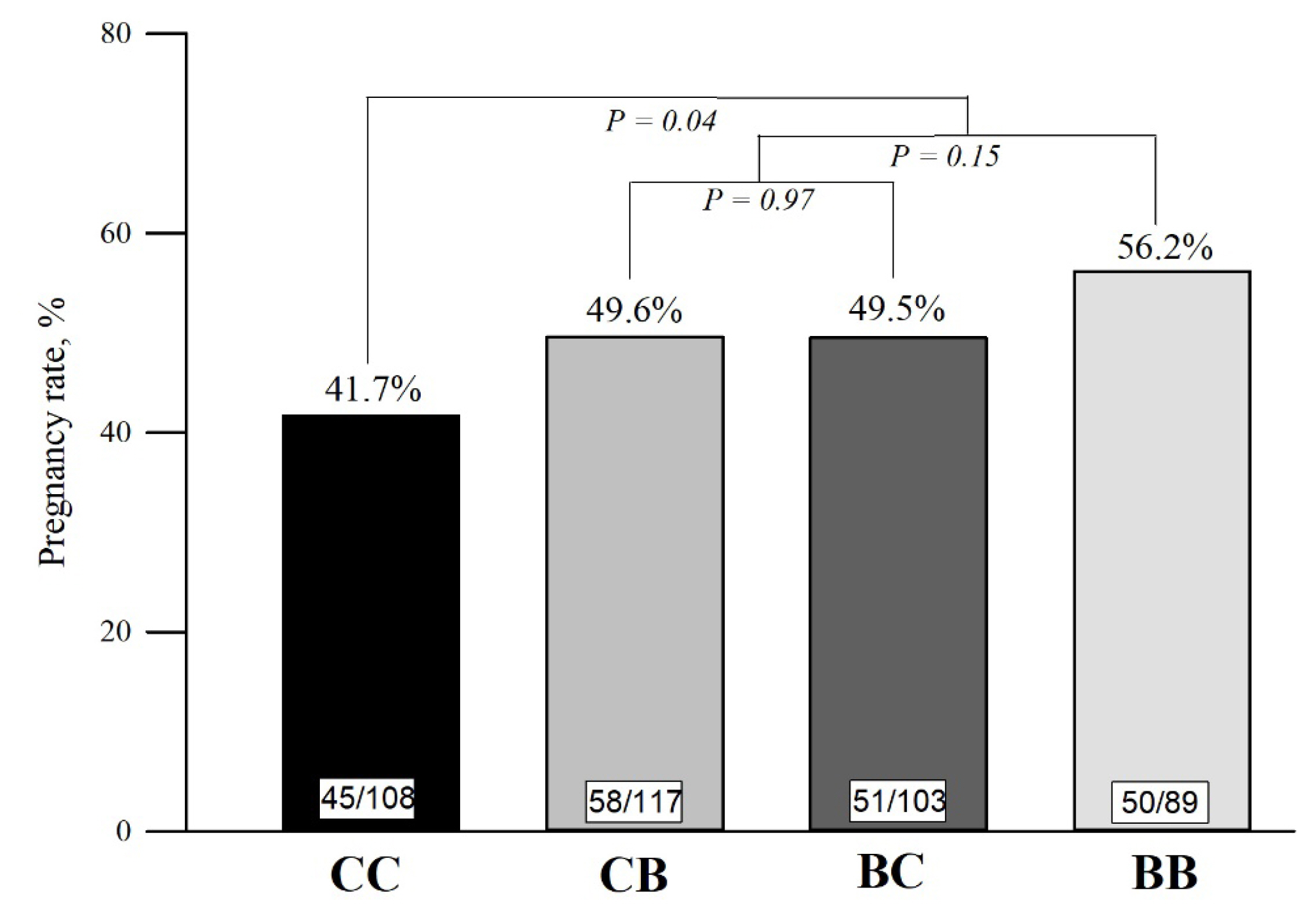
Figure 4
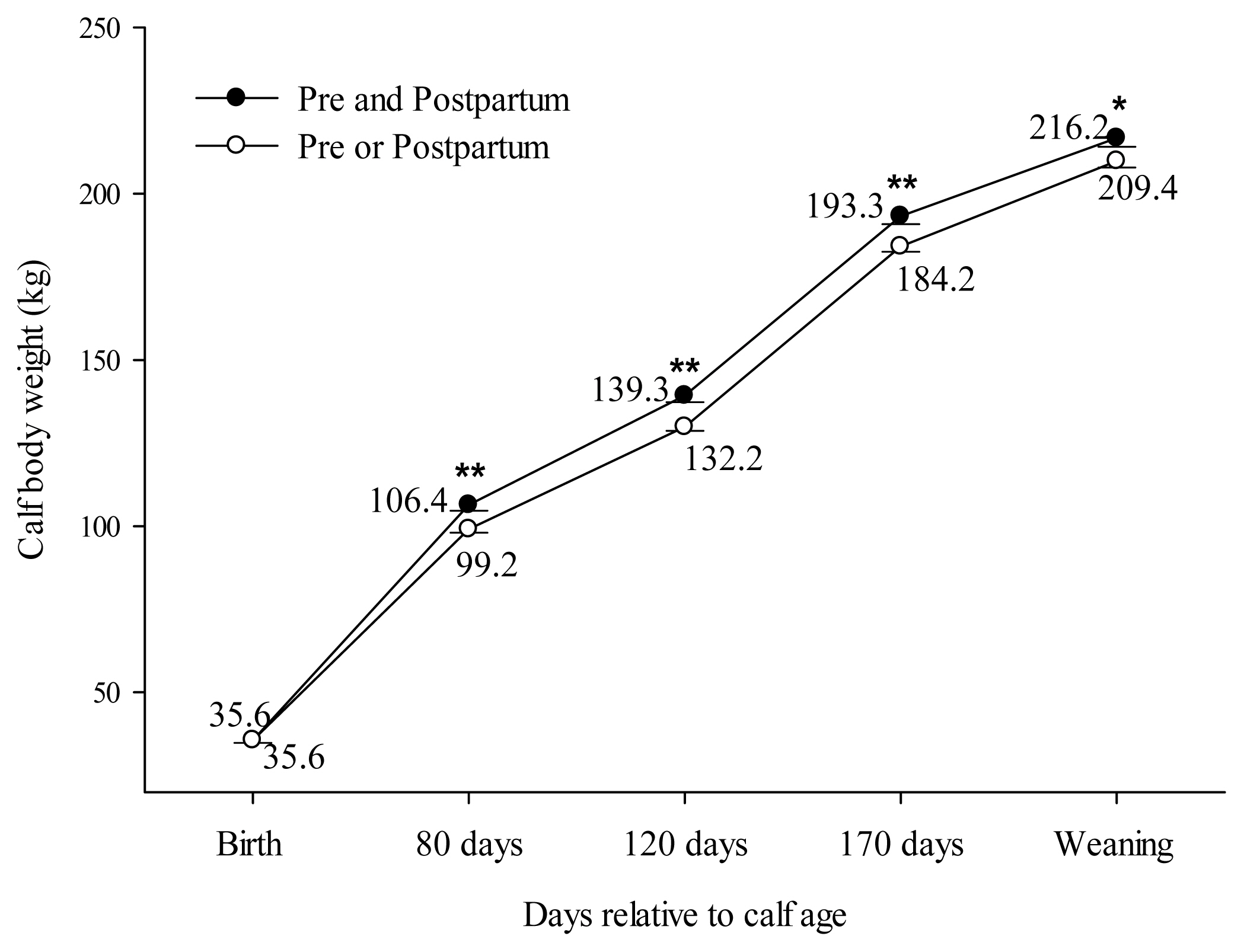
Figure 5
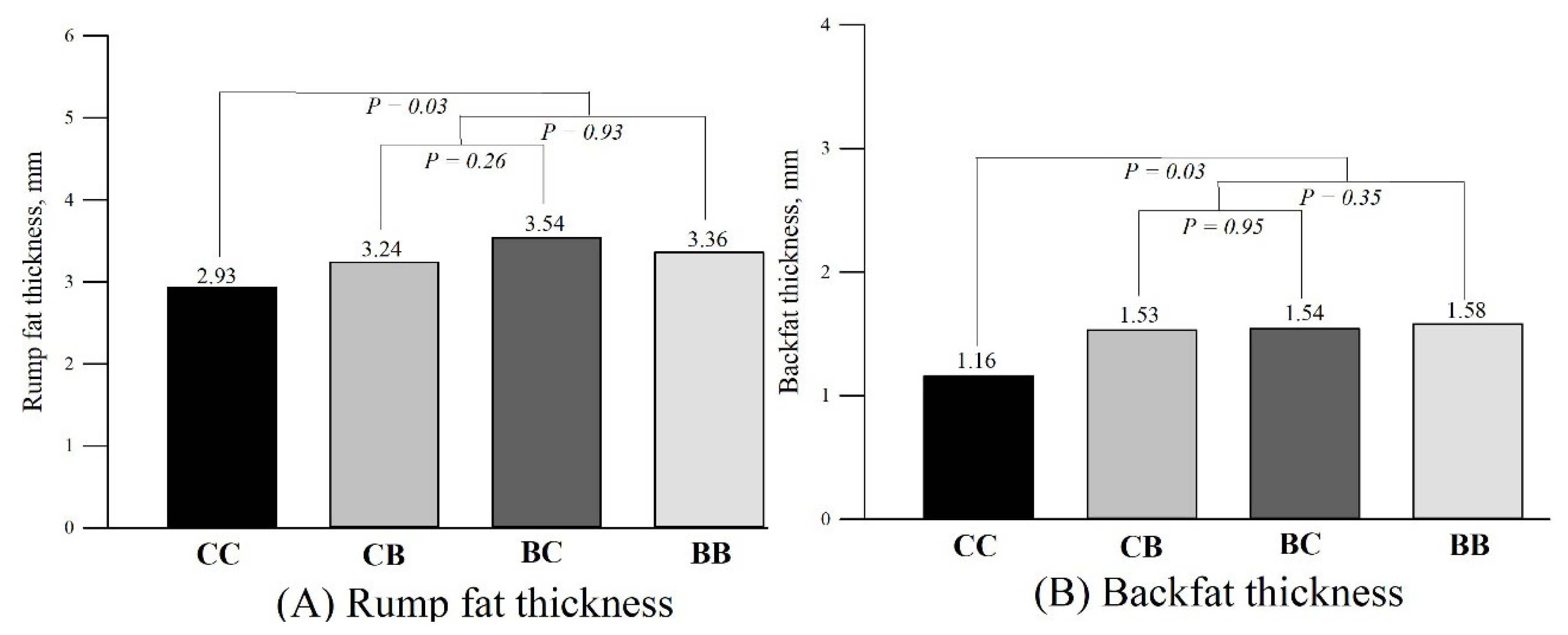
Figure 6
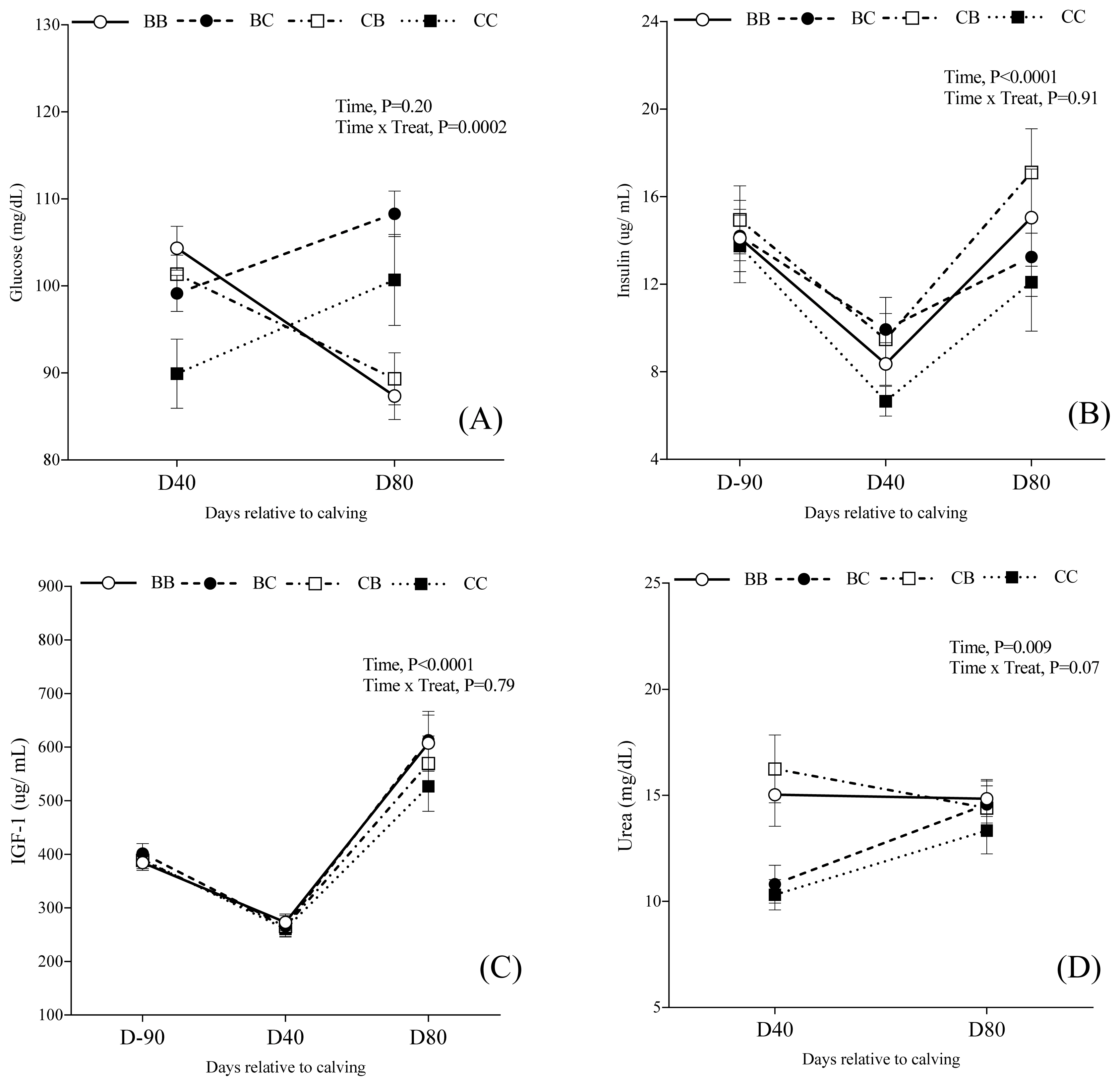
Table 1
| Item | Supplement1) | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| C | B | |
| DM (%) | 92.5 | 90.0 |
| TDN (%) | 35.0 | 40.0 |
| CP (%) | 40.0 | 35.0 |
| NPN (%) | 5.1 | 3.5 |
| Ca (g/kg) | 80 | 65 |
| P (g/kg) | 30 | 20 |
| Na (g/kg) | 50 | 40 |
| S (g/kg) | 5 | 4 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 1,400 | 920 |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 400 | 230 |
| I (mg/kg) | 20 | 13.5 |
| Co (mg/kg) | 22 | 17.5 |
| Se (mg/kg) | 7.2 | 9 |
| Mn (mg/kg) | 430 | 380 |
| Sodium monensin (mg/kg) | - | 300 |
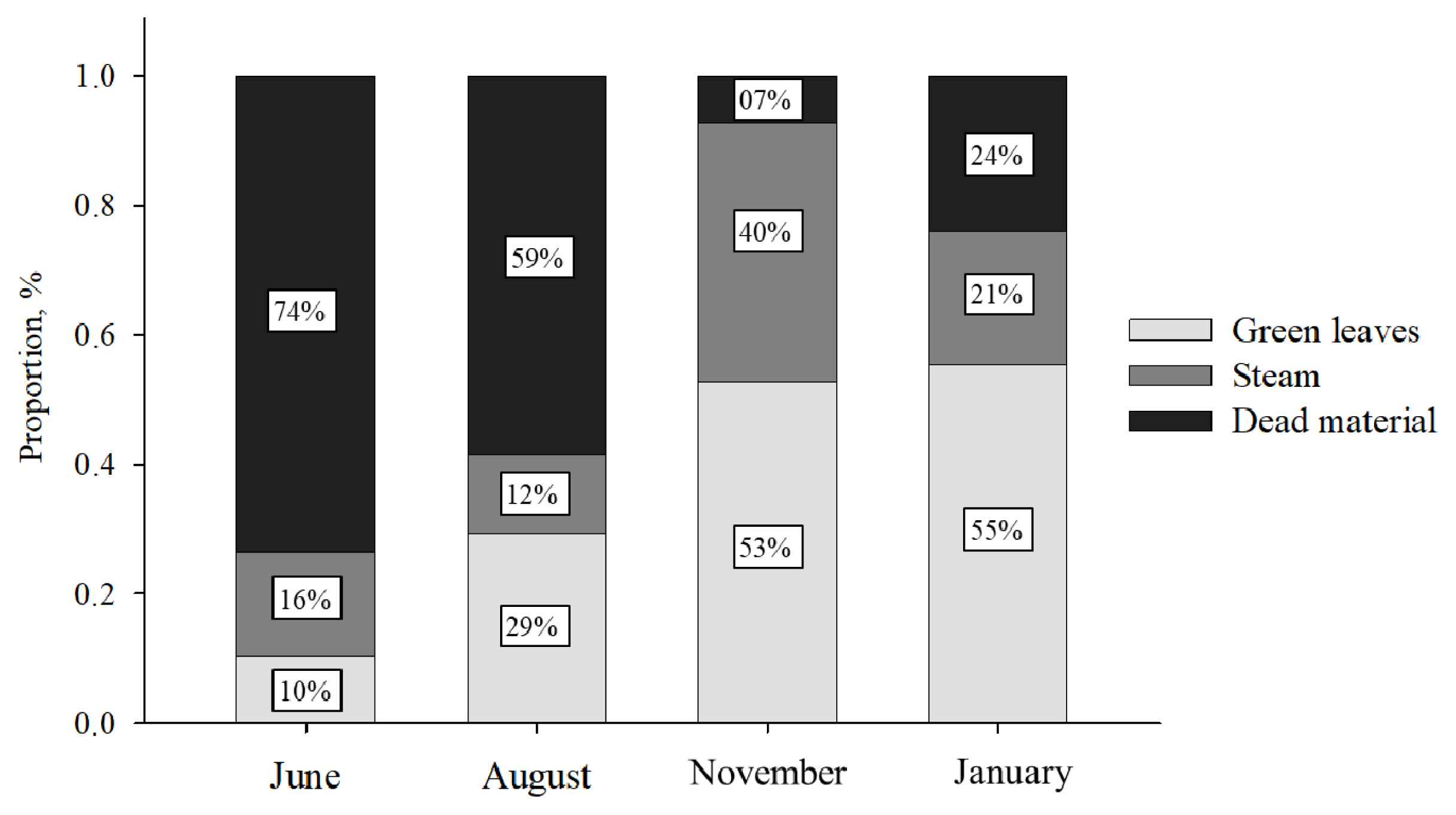
Table 2
| Item2) | Month1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||
| June | August | November | January | |
| HM (kg DM/ha) | 2.237 | 1.493 | 1.702 | 1.366 |
| Green leaves (%) | 10 | 29 | 53 | 55 |
| CP (%) | 14.8 | 14.3 | 8.8 | 9.6 |
| Ca (%) | 3.1 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 2.3 |
| P (%) | 2.1 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 1.6 |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 6.21 | 6.49 | 4.34 | 3.48 |
| Mn (mg/kg) | 82.66 | 77.63 | 52.26 | 32.53 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 17.84 | 16.53 | 15.23 | 7.04 |
Table 3
| Variable (%, n/n)1) | Treatments2) | p-value3) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
||||||
| CC | CB | BC | BB | C1 | C2 | C3 | |
| Postpartum cyclicity rate at D40 | 15.7 (17/108) | 18.8 (22/117) | 18.4 (19/103) | 22.5 (20/89) | 0.39 | 0.51 | 0.97 |
| Pregnancy rate at first FTAI | 41.7 (45/108) | 49.6 (58/117) | 49.5 (51/103) | 56.2 (50/89) | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.97 |
| Pregnancy loss of first FTAI | 8.9 (4/45) | 8.6 (5/58) | 5.9 (3/51) | 10.0 (5/50) | 0.98 | 0.30 | 0.60 |
| Pregnancy rate at second FTAI | 46.0 (29/63) | 47.5 (28/59) | 48.1 (25/52) | 48.7 (19/39) | 0.70 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| Pregnancy loss of second FTAI | 3.4 (1/29) | 7.1 (2/28) | 4.0 (1/25) | 5.3 (1/19) | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.63 |
| Pregnancy rate at NM | 35.9 (14/39) | 49.5 (19/38) | 41.9 (13/31) | 53.8 (14/26) | 0.28 | 0.72 | 0.51 |
| Overall pregnancy rate at end of BS | 76.9 (83/108) | 83.8 (98/117) | 82.5 (85/103) | 86.5(77/89) | 0.05 | 0.54 | 0.81 |
1) Cyclicity rate, presence of corpus luteum at the onset of the FTAI protocol (D40); FTAI, fixed-time artificial insemination; NM, natural mating; Overall pregnancy rate = 1st FTAI+2nd FTAI+NM; BS, breeding season.
2) CC: heifers received control supplement (C) in loose meal form (0.06% of body weight [BW] offered daily before and after parturition; n = 108); CB: received C before parturition and block supplementation (B) after parturition (0.07% of BW offered weekly after parturition; n = 117); BC: received B before and C after parturition (n = 103); BB: received B before and after parturition (n = 89).
3) Orthogonal contrasts: C1 (Block supplementation effect): Control (CC) vs block supplementation (BB+BC+CB); C2 (Block supplementation effect in both pre and postpartum periods): Pre and postpartum (BB) vs Pre or postpartum (BC+CB); and C3 (Pre or postpartum effect): prepartum (BC) vs postpartum (CB).
Table 4
| Itens1) | Treatment2) | SEM | p-value3) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| CC | CB | BC | BB | T | T×treat | C1 | C2 | C3 | ||
| BW (kg) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.83 | 0.98 | 0.76 | |||||
| 90 days prepartuma | 435.8 | 441.0 | 473.1 | 440.1 | 1.78 | - | - | 0.25 | 0.68 | 0.18 |
| 40 days postpartumb | 400.8 | 412.2 | 400.9 | 413.3 | 1.70 | - | - | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.001 |
| 120 days postpartumd | 432.9 | 431.3 | 432.9 | 429.0 | 1.79 | - | - | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.11 |
| BCS, 1–5 | <0.0001 | 0.002 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.60 | |||||
| 90 days prepartum4) | 2.91 | 2.95 | 2.93 | 2.94 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.15 | 0.45 | 0.64 |
| Parturition | 3.01 | 3.00 | 3.11 | 3.10 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.04 | 0.25 | <0.001 |
| 40 days postpartum5) | 2.83 | 2.90 | 2.90 | 2.95 | 0.02 | - | - | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.99 |
| 80 days postpartum6) | 2.84 | 2.91 | 2.85 | 2.98 | 0.02 | - | - | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.12 |
| 120 days postpartum7) | 3.00 | 3.07 | 2.99 | 3.04 | 0.02 | - | - | 0.56 | 0.65 | 0.20 |
| 170 days postpartum8) | 2.78 | 2.87 | 2.74 | 2.84 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.001 |
2) CC: heifers received control supplement (C) in loose meal form (0.06% of body weight [BW] offered daily before and after parturition; n = 108); CB: received C before parturition and block supplementation (B) after parturition (0.07% of BW offered weekly after parturition; n = 117); BC: received B before and C after parturition (n = 103); BB: received B before and after parturition (n = 89).
3) Orthogonal contrasts: C1 (Block supplementation effect): control (CC) vs block supplementation (BB+BC+CB); C2 (Block supplementation effect in both pre and postpartum periods): Pre and postpartum (BB) vs Pre or postpartum (BC+CB); and C3 (Pre or postpartum effect): prepartum (BC) vs postpartum (CB); T = time, days relative to calving; T×treat = interaction between sampling time and treatment.
Table 5
| Items | Treatment1) | SEM | p-value2) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| CC | CB | BC | BB | T | Txtreat | C1 | C2 | C3 | ||
| CW (kg) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.13 | |||||
| Birth | 34.6 | 35.4 | 35.7 | 35.6 | 0.65 | - | - | 0.01 | 0.89 | 0.16 |
| 80 days3) | 97.8 | 98.7 | 99.7 | 106.4 | 0.78 | - | - | 0.03 | <0.001 | 0.75 |
| 120 days4) | 123.9 | 132.9 | 126.5 | 139.3 | 0.91 | - | - | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| 170 days5) | 182.9 | 183.7 | 184.8 | 193.3 | 1.18 | - | - | 0.55 | 0.002 | 0.93 |
| Weaning6) | 207.7 | 208.8 | 210.0 | 216.2 | 1.45 | - | - | 0.38 | 0.02 | 0.74 |
1) CC: heifers received control supplement (C) in loose meal form (0.06% of body weight [BW] offered daily before and after parturition; n = 108); CB: received C before parturition and block supplementation (B) after parturition (0.07% of BW offered weekly after parturition; n = 117); BC: received B before and C after parturition (n = 103); BB: received B before and after parturition (n = 89).
2) Orthogonal contrasts: C1 (Block supplementation effect): Control (CC) vs block supplementation (BB+BC+CB); C2 (Block supplementation effect in both pre and postpartum periods): Pre and postpartum (BB) vs Pre or postpartum (BC+CB); and C3 (Pre or postpartum effect): prepartum (BC) vs postpartum (CB). T, time, days relative to calf age; T×treat, interaction between sampling time and treatment.
Table 6
| Items | Treatment1) | SEM | p-value2) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| CC | CB | BC | BB | T | TreatxT | C1 | C2 | C3 | ||
| Insulin (μg/mL) | (10.80) | (13.88) | (12.39) | (12.55) | 0.49 | <0.0001 | 0.91 | 0.008 | 0.13 | 0.26 |
| 90 days prepartum3) | 13.75 | 14.94 | 14.21 | 14.11 | 0.78 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 40 days postpartum4) | 6.66 | 9.49 | 9.93 | 8.63 | 0.58 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 80 days postpartum5) | 12.10 | 17.11 | 13.25 | 15.04 | 1.05 | - | - | - | - | - |
| IGF-1 (ng/mL) | (388.5) | (405.8) | (423.8) | (418.7) | 11.16 | <0.0001 | 0.79 | 0.24 | 0.35 | 0.99 |
| 90 days prepartum3) | 390.6 | 388.7 | 401.3 | 384.6 | 7.57 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 40 days postpartum4) | 260.7 | 265.4 | 265.7 | 273.1 | 7.59 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 80 days postpartum5) | 526.9 | 569.4 | 613.0 | 607.4 | 20.70 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 0.20 | 0.0002 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.20 | |||||
| 40 days postpartum4) | 89.9 | 101.6 | 99.1 | 104.3 | 1.83 | - | - | 0.01 | 0.34 | 0.65 |
| 80 days postpartum5) | 100.7 | 108.3 | 89.3 | 87.4 | 3.16 | - | - | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.03 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 0.009 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.22 | |||||
| 40 days postpartum4) | 10.31 | 16.24 | 10.81 | 15.03 | 0.70 | - | - | 0.03 | 0.33 | 0.004 |
| 80 days postpartum5) | 13.34 | 14.40 | 14.57 | 14.44 | 0.51 | - | - | 0.41 | 0.97 | 0.91 |
1) CC: heifers received control supplement (C) in loose meal form (0.06% of body weight [BW] offered daily before and after parturition; n = 108); CB: received C before parturition and block supplementation (B) after parturition (0.07% of BW offered weekly after parturition; n = 117); BC: received B before and C after parturition (n = 103); BB: received B before and after parturition (n = 89).
2) Orthogonal contrasts: C1 (Block supplementation effect): Control (CC) vs block supplementation (BB+BC+CB); C2 (Block supplementation effect in both pre and postpartum periods): Pre and postpartum (BB) vs Pre or postpartum (BC+CB); and C3 (Pre or postpartum effect): prepartum (BC) vs postpartum (CB).
REFERENCES
- TOOLS






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





