 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 31(8); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to observe whether high-pressure processing (HPP) affected aroma development and the degradation rate of umami taste-related ATP breakdown products, specifically inosinic acid in grass-fed beef during vacuum aging.
Methods
Strip loin (longissimus lumborum) cuts obtained from six grass-fed Friesian Holstein steers (32 months old) on day 4 post slaughter were vacuum-packed and subjected to pressurization at 300 and 500 MPa for 180 s at 15┬░C┬▒2┬░C. The samples were then stored for 4 weeks at 5┬░C┬▒0.5┬░C under vacuum and compared with the control (0.1 MPa).
Results
HPP increased the shear force value, promoted moisture loss and lipid oxidation, induced surface paleness, stabilized pH during aging, and reduced bacterial load and growth. The shear force value of 500 MPa-treated samples remained higher than the control after aging, while no significant differences were found between the control and 300 MPa-treated samples. Degradation of inosinic acid and inosine occurred during pressurization, resulting in an increase in hypoxanthine content. However, the degradation rate in HPP-treated samples during aging was slower; therefore, inosinic acid and inosine content remained higher than in control samples. No significant differences were found in hypoxanthine content at the end of aging. HPP intensified the levels of hexanal, octanal, 2-methylbutanal, 3-methylbutanal, benzaldehyde, and 2,5-dimethylpyrazine in cooked-aged beef samples.
Aging is known to impact meat tenderness and enhance its flavor. There are two techniques of beef aging that are currently used: vacuum aging and dry aging. Vacuum aging, or wet aging, is mostly used for beef in retail markets, while dry-aged beef is exclusive, available only through some meat processors. A comparative study revealed that dry aging resulted in more tender and preferable beef than did vacuum aging under similar aging durations [1]. Prolonged aging time increased the tenderness of vacuum-aged beef [2]. Therefore, vacuum aging requires a longer duration for optimal tenderization than dry aging.
High-pressure processing (HPP) is a cold-pasteurization process applied globally in several meat and seafood industries in order to reduce bacterial counts and minimize nutrient deterioration and, therefore, extend freshness [3]. Many studies have reported that HPP has a positive impact on the microbiological quality of beef [4,5]. Therefore, HPP could potentially maintain beef freshness during aging. There is a possibility to apply this technology to shorten the duration of vacuum aging for beef. However, the tenderization effect of HPP varies with meat pH and processing temperature. A previous study found that HPP at low temperatures (<30┬░C) increased meat toughness, and no significant changes were found in tenderness after aging [6]. In contrast, another study found that HPP at low temperatures lowered the shear force value of dark cutting beef [7], which agrees with the findings in Neto et al [8].
Aroma is one quality of meat that affects eating satisfaction. Meat aroma is developed through a complex series of biochemical reactions, converting precursors into volatile products during aging and processing. In addition to aroma, umami flavor has been associated with the satisfaction of eating meat and meat products [9]. A study of the mechanism of umami sensation revealed that water-soluble inosine-5ŌĆ▓monophosphate, or inosinic acid, could enhance the umami sensation of glutamic acid [10]. Inosinic acid is an ATP breakdown product, which is generated in meat post-slaughter and further degraded to form hypoxanthine during prolonged aging. The fast degradation rate of inosinic acid has been used as an indicator of putrefaction in seafood. HPP above 200 MPa can maintain the freshness of prawn and tuna during storage, resulting in a lower putrefaction index (K-value) [11,12]. Information regarding the effect of HPP on aroma volatile development and inosinic acid degradation in beef is still limited. Therefore, the objective of this study was to determine whether HPP could induce aroma development and reduce the degradation rate of inosinic acid in beef.
The longissimus lumborum muscles (strip loin) were obtained from six grass-fed Friesian Holstein steers (32-month-old) on day 3 post slaughter from a local meat plant. The strip loins were sliced into 2.5 cm thick and prepared in triplicate on the following day, vacuum packaged in nylon polyethylene vacuum bags (30├Ś20 cm) and transported to an HPP plant in an ice box. Samples (n = 6) were treated at 300 and 500 MPa in a 350 L chamber (QFP 350L-600, Avure Technologies, Inc., Kent, WA, USA) using water as a pressurization medium at 15┬░C┬▒2┬░C. Pressurization, holding, and depressurization times were 56.3 s, 180 s, and 12.2 s, respectively [8]. Samples were then stored under vacuum at 5┬░C┬▒0.5┬░C for 4 weeks. Non-treated samples at atmospheric pressure (0.1 MPa), were used as a control. Proximate composition of non-treated and HPP-treated samples was measured on day 0 of aging [13]. Other measurements were done on day 0 and 28 of the aging process.
The instrumental surface color was recorded by measuring International Commission on IlluminationŌĆÖs system for lightness (CIE L*), redness (CIE a*) and yellowness (CIE b*) using a chromameter (CR-400, Konica Minolta Inc., Tokyo, Japan). The light source of illuminant C (2┬░ observer) with 8 mm aperture and attached-closed cone was calibrated using a white plate (Y = 93.6, X = 0.3134, y = 0.3194). Each sample was assessed at 5 different locations immediately after being removed from the vacuum bag to determine the actual condition of vacuum-packaged beef in retail.
Sample (5 g) in triplicate was added with 45 mL of distilled water (DW) and homogenized at 10,000 rpm for 60 s using a homogenizer (PH91, SMT Co., Ltd., Chiba, Japan). The pH value of the homogenized sample was recorded using a pH meter calibrated with acid (pH 4.01) and neutral (pH 7.00) technical buffer solutions (Seven Easy pH, Mettler-Toledo GmbH, Greifensee, Switzerland) at 22┬░C according to manufacturerŌĆÖs instruction.
The 2.5 cm thick-samples were cooked in the polyethylene zipper bags by immersing in water bath set at 80┬░C for 30 min. The cooked samples were cut into eight pieces (1.5├Ś1 cm with 1 cm thickness) for each sample and subjected to shear force measurement using TA-XT2i Plus with the V blade (Stable Micro Systems Ltd., Godalming, UK). Assay parameters were: pre-test speed: 2.0 mm/s; test speed: 1.0 mm/s; post-test speed: 5.0 mm/s. The peak point was accounted as shear force value.
Lipid oxidation was analyzed using the 2-thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) method by Sinnhuber and Yu [14] with slight modification. A total of 0.5 g of sample was prepared in triplicate and vortex-mixed with 0.1 g of antioxidant mixture (consisting of 54% propylene glycol, 40% Tween 20, 3% butylated hydroxytoluene, and 3% butylated hydroxyanisole), 3 mL of 1% thiobarbituric acid in 0.3% NaOH, and 17 mL of 2.5% trichloroacetic acid in 36 mM HCl (Sigma-Aldrich Corp., LLC., St. Lois, MO, USA). The sample was heated in a water bath (BW-20G, Biotechnical Services, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) at 100┬░C for 30 min and then immersed in ice water for 15 min. Subsequently, 5 mL of aqueous sample was mixed with 3 mL of chloroform (Daejung Chemical and Metals Co. Ltd., Shiheung, Korea) to remove the dirt. The absorbance value of the upper layer was recorded at 532 nm (UV Mini 1240 PC, Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) against blank after centrifuging at 2,400├Śg for 30 min at 4┬░C (1248R, Labogene, Liller├Ėd, Denmark). The result was expressed in mg of malondialdehyde per kg of meat.
Total volatile basic nitrogen (TVBN) and bacterial growth were measured according to the Korea Food Standards Codex from Ministry of Food and Drug Safety [15]. Sample (5 g) was homogenized (UltraTurrax T25 basic, IkaWerke GmbH and Co., Staufen, Germany) for 1 min with 90 mL of DW. The supernatant solution was filtered using a filter paper #4 (Whatman, Little Chalfont, UK). A 0.01 N of boric acid was placed in the inner section of a Conway micro-diffusion cell (Sibata Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). One mL sample solution and 1 mL of saturated K2CO3 were also placed into the outer section of the same cell, and the lid was immediately closed. The cell was incubated at 37┬░C for 100 min, and it was then titrated against 0.02 N H2SO4. The VBN value was reported as mg/100 g or mg %. For bacterial growth measurement, 1 g of sample was put in sterile bags and prepared in triplicate (Whirl-Pak, Nasco, Fort Atkinson, WI, USA). Sample was homogenized with 9 mL sterilized 0.1% peptone water for 2 min using a stomacher (400, Seward Ltd., Worthing, UK). Decimal dilutions were prepared using 0.1% sterilized peptone water. Total mesophile bacteria were enumerated using plate count agar (Difco, Becton, Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). The plates were incubated at 37┬░C for 24 to 48 h. Microbial population was counted using a colony counter (C-C03, Chang Shin Scientific, Seoul, Korea) and expressed as log CFU/g.
The high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method described by Jayasena et al [16] was modified to measure ATP breakdown compounds with modification. Samples (5 g) were prepared in triplicate and homogenized with 25 mL of 0.7 M perchloric acid at 13,000 rpm for 15 s (UltraTurrax T25 basic, IkaWerke GmbH and Co., Germany). Samples were centrifuged at 2,090├Śg for 15 min at 2┬░C (1248R, Labogene, Denmark). The supernatant was filtered through #4 filter paper (Whatman, UK) and adjusted to pH 7.0 with 5 N KOH. The pH-adjusted supernatant was placed in a volumetric flask and brought to a volume of 100 mL with HPLC-grade DW. Approximately 25 mL of supernatant was centrifuged at 1,130 ├Śg for 15 min at 2┬░C (1248R, Labogene, Denmark) and then filtered through a 0.45-╬╝m polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) syringe filter (Hyundai Micro Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea). The filtrate was analyzed using an Agilent 1260 Infinity HPLC system equipped with an Agilent C18 column (4.6├Ś250 mm, 5 ╬╝m particle size, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Mobile phase A was 0.04% (v/v) triethylamine in phosphate buffer (58.72 mM Na2HPO4, 40 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.02 at 22┬░C), and mobile phase B was a mixture of HPLC-grade DW and acetonitrile (40:60 v/v). The flow rate was 1.0 mL/min, and the injection volume was 10 ╬╝L. A linear gradient of 0 to 15% mobile phase B over 17 min and 15% to 100% mobile phase B over 3 min (maintained at 100% mobile phase B for another 5 min) was used, followed by re-equilibration using 100% mobile phase A for 10 min before the next injection. The column temperature was maintained at 35┬░C and UV absorbance at 260 nm was monitored using diode array detectors. Peaks were identified using the retention time of the known standards inosine-5ŌĆ▓-monophosphate (IMP or inosinic acid), inosine and hypoxanthine (Sigma-Aldrich Corp., LLC., USA), and the concentrations were quantified according to a standard curve. Data are presented as mg/100 g.
Samples were sliced into 3├Ś3├Ś2.5 cm pieces and cooked for 4 min on a skillet set to 165┬░C using an electric stove (Clerin, Zhongsan Tonsun Electric Appliance Co., Ltd., Guangdong, China). During cooking, samples were flipped every minute. Samples were then cooled for 5 min on aluminum foil, ground with a food blender (Hanil Electronics Co., Ltd., Seongnam, Korea), and aroma volatiles and patterns were immediately measured.
Aroma volatiles from cooked samples were separated and identified using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry using a modified version of the method described in Ba et al [17]. Samples (3 g) were put into a 50 mL headspace vial and prepared in duplicate. The vials were heated to 60┬░C in a drying oven for 10 min, and carboxen/polydimethylsiloxane fiber (Supelco, Sigma-Aldrich Corp., LLC., USA) with a 75 ╬╝m diameter was injected into the vial. Extraction was performed for 30 min after temperature adjustment. Following extraction, the fiber was injected into the gas chromatograph (GC) port, which was set to 250┬░C, and the volatiles were desorbed for 5 min at a 1:5 split ratio. Separation was performed using a DB5 fused silica column (30 m├Ś 0.25 mm inner diameter, 0.25 ╬╝m film thickness, J&W Scientific, Folsom, CA, USA) in a gas chromatograph (7890A Agilent Technologies, USA). The GC oven was programmed to operate at an initial temperature of 40┬░C for 2 min, increasing to 160┬░C (by 5┬░C/min), then to 180┬░C (6┬░C/min, holding time of 5 min), and finally to 200┬░C (by 10┬░C/min, holding time of 5 min). The interface and quadruple temperatures were 280┬░C and 150┬░C, respectively. Helium was used as the carrier gas with a flow rate of 1 mL/min. Volatile compounds were detected using a mass spectrometer (5975C, Agilent Technologies, USA). The ion source temperature of the MS was set to 280┬░C with an electron impact of 70 eV. A scanning mass range of 50 to 450 m/z with a scan rate of 1 scan/s was used. Tentative identification was performed by comparing the experimental spectra to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Mass Spectral Library. A series of n-alkanes (C8ŌĆōC20) were analyzed under the same conditions to obtain retention indices (RIs) for the identified volatiles. The RIs were then compared to a published database available at http://www.flavornet.org/. Data are presented as area unit├Ś106/g.
An electronic nose (FOX3000, Alpha MOS, Toulouse, France) was used to distinguish the effect of different levels of high-pressure treatment and vacuum aging on the aroma pattern. A total of 2 g cooked sample was placed into a 10 mL-headspace vial; the sample was prepared in duplicate. The vials were then sealed with rubber septa (Supelco 29176-U, Sigma-Aldrich Corp., LLC., USA). The samples were heated at 60┬░C for 600 s with an agitation speed of 500 rpm. The 2.5 mL of gas in the headspace of the samples was extracted with an automatic sampler syringe (HS 100, Alpha MOS, France) at 65┬░C, flow-injected into the carrier gas (synthetic air with a purity quotient >99.99%, pressure set to 0.5 bar) flow (150 mL/min) of the electronic nose and detected using a metal oxide sensor (MOS) array system. The sensor array was composed of 12 MOSs. Data processing was done using two-dimensional principal component analysis in Alpha Soft version 8.01.
Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was employed using pressure levels and aging as the independent variables and surface color, meat pH, shear force, lipid oxidation, TVBN, total plate count (TPC), ATP breakdown compounds and aroma volatiles as dependent variables. Proximate composition data were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA with pressure levels as the independent variable. The statistical significance of the differences between means from different treatments was determined by DuncanŌĆÖs multiple range test at p<0.05. Analyses were performed using R-version 3.3.2 with the ŌĆ£AgricolaeŌĆØ library (The R-foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
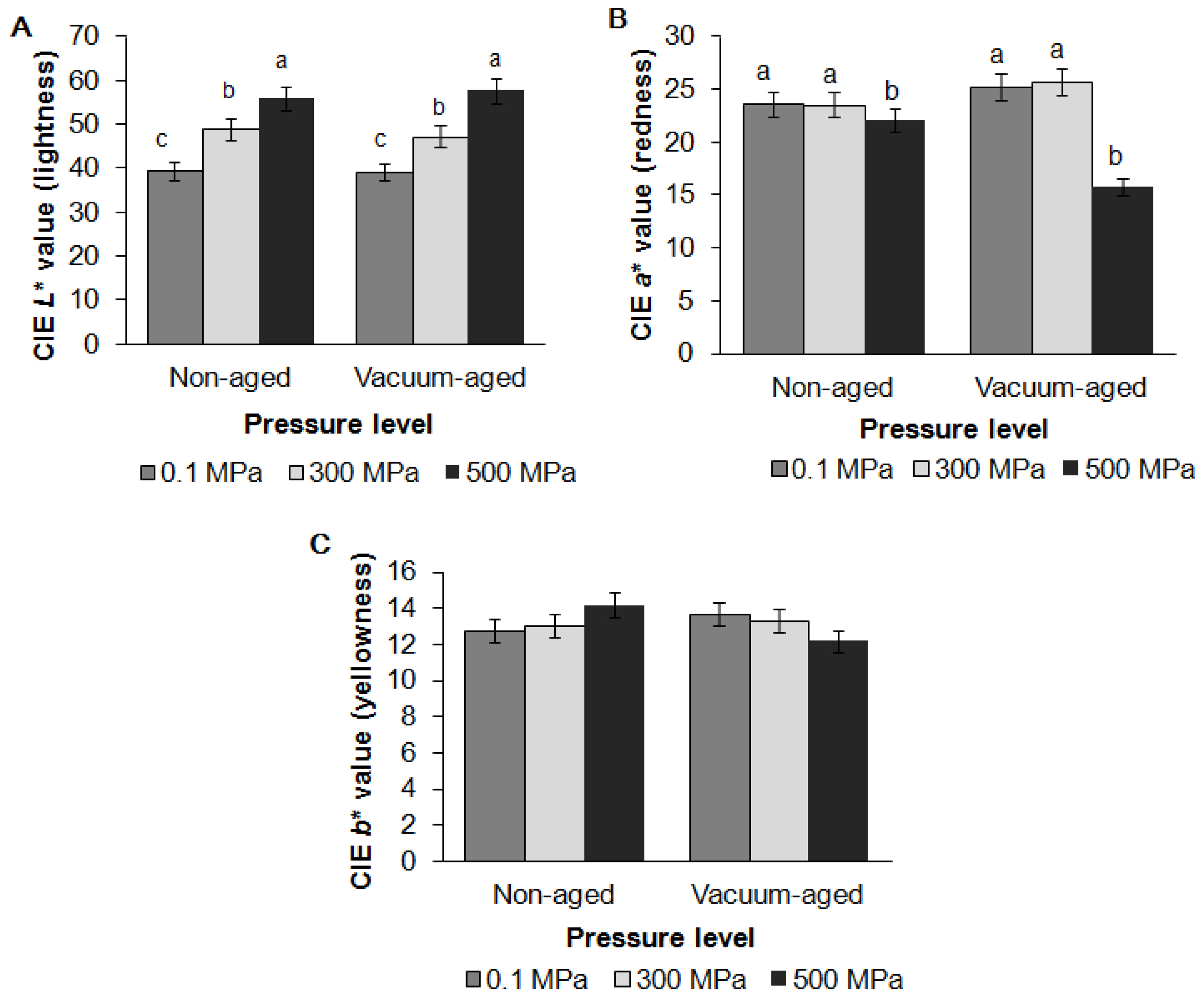
Changes in surface color are shown in Figure 1. HPP increased the CIE L* value (lightness) but reduced the CIE a* value (redness) resulting in a pale and gray appearance for samples treated at 500 MPa. The redness also decreased during vacuum aging. However, the CIE a* value of samples treated at 300 MPa and the control remained unchanged. In contrast with a previous study using DFD beef, no significant differences were found in the CIE b* value (yellowness) [7].
The effects of HPP and vacuum aging on meat pH and shear force values are shown in Table 1. The mean initial meat pH value was 5.88 for non-treated samples. HPP tended to increase mean pH values (p = 0.08) to 5.95 and 5.94 for groups treated at 300 MPa and 500 MPa, respectively. Interaction effects were found in non-treated samples subjected to four weeks of vacuum aging, after which the pH increased to 6.05. However, significant changes in meat pH were not found in HPP-treated samples. Samples also lost their moisture content (Supplementary Table S1) after HPP treatment. A similar pattern for meat pH and moisture loss has been previously reported [7].
Meat pH affects shear force value of HPP-treated meat [18]. In contrast to our previous study that using beef with pH higher than 6.0 [7], HPP increased the shear force value of cooked samples significantly (p<0.001). Beef with pH lower than 6.0 is likely to get more tough after HPP treatment as myofibrillar diameter size increases, but the sarcomere length gets shortened [19]. Furthermore, meat samples were treated on day 4 post slaughter in present study, allowing a natural tenderization process. After aging, the shear force value decreased significantly for both non-treated and HPP-treated groups (p<0.001). An interaction effect was found (p<0.001), in which the shear force value of samples treated at 500 MPa remained higher than samples treated at 300 MPa and non-treated samples. The tenderization rate was not significantly different between non-treated samples and samples treated at 300 MPa. This suggests that proteolysis was slower in samples treated at 500 MPa than in samples treated at 300 MPa and non-treated samples. HPP at 500 MPa may disrupt the activity of endogenous proteolytic enzymes in beef. Although HPP at 520 MPa was found to activate lysosomal enzymes, such as cathepsin D and acid phosphatase, the natural tenderization rate during aging has been shown to be reduced by high-pressure treatment [6].
HPP increased the TBARS value significantly (p = 0.02), as did aging time (p<0.01). Interaction effects on the TBARS value were also found (Table 1). The use of HPP for meat and meat products is limited by its oxidation triggering effect. Several studies have shown a positive correlation between pressure level and the amount of malondialdehyde produced [7,20]. Study on radical formation kinetics revealed the existence of a pressure threshold at 400 MPa (at 25┬░C) for the formation of radicals as initiators of lipid oxidation [21]. Ma et al [20] suggested that HPP triggers lipid oxidation through the release of iron, a major oxidation catalyst from myoglobin, as the rupture of the muscle cell occurs.
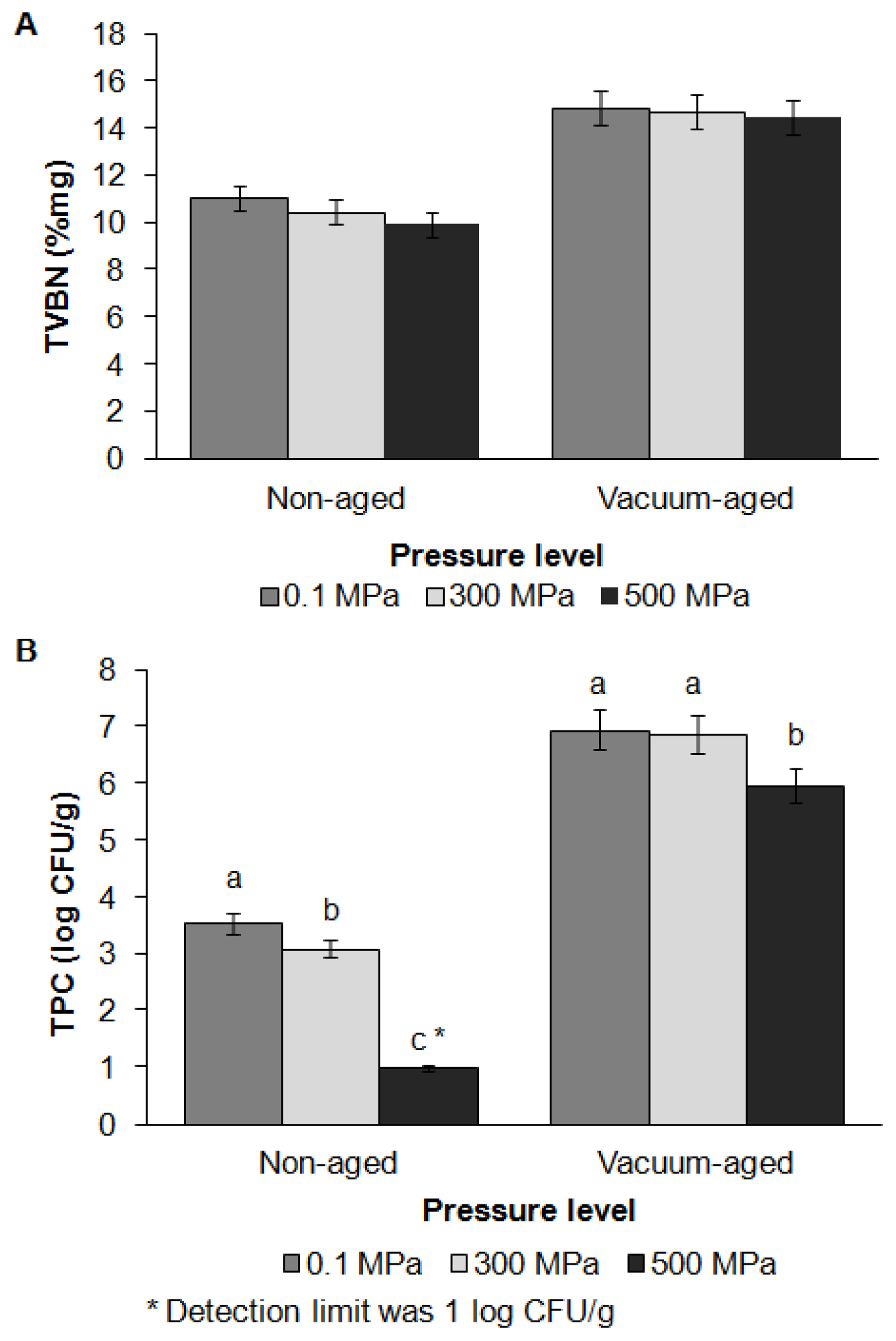
The effects of HPP and vacuum aging on TVBN and TPC are shown in Figure 2. HPP tended to lower TVBN (p = 0.06), but the effect was not statistically significant. TVBN increased during aging (p = 0.02). An effect of HPP on bacterial counts was observed, in which HPP at 300 MPa lowered TPC, and HPP at 500 MPa reduced TPC values to the detection limit of 1 log CFU/g. TVBN is used along with bacterial counts to determine the freshness and shelf life of meat-based products. Protein degradation occurs due to bacterial and endogenous meat protease activity, resulting in the production of free amino acids and their breakdown compounds, such as ammonia [22]. Although TVBN and TPC increased during aging, TVBN values did not exceed the edible limit of 20%/mg, and TPC values remained below the 7 log CFU/g limit suggested in the Korea Food Standards Codex by the Ministry of Food and Drugs Safety [23,15].
Gradual postmortem breakdown of ATP has been used to determine K-value, which is an indicator of meat freshness for crustacean, fish and chicken [11,12,24]. When depletion of muscle glycogen occurs, ATP starts to degrade quickly. ATPase hydrolyzes ATP into ADP, an adenylate kinase reaction further produces AMP from ADP, and IMP, or inosinic acid, then accumulates through deamination of AMP by AMP deaminase. Inosinic acid is then slowly degraded, producing inosine and hypoxanthine through phosphatase and nucleoside hydrolase activity, respectively [25]. Although ATP breakdown products are associated with putrefaction of meat, some compounds are taste enhancers. Inosinic acid is positively associated with umami taste, whereas the bitterness of cured meat is associated with hypoxanthine [26,27]. Inosinic acid itself does not have any taste, but it enhances the umami taste of glutamic acid [10]. As inosinic acid is degraded to form the purine base hypoxanthine, free ribose (a reducing sugar) and phosphate are released. Prolonged storage time decreases the level of inosinic acid but increases the level of hypoxanthine [28].
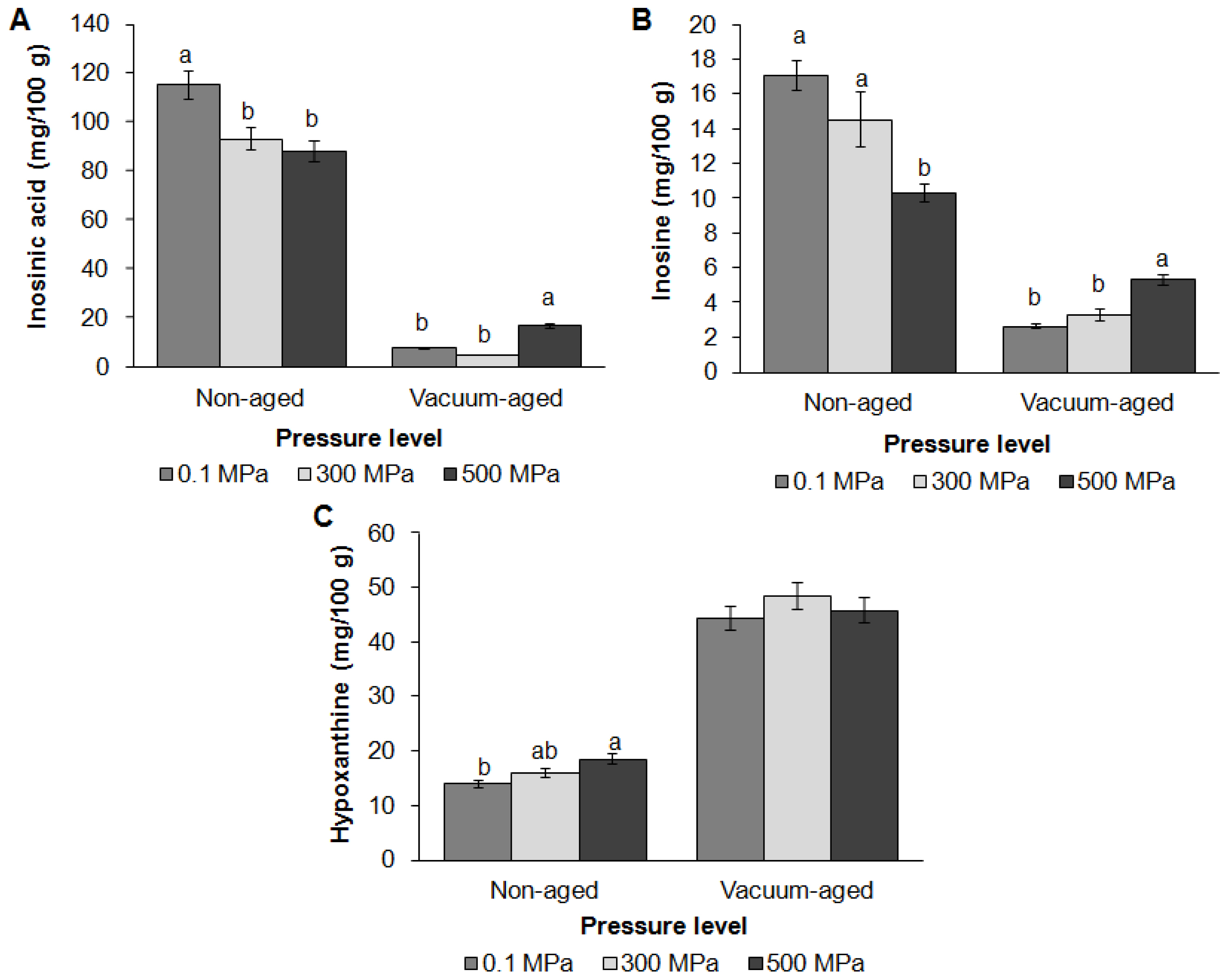
The effects of HPP and vacuum aging on the content of water-soluble ATP breakdown compounds (inosinic acid, inosine and hypoxanthine) in beef are shown in Figure 3. Previous studies reported that the effects of HPP on ATP breakdown products vary among samples and pressure levels [11,12]. In this study, HPP reduced inosinic acid and inosine content but increased hypoxanthine content on day 0 (p<0.001). HPP induced moisture loss in this study, and it is assumed that water-soluble inosinic acid and inosine were released from muscle cells during pressurization. Since hypoxanthine is the breakdown product of inosinic acid and inosine, HPP may induce activation of phosphatase and nucleoside hydrolase enzymes during pressurization to convert inosinic acid and inosine into hypoxanthine. Vacuum aging further reduced inosinic acid and inosine content but increased hypoxanthine content (p< 0.001). HPP effects were found in inosinic acid (p = 0.02) and inosine content (p = 0.03), in which the degradation rate of these compounds in samples treated at 500 MPa was slower than in other groups. Inosinic acid and inosine content in samples treated at 500 MPa remained higher than in other groups after four weeks of aging. However, no significant differences were found in hypoxanthine content among control and treatment groups after aging. These suggest that HPP can reduce the activity of phosphatase and nucleoside hydrolase enzymes during aging, lower the degradation rate of inosinic acid, and therefore maintain higher levels of umami taste enhancer.
Aroma patterns among treated, control, and blank samples were successfully discriminated by an electronic nose and are shown in Supplementary Figure S1 to have a total contribution rate higher than 85% (C1, 99.19% and C2, 0.59%), which agrees with previous study [7]. Discrimination patterns are arranged by aroma intensity from blank (left) to the most intense group (right). Higher pressures (500 MPa) and aging resulted in more intense aroma release from heated samples. Different aroma patterns caused by HPP were also previously found in goat meat [29].
The effects of HPP and vacuum aging on aroma volatiles are shown in Table 2. Based on peak area, HPP increased the generation of total identified n-aldehydes (p = 0.036), total Strecker aldehydes (p<0.001) and 2,5-dimethylpyrazine (p = 0.005). An effect of vacuum aging on the levels of total identified n-aldehydes (p = 0.040) and Strecker aldehydes (p = 0.009) was also observed. No significant effects were found on 2-pentylfuran levels. Hexanal and nonanal were more abundant than other n-aldehydes. HPP increased the release of hexanal (p = 0.031) and octanal (p = 0.041). However, effects were not clear for other identified n-aldehydes. Hexanal (p = 0.043) and heptanal (p = 0.037) were significantly increased after aging. The generation of 2-methylbutanal, 3-methylbutanal and benzaldehyde was increased by HPP, while aging only influenced 2-methylbutanal levels. Interaction effects were only observed in 2-methylbutanal levels, where no differences were found between HPP-treated groups on day 0. However, after aging, samples treated at 500 MPa released more intense 2-methylbutanal than samples treated at 300 MPa. Lipid oxidation and the loss of inosinic acid after pressure treatments and during aging are attributed to the generation of n-aldehydes, Strecker aldehydes and pyrazines. Degradation of inosinic acid and proteins provides free ribose and amino acids that generate Maillard reaction products, such as Strecker aldehydes and pyrazines, while lipid oxidation is associated with n-aldehydes [30]. Watanabe et al [31] reported that aging positively contributes to the generation of pyrazines, which is responsible for roast aroma. Although the effect of HPP was found, no significant effects of aging on 2,5-dimethylpyrazine were observed in this study. These data suggest that HPP induces aroma volatile development of the roasted samples.
The present study reveals that HPP intensifies the aroma of cooked vacuum-aged beef and reduces bacterial growth and the degradation rate of inosinic acid during aging. However, physical quality deteriorations, such as surface paleness (resulting in an unattractive appearance) and moisture loss, could not be avoided. HPP at 15┬░C also induced toughness and reduced the tenderization rate during aging for beef with pH of 5.88. Therefore, HPP cannot be easily applied to reduce the aging time of vacuum-packed beef.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by High Value-added Food Technology Development Program from Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, Republic of Korea. The authors thank the staffs of Samyang Foods Co., Ltd., Wonju, Korea and the staffs of Hyungkuk F&B Co., Ltd., Eumseong, Korea for providing beef samples and technical assistance when using pressure chamber, respectively.
Figure┬Ā1
Effects of high pressure processing and vacuum aging on instrumental surface Commission Internationale de lŌĆÖEclairage (CIE) L* value (A), a* value (B) and b* value (C) of grass-fed beef strip loin. These data are presented as mean┬▒standard error. Different letters (a, b, c) on the bar chart show that means within same aging group but different level of pressure are significantly different (p<0.05).
Figure┬Ā2
Effects of high pressure processing and vacuum aging on total volatile basic nitrogen content (A) and total plate count (B) of grass-fed beef strip loin. These data are presented as mean┬▒standard error. Different letters (a, b, c) on the bar chart show that means within same aging group but different level of pressure are significantly different (p<0.05).
Figure┬Ā3
Effects of high pressure processing and vacuum aging on the concentration of inosinic acid (A), inosine (B) and hypoxanthine (C) in grass-fed beef strip loin. These data are presented as mean┬▒standard error. Different letters (a, b) on the bar chart show that means within same aging group but different level of pressure are significantly different (p<0.05).
Table┬Ā1
Effects of high pressure processing and vacuum aging on meat pH, shear force value and malondialdehyde concentration in grass-fed beef strip loin
| Variables | Aging1) | Pressure (MPa) | SEM | p value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 0.1 | 300 | 500 | Pressure | Aging | Interaction | |||
| pH | Non-aged | 5.88B | 5.95 | 5.94 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.31 | 0.02 |
| Vacuum-aged | 6.05A | 5.99 | 5.97 | - | - | - | - | |
| Shear force (kgf) | Non-aged | 4.81b | 5.18a | 5.15a | 0.51 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Vacuum-aged | 3.16b | 3.28b | 4.10a | - | - | - | - | |
| TBARS (mg/kg) | Non-aged | 0.12bB | 0.30aB | 0.44aB | 0.09 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.02 |
| Vacuum-aged | 0.43bA | 0.61aA | 0.78aA | - | - | - | - | |
Table┬Ā2
Effects of high pressure processing and vacuum aging on volatile compounds of grass-fed beef strip loin
| Volatile compounds | Non-aged | Vacuum-aged1) | SEM | p value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
| Area unit (├Ś106) | 0.1 Mpa | 300 Mpa | 500 Mpa | 0.1 Mpa | 300 Mpa | 500 Mpa | Pressure | Aging | Interaction | |
| n-aldehydes | ||||||||||
| ŌĆāHexanal | 12.24bB | 14.39bB | 25.38aB | 27.84bA | 29.13bA | 34.99aA | 2.17 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.65 |
| ŌĆāHeptanal | 2.47B | 2.28B | 3.68B | 4.21A | 3.40A | 5.83A | 0.46 | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.37 |
| ŌĆāOctanal | 3.87b | 4.13b | 7.16a | 5.22b | 5.99b | 8.71a | 0.98 | 0.04 | 0.60 | 0.63 |
| ŌĆāNonanal | 21.01 | 21.66 | 24.31 | 25.52 | 26.44 | 27.31 | 3.02 | 0.38 | 0.70 | 0.59 |
| ŌĆāSum | 39.59bB | 42.46aB | 60.53aB | 62.79bA | 64.96bA | 76.84aA | 2.54 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.58 |
| Strecker aldehydes | ||||||||||
| ŌĆāButanal, 3-methyl | 0.01b | 0.27a | 0.25a | 0.02b | 0.49a | 0.45a | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.88 |
| ŌĆāButanal, 2-methyl | 0.28bB | 0.44aB | 0.40aB | 0.41cA | 0.74bA | 1.24aA | 0.11 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.01 |
| ŌĆāBenzaldehyde | 0.78b | 1.11a | 1.13a | 0.77b | 1.43a | 1.67a | 0.15 | <0.01 | 0.22 | 0.34 |
| ŌĆāSum | 1.07b | 1.82aB | 1.78aB | 1.20c | 2.66bA | 3.36aA | 0.29 | <0.001 | <0.01 | 0.06 |
| Pyrazine | ||||||||||
| ŌĆāPyrazine, 2,5-dimethyl | 0.30c | 0.41b | 0.66a | 0.27b | 0.52a | 0.54a | 0.06 | <0.01 | 0.67 | 0.64 |
| ŌĆāFuran | ||||||||||
| ŌĆāFuran, 2-pentyl | 1.20 | 1.53 | 1.45 | 2.44 | 1.80 | 2.45 | 0.40 | 0.88 | 0.16 | 0.80 |
REFERENCES
1. Li X, Babol J, Bredie WLP, et al. A comparative study of beef quality after aging longissimus muscle using a dry aging bag, traditional dry aging or vacuum package aging. Meat Sci 2014; 97:433ŌĆō42.


2. Djenane D, Beltr├Īn JA, Camo J, Roncal├®s P. Influence of vacuum-aging duration of whole beef on retail shelf life of steaks packaged with oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) active film under high O2. J Food Sci Technol 2016; 53:4244ŌĆō57.




3. Campus M. High pressure processing of meat, meat products and seafood. Food Eng Rev 2010; 2:256ŌĆō73.

4. Jiang Y, Scheinberg JA, Senevirathne R, Cutter CN. The efficacy of short and repeated high-pressure processing treatments on the reduction of non-O157:H7 Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli in ground beef patties. Meat Sci 2015; 102:22ŌĆō6.


5. Zhou Y, Karwe MV, Matthews KR. Differences in inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains in ground beef following repeated high pressure processing treatments and cold storage. Food Microbiol 2016; 58:7ŌĆō12.


6. Jung S, Ghoul M, de Lamballerie-Anton M. Changes in lysosomal enzyme activities and shear values of high pressure treated meat during aging. Meat Sci 2000; 56:239ŌĆō46.


7. Utama DT, Lee SG, Baek KH, et al. High pressure processing for dark-firm-dry beef: effect on physical properties and oxidative deterioration during refrigerated storage. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2017; 30:424ŌĆō31.



8. Neto OC, Rosenthal A, Deliza R, et al. Effects of hydrostatic pressure processing on texture and color of Zebu beef. Food Bioproc Technol 2015; 8:837ŌĆō43.

9. Suzuki K, Shioura H, Yokota S, et al. Search for an index for the taste of Japanese Black cattle beef by panel testing and chemical composition analysis. Anim Sci J 2016; 88:421ŌĆō32.


10. Zhang F, Klebansky B, Fine RM, et al. Molecular mechanism for the umami taste synergism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105:20930ŌĆō4.



11. Ginson J, Kamalakanth CK, Bindu J, et al. Changes in K value, microbiological and sensory acceptability of high pressure processed Indian white prawn (Fenneropenaeus indicus). Food Bioproc Technol 2013; 6:1175ŌĆō80.

12. Kamalakanth CK, Ginson J, Bindu J, et al. Effect of high pressure on K-value, microbial and sensory characteristics of yellow fin tuna (Thunnus albacares) chunks in EVOH films during chill storage. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 2011; 12:451ŌĆō5.

13. AOAC. Official methods of analysis. 17th edGaithersburg, MD, USA: AOAC International; 2002.
14. Sinnhuber RO, Yu TC. The 2-thiobarbituric acid reaction, an objective measure of the oxidative deterioration occurring in fat and oil. J Oleo Sci 1977; 26:259ŌĆō67.

15. MFDS. The guideline of processing and composition standard of animal resource food products. (Korean Food & Drug Administration, Notification No. 2014-135)Osong, Korea: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety; 2014.
16. Jayasena DD, Jung S, Kim HJ, et al. Comparison of quality traits of meat from Korean native chickens used in two different traditional Korean cuisines. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2013; 26:1038ŌĆō46.




17. Ba HV, Oliveros MC, Ryu K, Hwang I. Development of analysis condition and detection of volatile compounds from cooked Hanwoo beef by SPME-GC/MS analysis. Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour 2010; 30:73ŌĆō86.


18. Macfarlane JJ. Pre-rigor pressurisation of muscle: Effect of pH, shear value and taste panel assessment. J Food Sci 1973; 38:294ŌĆō8.

19. Jung S, de Lamballerie-Anton M, Ghoul M. Modifications of ultrastructure and myofibrillar proteins of post-rigor beef treated by high pressure. Lebenson Wiss Technol 2000; 33:313ŌĆō9.

20. Ma HJ, Ledward DA, Zamri AI, Frazier RA, Zhou GH. Effects of high pressure/thermal treatment on lipid oxidation in beef and chicken muscle. Food Chem 2007; 104:1575ŌĆō9.

21. Bolumar T, Skibsted LH, Orlien V. Kinetics of the formation of radicals in meat during high pressure processing. Food Chem 2012; 134:2114ŌĆō20.


22. Huang X, Lv R, Yao L, et al. Non-destructive evaluation of total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and K-values in fish using colorimetric sensor array. Anal Methods 2015; 7:1615ŌĆō21.

23. MFDS. Korea Food Standards Codex. (Korean Food & Drug Administration, Notification No. 2017-24)Osong, Korea: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety; 2017.
24. Feng L, Shi C, Bei Z, et al. Rosemary extract in combination with ╔ø-polylysine enhance the quality of chicken breast muscle during refrigerated storage. Int J Food Prop 2016; 19:2338ŌĆō48.

25. Massa AE, Palacios DL, Paredi ME, Crupkin M. Postmortem changes in quality indinces of ice-stored flounder (Paralichthys patagonicus). J Food Biochem 2005; 29:570ŌĆō90.

26. Nishimura T, Goto S, Miura K, et al. Umami compounds enhance the intensity of retronasal sensation of aromas from model chicken soups. Food Chem 2016; 196:577ŌĆō83.


27. Ichimura S, Nakamura Y, Yoshida Y, Hattori A. Hypoxanthine enhances the cured meat taste. Anim Sci J 2016; 88:379ŌĆō85.



28. Tikk M, Tikk K, T├Ėrngren MA, et al. Development of inosine monophosphate and its degradation products during aging of pork of different qualities in relation to basic taste and retronasal flavor perception of the meat. J Agric Food Chem 2006; 54:7769ŌĆō77.


29. Kang G, Cho S, Seong P, et al. Effects of high pressure processing on fatty acid composition and volatile compounds in Korean native black goat meat. Meat Sci 2013; 94:495ŌĆō9.


30. Back HH. Process flavors. Nollet LML, editorHandbook of meat, poultry, and seafood quality. Ames, IA, USA: Blackwell Publishing; 2007. p. 311ŌĆō26.






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement
Supplement Print
Print





