 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 30(1); 2017 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to examine shifts in the composition of the bacterial population in the intestinal tracts (ITs) of weaning piglets by antibiotic treatment using high-throughput sequencing.
Methods
Sixty 28-d-old weaning piglets were randomly divided into two treatment groups. The Control group was treated with a basal diet without antibiotics. The Antibiotic groupŌĆÖs basal diet contained colistin sulfate at a concentration of 20 g per ton and bacitracin zinc at a concentration of 40 g per ton. All of the pigs were fed for 28 days. Then, three pigs were killed, and the luminal contents of the jejunum, ileum, cecum, and colon were collected for DNA extraction and high-throughput sequencing.
Results
The results showed that the average daily weight gain of the antibiotic group was significantly greater (p<0.05), and the incidence of diarrhea lower (p>0.05), than the control group. A total of 812,607 valid reads were generated. Thirty-eight operational taxonomic units (OTUs) that were found in all of the samples were defined as core OTUs. Twenty-one phyla were identified, and approximately 90% of the classifiable sequences belonged to the phylum Firmicutes. Forty-two classes were identified. Of the 232 genera identified, nine genera were identified as the core gut microbiome because they existed in all of the tracts. The proportion of the nine core bacteria varied at the different tract sites. A heat map was used to understand how the numbers of the abundant genera shifted between the two treatment groups.
Antibiotics are becoming an essential component of modern agricultural to improve the feed efficiency of animals, treat disease, and kill harmful germs [1]. Colistin sulfate and bacitracin zinc are commonly used growth-promoting antibiotics in farm production and are rarely assimilated by animal intestines. Antibiotics were shown to have an important effect on the growth of bacteria by suppressing bacterial wall synthesis [2], thereby improving the growth rate or reducing the incidence of diarrhea in piglets. A previous study showed that colistin sulfate could increase the activities of amylase, lipase and protease in broiler chickens [3]. Supplementation with bacitracin zinc can change the intestinal microbiota and improve the growth performance of broiler chickens challenged with Eimeria acervulina and E. tenella [4]. However, how these two antibiotics work in weaning piglets has not been measured. Performance-enhancing antibiotics used at low levels in feeds can enhance the efficiency of feed utilization, thereby improving the growth performance of animals. Antibiotics are also used at higher levels to prevent and treat diseases in the livestock and poultry industries [5]. Improvement in the growth performance of piglets may be due to changes in the composition of the bacterial community that provides nutrition and performs defensive functions in the host [6,7]. Growth-promoting antibiotics also benefit protein metabolism and reduce growth-depressing microbial metabolites.
The microbiota of livestock and poultry ITs is an essential ŌĆ£organŌĆØ than can comprise up to one thousand species in a dynamic environment [8]. Previous studies have also shown that the intestinal microbiota could influence many metabolic steps and affect many aspects of host physiology, such as nutritional status, host behavior and stress responses [9]. The gut microbiota could carry out the following functions for its host: acting as a physical barrier by competitive attachment, digestion of nutrient sources, and the production of antimicrobial substances. However, which bacteria of the microbiota play beneficial or harmful roles remain largely undefined. Previous cultivation technology has limited our capacity to separate strictly anaerobic bacteria members or members needing complex nutrient substances. It should be observed that different diets affect the intestinal ecology of piglets, mainly by transforming the circumstances in the proximal gastrointestinal tract, leading to a more stable environment and reduced reproduction of pernicious bacteria in the gut [10].
The weaning period, corresponding to changes in diet and the gut environment, is a stressful period, therefore, it can easily lead to low growth performance, a high incidence of diarrhea and imbalanced intestinal flora [11]. The number and species of microorganisms living in the mammalian gut shows variation among the jejunum, ileum, cecum and colon [12]. For example, the contents of the small intestine were abundant in members of the Proteobacteria and Cyanobacteria phyla, but Bacteroidetes were more prevalent in the large intestine samples. Colistin sulfate and bacitracin zinc are commonly used in broiler chickens but rarely used in weaning piglets [13]. Previously, there were limited techniques for the measurement of the effects of antibiotic supplementation on pigs. In this research, high-throughput MiSeq platforms were used to give us an efficient method for understanding the complex relationship between the two antibiotics and weaning pigletsŌĆÖ core microbiome in the different tracts.
A total of sixty weaning piglets at 28 days of age were randomly placed into two growth trials. The following dietary treatments were carried out: i) Control (basal diet based on corn and soybean meal without antibiotics) and ii) Antibiotic (basal diet supplemented with colistin sulfate at 20 g per ton and bacitracin zinc at 40 g per ton). All of the pigs were housed in a controlled environmental room for 28 days. At the end of the experiment, three pigs were randomly selected for euthanization by a method approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Zhejiang University. The sections of the gastrointestinal tract were immediately removed from the carcasses. The luminal contents of the intestinal tracts were collected from the jejunum, ileum, cecum, and colon sites. The samples were placed on ice and immediately transported to the laboratory.
Total genomic DNA was extracted from each of the luminal content samples containing the microbial communities using the QIAamp DNA Stool Mini Kit (QIAGEN, CA, Hamburg, Germany) according to the manufacturerŌĆÖs instructions. The quantity of DNA was measured using a NanoDrop 1000 Spectrophotometer.
The V3-V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified and sequenced. The polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) were carried out in triplicate in a total volume of 25 ╬╝L containing 5 ╬╝M of each primer, 10 ng of DNA template, 4 ╬╝L 1├Ś FastPfu buffer, 2.5 mM dNTPs, and 0.4 ╬╝L of FastPfu polymerase (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China). The PCR protocol included 30 cycles. PCR products were separated by electrophoresis in a 2% (w/v) gel, and the band was purified using the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen, Union City, CA, USA). Amplicons produced from different luminal content samples were sent to a commercial company (Majorbio, Shanghai, China) for sequencing on the Illumina MiSequencing platform.
First, all of the raw reads with one or more ambiguous nucleotides or with incorrect barcode or primer sequences were discarded. Illumina sequencing produced a pair of reads from each end for each DNA fragment. A self-written script was developed to generate the reverse complement of one of the paired-end reads and then compare it with its matching read. Then, the tagged sequences were classified into different individual files according to the barcodes of the samples [14]. Richness and diversity indices were produced using Mothur, and sets of sequences with Ōēź97% identity were defined as operational taxonomic units (OTUs). The representative sequences were distributed into phyla and genera according to the SILVA bacteria database (SILVA version 108, Silva, Bremen, Germany) following the Bayesian approach and using a cutoff of 97%. Clusters were generated using a dissimilarity cutoff of 3% and served as OTUs for constructing predictive rarefaction curves and for calculating the Shannon and Simpson diversity indices, Chao1 richness, abundance-based coverage estimators and coverage percentage by GoodŌĆÖs method. Principal component analysis was carried out at the genus level [15].
Antibiotics have obvious effects on feed intake and growth performance. The ADG (average daily gain) (263.81) of the antibiotics group was significantly higher (p<0.05; Table 1) than the ADG of the control group (193.33). No obvious differences in the F:G (feed rate: gain rate) (p>0.05) were observed between the two groups. Throughout the experiment, the incidence of diarrhea in the antibiotic group was lower than in the control group but no significant difference was observed (p>0.05). This difference was indicated by the ADG and average daily feed intake of the antibiotic group. In this study, the results suggested that colistin sulfate and bacitracin zinc could promote pigletŌĆÖ growth performance by increasing the rate of the development and maturation of the microbiota to the form found in adults [16].
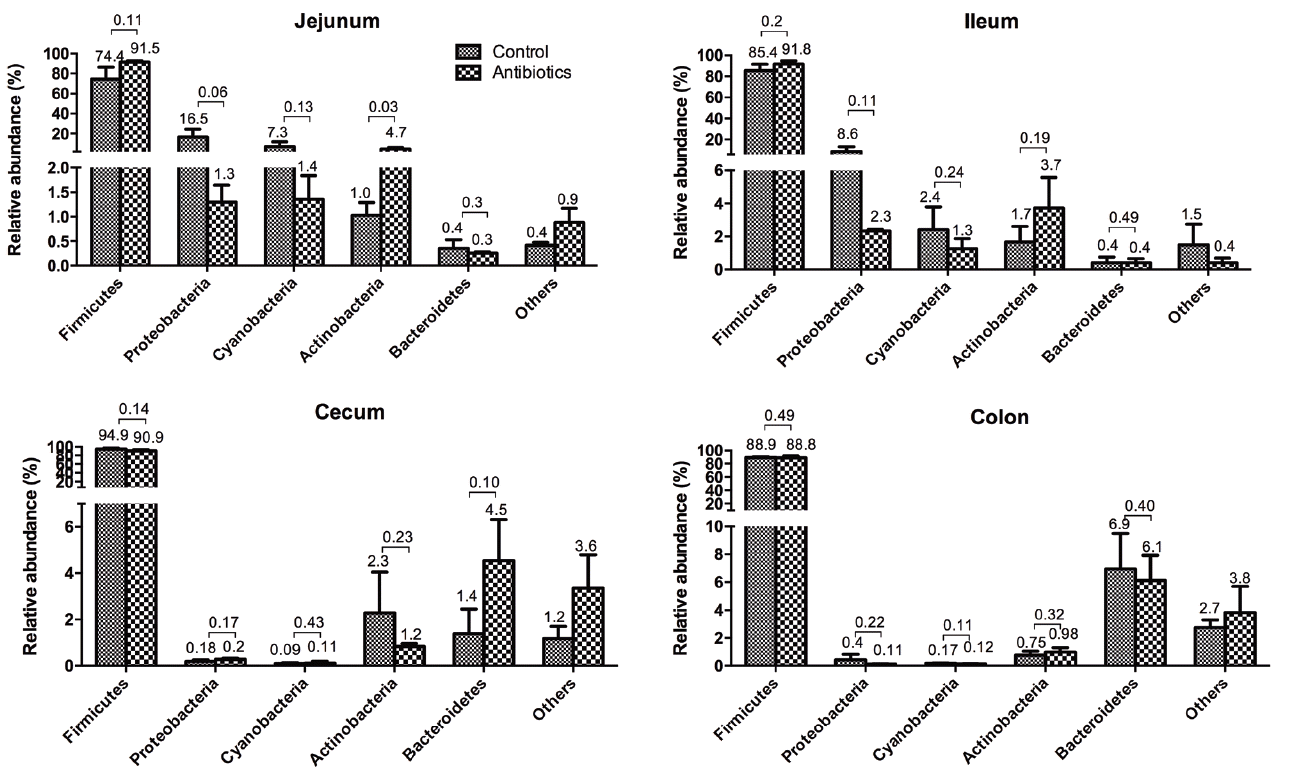
Although antibiotics are an important dietary supplement with many positive effects, data about their characteristics from an ecological perspective are limited. Therefore, a more qualitative and quantitative method is necessary to monitor intestinal microbial communities. In this study, high-throughput sequence technology was adopted, and a total of 812,607 valid sequence reads that corresponded to 855 OTUs (97% identity) were generated from the 24 samples as indicated (Table 2). The 38 OTUs that existed in all of the samples in the two groups were defined as core OTUs in our study. Although core OTUs composed only 4.44% of the total OTUs, they contained 60.7% of the total sequences. These observations reveal that weaning piglets share a core set of bacteria that are represented by a small number of dominant species in different individuals. In addition, 97% of the core sequences were from members of the Firmicutes phyla. The other two core phyla were the Cyanobacteria and Actinobacteria. The bacterial composition at the phylum and class levels are shown in Figure 1 and 2.
At the phylum level (Figure 1), we identified a total of 21 phyla, and the majority of the classifiable sequences (approximately 90%) from all four intestinal tract regions belonged to the Firmicutes. The others represent less than 4% of the total bacteria. We have confirmed that there are differences in the compositions of the microbiota in different locations of the pigletsŌĆÖ guts. For example, Proteobacteria and Cyanobacteria were more abundant in the jejunum and ileum but were rarely found in the other regions. The reasons for these variations may be related to the GITŌĆÖs functional and anatomical diversity by location. The effect of antibiotics on the shift in Firmicutes was different from the jejunum to the colon. Their relative abundance was slightly increased in the jejunum and ileum but reduced in the cecum and colon (p>0.05). The percentages of bacteria in the Proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria, and Actinobacteria phyla decreased from the jejunum to the colon; however, the percentage of bacteria in the Bacteroidetes phyla increased. Similar shifts were observed in both groups. However, there were no significant differences between the control and antibiotic groups within the different regions of the tract (Figure 1).
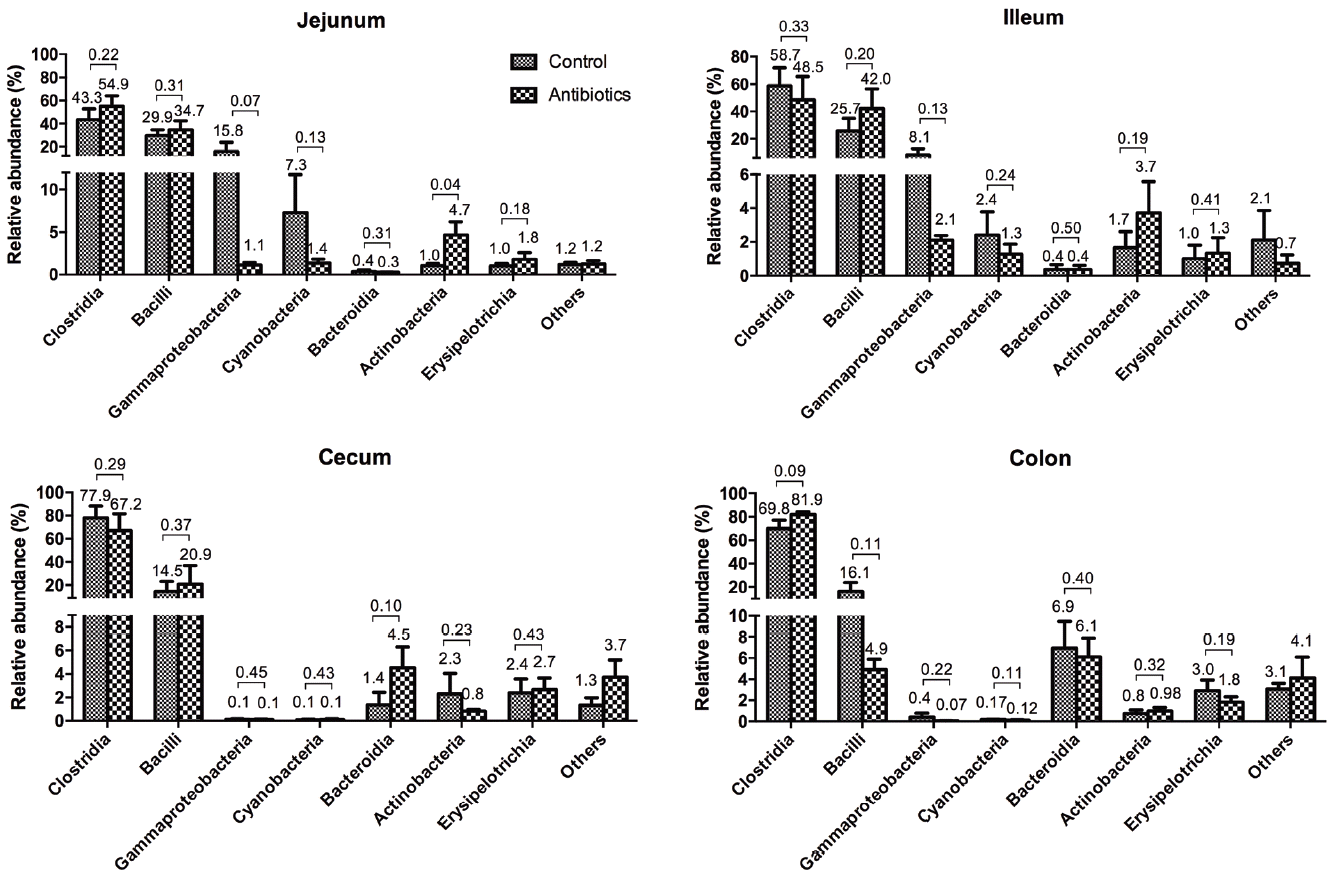
The Firmicutes are typically divided into three classes: the Clostridia, which are anaerobic, the Bacilli, which are obligate or facultative aerobes, and the Mollicutes. The Firmicutes also represent the largest proportion of the mouse and human gut microbiomes [17] and are involved in energy resorption and obesity [18]. The proportion of Proteobacteria and Cyanobacteria in the antibiotic group was reduced but not significantly. Cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins and obtain energy through photosynthesis. They are the most genetically diverse bacteria, they occupy a broad range of habitats across all latitudes, and they can survive in harsh environments [19]. Actinobacteria contains one of the largest bacterial genera, Streptococcus, which was one of the dominant bacterial genera (Figure 3). Streptococcus are recognized as producers of many bioactive metabolites, such as antibiotics, which provide useful medicine for humans [20]. Only one class of Bacteroidetes, Bacteroidia, are abundant organism in the feces of animals and humans. However, the Bacteroides and Porphyromonas genera were not detected in the intestinal tracts of weaning piglets.
We identified a total of 42 classes dominated by the Clostridia and Bacilli, which are the most common classes of the phylum Firmicutes. The numbers of Clostridia increased, but the numbers of Bacilli decreased from the jejunum to the colon. The other classes also showed variable distributions among the four regions of the intestinal tract. The proportion of Gammaproteobacteria and Cyanobacteria was higher in the small intestinal regions, whereas the numbers of Bacteroidia, Actinobacteria, and Erysipelotrichia were greater in the regions of the large intestine. These seven classes accounted for almost 96% of the total sequences.
We identified a total of 232 genera from the 24 samples. The most abundant genera including Clostridium, Lactobacillus, Ruminococcus, Streptococcus, Subdoligranulum, Peptostreptococcaceae_incertae_sedis, Escherichia, Lachnospiraceae_unclassified, and Cyanobacteria_norank were identified as the core gut microbiome because these genera were found in all regions of the intestinal tracts in piglets (Figure 3). Among the nine core bacteria, the proportion of Ruminococcus, Subdoligranulum, and Lachnospiraceae_unclassified showed increases from the jejunum to the colon, whereas the other genera decreased. To understand how the number of core bacteria shifted between the two treatment groups, a heat map was used to identify differences in the abundance of genera (Supplementary Figure S1). We also found that Streptococcus, Escherichia, and Cyanobacteria_norank were more abundant in the small intestine and that their relative abundance tended to decrease after treatment with antibiotics.
It was obvious that Clostridium dominated the pigletsŌĆÖ gut tracts and that bacteria of this genus were reduced during treatment with antibiotics. Previous studies have shown similar frequencies of Clostridium in the ileum of pigs [21]. The unifying feature of the species C. botulinum is the production of neurotoxins [22]. C. difficile, the other important species of Clostridium, can flourish when other germs in the gut are killed during antibiotic treatment [23]; this result is similar to our results in the colon. Ruminococcus is the genera frequenting the colon of piglets. Lactobacillus is a major part of the lactic acid bacterial group and can produce energy through glycolysis and fermentation without oxygen [24].
Most Lactobacillus species are considered to be harmless and is possibly effective at preventing bacterial infections. Lactobacilli can also be used in animal feeds to restore particular aspects of physiological balance and improve the growth of piglets [25] because some Lactobacillus species can generate lactic acid, which may produce an acidic environment that could restrain the growth of many pathogenic genera [26]. Many Streptococcus species are not harmful and form part of the commensal bacteria of animal intestinal tracts. Escherichia was more abundant in the regions of the small intestine than in the large intestine and decreased significantly (p = 0.07, p = 0.12) after antibiotic experiment. Many species of Escherichia are the most common causes of intestinal tract infections and cause serious food poisoning in their hosts [27]. Virulent strains of E. coli can cause gastroenteritis, diarrhea and sometimes bloody bowels within 24 hours. Antibiotics have been shown to markedly decrease the number of E. coli in the jejunum; therefore, they could reduce the incidence of diarrhea in piglets as shown in Table 1. Many bacterial species can metabolize dietary fiber to SCFAs, which accounts for a significant part of the animalŌĆÖs energy source [28]. These core genera of weaning piglets should be studied more precisely and quantitatively associated with the hostŌĆÖs genome, metabolome, and growth performance.
Antibiotics have been used for sixty years to improve the growth of pigs. We can expect that advanced modeling and analysis, including sequence platforms, will help us to gain a much better understanding of the microbiomes in different regions of the gut and due to different diets and stages of development, in various geographical regions, and in response to various environmental conditions. Although there is still much controversy surrounding the overuse of antibiotics in agriculture, antibiotics have improved piglet growth performance and altered the proportions of bacteria in the microbiome, as this study has shown. This research is important because the microbiome is a cornerstone of health and productivity, and it will enrich our knowledge of the microbiomeŌĆÖs role in pigletsŌĆÖ health and disease. Future research should focus on gene expression or the proteins and metabolites of the gut microbiota while reducing underlying risks to animal or human health.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31402083) and Key project of Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LZ15C170001).
Figure┬Ā1
Spatial distribution of bacterial phyla and their abundance among the gastrointestinal tract microbiota of weaning piglets. The error bars represent standard deviations. p-values and means are marked on the bars.
Figure┬Ā2
Spatial distribution of bacterial classes and their abundance among the gastrointestinal tract microbiota of weaning piglets. The error bars represent standard deviations. p-values and means are marked on the bars.
Figure┬Ā3
Spatial distribution of bacterial genera and their abundance among the gastrointestinal tract microbiota of weaning piglets. The error bars represent standard deviations. p-values and means are marked on the bars.

Table┬Ā1
Effect of dietary supplementation with antibiotics on the growth performance of weaning piglets
| Item | Control | Antibiotics | SEM1) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial BW (kg) | 6.73 | 6.63 | 0.11 | 0.970 |
| Final BW (kg) | 12.15b | 14.05a | 0.26 | 0.017 |
| ADG (g) | 193.33a | 263.81b | 8.75 | 0.004 |
| ADFI (g) | 337.96a | 449.63b | 14.43 | 0.009 |
| F:G | 1.74 | 1.71 | 0.33 | 0.740 |
| Incidence of Diarrhea | 6.67 | 5.10 | 0.35 | 0.450 |
REFERENCES
1. Looft T, Allen HK. Collateral effects of antibiotics on mammalian gut microbiomes. Gut Microbes 2012; 3:463ŌĆō7.



2. Park JC, Lee SH, Hong JK, et al. Effect of dietary supplementation of procyanidin on growth performance and immune response in pigs. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2014; 27:131ŌĆō9.



3. Zhang L, Zhang L, Zhan X, et al. Effects of dietary supplementation of probiotic, Clostridium butyricum, on growth performance, immune response, intestinal barrier function, and digestive enzyme activity in broiler chickens challenged with Escherichia coli K88. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 2016; 7:3



4. Bortoluzzi C, Menten JFM, Pereira R, et al. Hops ╬▓-acids and zinc bacitracin affect the performance and intestinal microbiota of broilers challenged with Eimeria acervulina and Eimeria tenella. Anim Feed Sci Technol 2015; 207:181ŌĆō9.

5. Cromwell GL. Why and how antibiotics are used in swine production. Anim Biotechnol 2002; 13:7ŌĆō27.


6. Gaskins HR, Collier CT, Anderson DB. Antibiotics as growth promotants: Mode of action. Anim Biotechnol 2002; 13:29ŌĆō42.


7. Pedroso AA, Menten JFM, Lambais MR, et al. Intestinal bacterial community and growth performance of chickens fed diets containing antibiotics. Poult Sci 2006; 85:747ŌĆō52.


9. Lankelma JM, Nieuwdorp M, de Vos WM, Wiersinga WJ. The gut microbiota in internal medicine: implications for health and disease. Neth J Med 2015; 73:61ŌĆō8.

10. Canibe N, Hojberg O, Hojsgaard S, Jensen BB. Feed physical form and formic acid addition to the feed affect the gastrointestinal ecology and growth performance of growing pigs. J Anim Sci 2005; 83:1287ŌĆō302.


11. Giang HH, Viet TQ, Ogle B, Lindberg JE. Growth performance, digestibility, gut environment and health status in weaned piglets fed a diet supplemented with a complex of lactic acid bacteria alone or in combination with Bacillus subtilis and Saccharomyces boulardii. Livest Sci 2012; 143:132ŌĆō41.

13. Li X, Liu L, Li K, Hao K, Xu C. Effect of fructooligosaccharides and antibiotics on laying performance of chickens and cholesterol content of egg yolk. Br Poult Sci 2007; 48:185ŌĆō9.


14. Mao Y, Xia Y, Zhang T. Characterization of Thauera-dominated hydrogen-oxidizing autotrophic denitrifying microbial communities by using high-throughput sequencing. Bioresour Technol 2013; 128:703ŌĆō10.


15. Oberauner L, Zachow C, Lackner S, et al. The ignored diversity: complex bacterial communities in intensive care units revealed by 16S pyrosequencing. Sci Rep 2013; 3:1413



16. Kim HB, Borewicz K, White BA, et al. Microbial shifts in the swine distal gut in response to the treatment with antimicrobial growth promoter, tylosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109:15485ŌĆō90.



17. Ley RE, Peterson DA, Gordon JI. Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell 2006; 124:837ŌĆō48.


18. Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006; 444:1022ŌĆō3.


19. Sivonen K. Chapter 24: Emerging high throughput analyses of cyanobacterial toxins and toxic cyanobacteria. Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs 2008; 619:539ŌĆō57.

20. Mahajan GB, Balachandran L. Antibacterial agents from actinomycetes - a review. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 2012; 4:240ŌĆō53.


21. Dowd SE, Sun Y, Wolcott RD, Domingo A, Carroll JA. Bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP) for microbiome studies: bacterial diversity in the ileum of newly weaned Salmonella-infected pigs. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2008; 5:459ŌĆō72.


22. Dover N, Barash JR, Hill KK, Xie G, Arnon SS. Molecular characterization of a novel botulinum neurotoxin type H gene. J Infect Dis 2014; 209:192ŌĆō202.


23. McFarland LV. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea: epidemiology, trends and treatment. Future Microbiol 2008; 3:563ŌĆō78.


24. Petrova MI, Lievens E, Malik S, Imholz N, Lebeer S. Lactobacillus species as biomarkers and agents that can promote various aspects of vaginal health. Front Physiol 2015; 6



25. Pascual LM, Daniele MB, Ruiz F, Giordano W, Pajaro C, Barberis L. Lactobacillus rhamnosus L60, a potential probiotic isolated from the human vagina. J Gen Appl Microbiol 2008; 54:141ŌĆō8.


26. Kim HB, Isaacson RE. The pig gut microbial diversity: Understanding the pig gut microbial ecology through the next generation high throughput sequencing. Vet Microbiol 2015; 177:242ŌĆō51.







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement
Supplement Print
Print





