 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 29(3); 2016 > Article |
|
Abstract
This study was designed to examine the characteristics of sawdust and cocopeat bedding materials, including physicochemical properties (Exp. I) and on-farm trial (Exp. II). In Exp. I, the proportion of particle size was in the order of sawdust> cocopeat India>cocopeat Vietnam (p<0.05), and cocopeat contained higher proportion of small particles (250 μm+below 250 μm) than sawdust, causing a dust production problem. Bulk density was cocopeat India>cocopeat Vietnam>sawdust (p<0.05), thus cocopeat treatments showed 4.4 times higher bedding cost than sawdust. The water absorption rates were 702.0% in cocopeat India, 678.3% in cocopeat Vietnam, and 444.0% in sawdust, showing cocopeat had approximately 1.5 times higher water absorption rate than sawdust. Moisture evaporation rates after 12 h of air blowing (2.00 m/s) were higher (p<0.05) in cocopeat Vietnam (80.4%) than sawdust (71.2%) and cocopeat India (72.8%). In vitro ammonia emissions were higher (p<0.05) in sawdust (2.71 mg/m2/h) than cocopeat India (1.59 mg/m2/h) and Vietnam (1.22 mg/m2/h), and total ammonia emissions were higher (p<0.05) in sawdust (37.02 mg/m2) than cocopeat India (22.51 mg/m2) and Vietnam (13.60 mg/m2). In Exp. II, an on-farm trial was conducted with 48 Hanwoo cattle in 16 pens using the same bedding materials as in Exp. I, with fan (blowing 2.00 m/s) and no fan treatments, and feed bunk side (FB) and water supply side (WS) within a pen (4.5 m, width×9.0 m, length). Beddings were replaced with fresh bedding materials when moisture concentrations were over 65%. No interactions among treatments were detected for moisture concentration and increment rates, and ammonia concentrations, but a significant effect was observed (p<0.01) for each of the treatments. Both concentrations and increment rate of moisture were higher (p<0.01) in the beddings without fan than with fan. Moisture concentrations and increment rate within a pen were also higher (p<0.01) in FB than WS. Thus, the whole no-fan-FB and sawdust-fan-FB were replaced with fresh bedding material between 4 to 5 experimental weeks. The ammonia concentrations and pH of beddings were not significantly different among treatments. Therefore, using cocopeat bedding with a blowing fan can extend twice the bedding utilization period, and WS within a pen showed twice the bedding-life compared to FB. Despite the outstanding characteristics of cocopeat compared with sawdust, using cocopeat as an alternative for sawdust bedding is not recommended for cattle management, considering it has 4.4 times higher bedding cost and a dust production problem.
Proper environmental management is important to maximize productivity of farm livestock. The indications of successful environmental management include four scientific satisfactions, such as thermal comfort, physical comfort, disease control and behavioral satisfaction (Webster, 1993). In addition, considering farm animal welfare is important not only since the introduction of animal welfare certification in South Korea but also in terms of the act of pure humanity. In the matter of farm animal welfare, the five freedoms identified by Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (RSPCA, 2015) must be considered; i) freedom from hunger or thirst, ii) freedom from discomfort, iii) freedom from pain, injury or disease, iv) freedom to express normal behavior, v) freedom from fear and distress. A proper environment by management of beddings can be relevant to 3 of the 5 freedoms, ii) freedom from discomfort, iii) freedom from pain, injury or disease and iv) freedom from fear and distress.
Because bedding materials can influence all of four scientific satisfactions, the use of proper bedding materials is important for successful environmental management. In lactating cows, the population and number of bacteria in bedding materials are related to the microbial load on teat ends and incidence rate of clinical mastitis (Hogan et al., 1989). The use of bedding materials also has an important role in the behavior and welfare of dairy cows. There were preferences for soft surfaces such as sawdust in contrast to sand and mattress beddings (Tucker et al., 2003).
In general, sawdust and rice hulls are the most popular bedding materials in South Korea, but the price of sawdust is relatively expensive and unstable, because most sawdust is imported from abroad. Rice hulls are less suitable as a bedding material, because of lower rates of water absorption and moisture evaporation than sawdust. Therefore, studies are needed to identify bedding materials which can replace sawdust and rice hulls.
Cocopeat originates from coconut husks, which are byproducts of some industries using coconuts. During processing of coconut husk the long fiber is removed and the coir fiber pith or coir dust is obtained. The pith or dust, a byproduct of extracting fibers from the husk of a coconut, is called cocopeat (Wikipedia, 2015). Coconut husks are composed of bristle fiber, mattress fiber and coir dust with shorts or wastes. Thus, cocopeat comes from the fiber portion of the coconut husks, and is used in building construction as fire resistant, insulation and acoustic panels. However, there were no studies about the use of cocopeat as a bedding material.
The objectives of this study are, i) To investigate the characteristics (water absorption rate, bulk density, particle size distribution, in vitro ammonia emission, concentration of moisture, moisture increment rate, ammonia and pH) of sawdust and cocopeat as a bedding material. ii) To evaluate the replacement possibility of cocopeat for sawdust beddings. iii) To evaluate the efficiency of using a fan for bedding materials. iv) To evaluate the location effect within a pen (feed bunk side [FB] vs water supply side [WS]) on bedding materials.
Both sawdust and cocopeat imported from two different countries were prepared to measure physicochemical properties and evaluate as bedding materials for Hanwoo cows. The raw material of sawdust was pine trees originating from Russia and New Zealand. Sawdust was obtained from a wood-processing company in Namdong industrial complex, Incheon, South Korea. Cocopeat were imported from India and Vietnam.
Particle size distribution of sawdust and cocopeat from India and Vietnam was measured by dry sieving (Testing sieve, Chunggyesanggongsa, Seoul, Korea). Unprocessed bedding samples (100 g) were passed through five mesh screens with sizes of 11.2, 3.35, 2.00, and 1.00 mm and 250 μm, respectively. Each bedding material retained by the mesh screen was weighed. Sieving test was replicated six times and the percentage of particle size distribution was calculated from the weight value.
Bulk density is a weight of each bedding materials per volume unit. In our study, bulk density was determined by calculating kilograms of each bedding material in a 100×100×5 cm (width×length×height) box and multiplied by 20 times for calculating weight of 1 cubic meter of each beddings. Because bedding materials are commonly imported and delivered as cubic meter units (kg/m3) in South Korea.
The water absorption rate of bedding materials was measured in a beaker with filtration through filter paper (No. 417, VWR, Radnor, PA, USA). Sawdust (40 g), cocopeat India (50 g), and Vietnam (50 g) put into a 500 mL tall beaker and filled with distilled water (DW). Six samples per bedding material were placed in a beaker and fully submerged in water for 24 h. Water absorption rate was calculated at 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, and 24 h after submersion. The water absorption rate was calculated as follows;
Unused dry bedding materials were allocated for evaluation of moisture evaporation rates. Before measuring moisture evaporation rates of bedding materials, triplicated 140 g of each bedding material were soaked in DW for over 24 hours.
Water-saturated bedding materials were placed onto an aluminum plate (17 cm, width×22 cm, length×5 cm, height), and a fan (SIF-20FOG, Shinil, Seoul, Korea) was operated at 2 m/s (measured by digital anemometers; AR-836, Smart Sensor, Guangdong, China) as the same condition as blowing fan environment at the farm. Moisture evaporation rate was calculated at every hour for 12 h.
Because of their different water absorption rates and other physicochemical characteristics of bedding materials, the numerical value of water absorbed in bedding materials would be different. Thus, moisture evaporation of bedding materials was calculated as a percentage rate rather than the amount of water absorbed and released. The moisture evaporation rate was calculated as follows;
In vitro ammonia emission experiments were conducted using a system of 4 laboratory chambers (Figure 1). Triplicate chambers were prepared for each bedding material.
The laboratory chamber system used in this study was similar to the system described by Misselbrook et al. (2005). The laboratory set-up chambers were made of glass (26 cm×20 cm×13 cm = 6.76 L) with a lid which connected to an acid trap to capture ammonia emission gas through fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) tubing. Glass chamber and FEP tube was used to minimize adsorption of ammonia. The chamber lid was fitted to the top with silicone airtight seal. Each chamber lid had inlet and outlet ports connected to acid traps.
A gas pump (13 watts, YP-15A, YONUGNAM AIR PUMP INC., Busan, Korea) was connected by FEP tubes to a manifold, air was pulled into each chamber and ammonia gas was pulled through FEP tube to an acid trap (100 mL of 0.9 M sulfuric acid; Burkholder et al., 2004). Acid traps were replaced with fresh traps at each sampling time (0, 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, and 36 h). Samples from each acid trap were sealed and refrigerated until the analysis of ammonia concentrations. Inlet acid traps were also used to remove ammonia gas from outside air.
Fresh feces were collected from Hanwoo cows and immediately composited and stored at 0°C. Distilled water was added to the mixture of bedding materials (400 g) and feces (200 g) to adjust moisture concentration at 60%. Although bulk density was different by the type of bedding materials, the height of the mixture in a measuring chamber became similar after mixing of bedding materials, feces and water. The quantity of feces added was equal to 1% of the daily excretion by a cow (Cole et al., 2005; Archibeque et al., 2007). According to the Korean feeding standard for Hanwoo (National Institute of Animal Science, 2012), daily excretion of feces and urine of a cow (487 kg) were 15.5 kg and 4.6 L (approximately 20 kg a day), respectively.
The empty space in the chamber after adding a mixture of bedding material and feces was 4.16 L. The flow rate through each chamber was controlled by gas flow meter (RMA-26-SSV, Dwyer Instruments, Michigan City, IN, USA) and airflow rate of each chamber was 4 L/min, thus the turnover rate of each chamber was approximately 1 time/min. All experiments were conducted at a constant room temperature (25°C). The ammonia concentration in the acid trap was analyzed as described by Chaney and Marbach (1962).
Ammonia emission (F, mg of N/m2/h) were calculated as;
Total ammonia emission value is total amount of ammonia emission from initial to each sampling time. Total ammonia emission value of each sampling time (F′, mg of N/m2) was calculated as;
Where, X is ammonia-N (NH3-N) concentration in an acid trap (mg/L), V is the volume of acid trap solution (L), A is the exposed surface area of a chamber (m2) and t is the duration of sampling period (h).
Data obtained from the analysis of physicochemical properties of bedding materials were subjected to statistical analysis using the general linear model (GLM) procedure of SAS (SAS Institute, 2002; version 9.01). Data were analyzed by analysis of variance and Duncan’s multiple range tests were used to determine significant differences (p<0.01 and 0.05) among bedding materials within each classification.
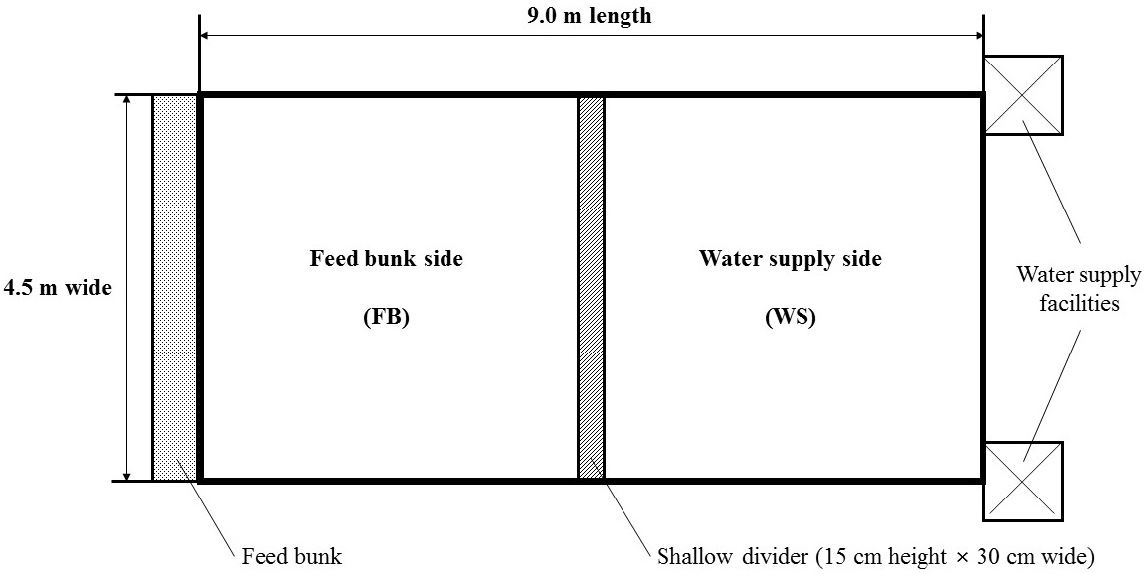
Experimental period was 56 days from September to November with 48 Hanwoo cows and three types of bedding materials in 16 pens. The cows were housed in pens (3 cows/pen; 4.5 m wide×9.0 m length = 40.5 m2/pen; 13.5 m2 for each cow) that had on one side a 4.5 m wide FB and another side equipped with WS. There was a shallow divider (15 cm height×30 cm wide) made of concrete between FB and WS. The ground plan of experimental pen is described in Figure 2.
Offered feeds in this study were rice straw and corn based concentrate (Roughage and concentrate ratio = 6:4, as fed basis). The chemical composition of the diets is described in Table 1. Feeds were offered 5 kg equally at 06:00 and 18:00 h on daily basis (10 kg/d for each cow). Cows were allowed to access fresh water and mineral block without any restriction during the whole experimental periods.
Experimental bedding materials were the same as Experiment I, i.e. sawdust and cocopeat from India and Vietnam. The group with sawdust bedding consisted of 12 cows with 4 pens, including fan treatment for 2 pens and no-fan treatment for 2 pens, respectively. Cocopeat India and Vietnam were consist of 18 cows in 6 pens, including fan treatment for 3 pens and no-fan treatment for 3 pens, respectively. The blowing fan (Diameter = 1,025 mm, 790 rpm; DVN-1007, Dongkun Industrial Co., Ltd, Incheon, Korea) was installed every two pen and working 24 h for fan treatments. The wind speed of a fan at the floor of pen was 2.00 m/s, measured by digital anemometers (AR-836, Smart Sensor, Guangdong, China).
Before bedding trial started, litters were removed and fresh bedding materials installed in the pens with a 5 cm-thickness. According to Kang et al. (1995), 5 cm thickness bedding was the most economical among 5, 10, 15, and 20 cm thickness of sawdust. The beddings were replaced with fresh bedding materials when moisture concentrations showed over 65%.
Bedding samples from all treatment pens were collected every week at 10:00 AM from 12 sampling spots per pen (grab sampling) to avoid sampling bias. Some part of bedding sample was dried for the determination of moisture concentration and increment rate (from the beginning of experiment) using a dry oven at 105°C overnight (SJ201D, Sejong Scientific Co., Seoul, Korea), and residual of sample was stored in freezer for ammonia (NH3-N) and pH (Model 530, Corning, Artington, UK). To estimate NH3-N concentrations in beddings, samples were centrifuged at 2,000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C and the supernatant was analyzed as described by Chaney and Marbach (1962). In brief, 0.02 mL of the samples were placed in glass tubes and 1 mL of phenol color reagent (50 g phenol and 0.25 g sodium nitroferricyanide per 1 L of DW) and alkali-hypochlorite reagent (25 g NaOH and 16.8 mL sodium hypochlorite per 1 L of DW) were added. Blue color was produced after incubation in water for 15 min at 37°C. For detecting OD (optical density) values, microplate reader (Gen5, Biotek instruments Inc, Winooski, VT, USA) was used after adding 8 mL of DW. The pH was measured with a sample-to-water ratio of 5 g to 30 mL using a pH meter (Model 530, Corning, Arlington, UK).
Data obtained from the analysis of on-farm trial were subjected to statistical analysis using the GLM procedure of SAS (SAS Institute, 2002; version 9.01). Data were analyzed by analysis of variance and Duncan’s multiple range tests were used to determine significant differences (p<0.01 and 0.05) among bedding materials within each classification.
The particle size distribution and bulk density of bedding materials are shown in Table 2. Sawdust and cocopeat India retained the smallest distribution of particles on sieve size with 11.2 mm screen (sawdust, 2.43%; cocopeat India, 5.45%), and cocopeat Vietnam retained the smallest distribution particles on sieve size with 2.00 mm screen (4.27%). Sawdust retained the largest distribution of particles size with 3.35 mm screen (27.9%) but cocopeat India and Vietnam retained the largest distribution of particles size with 250 μm screen (cocopeat India, 46.57%; Vietnam, 46.67%). The distribution of particles size with 250 μm+below 250 μm was the lowest (p<0.05) in sawdust (31.76%). Thus, sawdust contained larger distribution of big particle size than cocopeat India and Vietnam.
A lower proportion of 250 μm+below 250 μm was observed (p<0.05) in cocopeat India (59.70%) than Vietnam (69.20%), mainly due to higher proportion of particle size below 250 μm (India 13.13 vs Vietnam 22.53%). The particle size of bedding materials is important to avoid dust when operating fans or a blowing natural wind. According to Potgieter and Wilke (1996), smaller particles than 300 μm tends to make a dust generation problem. Cocopeat India and Vietnam emited a much larger amount of dust than sawdust during the on-farm trial (Experiment II), especially in the fan treatment, because cocopeat has a larger distribution of quite small particles (size with 250 μm+below 250 μm) than does sawdust.
Bulk density of three bedding materials were 104.5, 184.5, and 160.0 kg/m3 for sawdust and cocopeat India and Vietnam, respectively. Cocopeat India showed the highest bulk density (p<0.05) among the treatments, and cocopeat treatments showed 1.6 times higher bulk density than sawdust. Bulk density of bedding materials are affected by the particle size distribution and moisture concentration of bedding materials (Kim et al., 2007), because small particles have smaller gaps between each particle. Lower particle size of cocopeat treatments tends to increase the degree of bonding between particles, and as a consequence, showed higher bulk density than sawdust. In our study, moisture concentrations of sawdust and cocopeat India and Vietnam were 10.3%, 18.3%, and 13.0%, respectively. Moisture concentration of cocopeat India was higher than cocopeat Vietnam, thus bulk density of cocopeat India was higher than cocopeat Vietnam, despite of higher proportion of 250 μm+ < 250 μm in cocopeat Vietnam than India (69.2% vs 59.7%).
High bulk density usually has the disadvantage of increasing the transport cost, and reducing porosity and air capacity (Corti et al., 1998), which should be avoided in bedding materials. In South Korea, average price of sawdust and cocopeat including transport cost is KRW 105 and KRW 280 per kg, thus imported cocopeat is approximately 2.7 times more expensive than sawdust. In our study, the price of bedding materials per pen was KRW 22,219 and 97,694 for sawdust and cocopeat, respectively, considering bulk density and surface of pen (4.5 m wide×9.0 m length = 40.5 m2/pen; installed 5 cm height). Thus, using cocopeat for bedding material is approximately 4.4 times more expensive than sawdust. Because of the higher bulk density of cocopeat than sawdust, the gap of bedding cost between sawdust and cocopeat per pen become higher than the price gap of each bedding material itself (2.7 to 4.4 times higher).
The water absorption rates of bedding materials are shown in Table 3. After soaking bedding materials in water for 1 h, water absorption rate of bedding materials were increased up to 329.3% (sawdust), 514.9% (cocopeat India) and 557.9% (cocopeat Vietnam). Regardless of type of bedding materials, saturation occurred approximately at 4 h after submersion. Sawdust showed lower water absorption rate than cocopeat treatments (p<0.05) during all the experimental times. Water absorption rates after 12 h submersion were 443.8%, 701.7%, and 678.3% for sawdust, cocopeat India and Vietnam, respectively, thus cocopeat treatments showed approximately 1.5 times higher water absorption rate than sawdust.
Limited data are available about the water absorption rate of bedding materials. Olson (1940) reported a similar water absorption rate with sawdust (435%, 24 h after soaking in water) as this study. Lower cellulose concentration and the waxy surfaces of plant stems may contribute to the lower water absorption rate of sawdust in comparison to cocopeat. According to Olson (1940), water absorption for 24 h after soaking in water was 220%, 285%, and 228% for wheat straw, barley straw and oat straw, respectively. Ward et al. (2000) stated that wood shavings contained 80.1% distributions of passing 5 mm screen and showed high water holding capacity (more than 400%). Wood shavings originated from pine trees, the same as the sawdust in this experiment, thus more study is needed to evaluate wood shavings for bedding material.
Water absorption rates are important in cattle management, because they indicate the absorption rate of urine and ammonia (Misselbrook and Powell, 2005). In addition, low water concentration and soft floor surface is important for considering animal welfare (Burgess and Hutchinson, 2005).
Moisture evaporation rates are shown in Table 4. Blowing air at 2 m/s after 1 to 3 h from water saturation, moisture evaporation rates were slightly higher in sawdust than cocopeat, but did not show statistical differences. After 4 h blowing, moisture evaporation rate of cocopeat Vietnam (57.7%) was higher (p<0.05) than that of cocopeat India (51.4%), but sawdust (55.0%) was not different from cocopeat treatments. After blowing 5 h to the end of the experiment (12 h), cocopeat Vietnam showed the highest moisture evaporation rate (p<0.05), but no difference was detected between sawdust and cocopeat India. The determination of moisture evaporation rates of bedding materials ended after 8 h of blowing.
Moisture evaporations blowing after 1 to 3 h were numerically higher in sawdust than cocopeat, because sawdust containing large particles has higher porosity. On the other hand, cocopeat Vietnam containing high proportion of small particle size (250 μm+<250 μm) showed the highest moisture evaporation rates blowing after 4 h, because larger surface area of cocopeat Vietnam compared to sawdust may accelerate evaporation after ending of water-saturation.
Bedding materials can reduce ammonia emissions from cow housing. According to Chambers et al. (2003), ammonia emissions were 30% lower from a straw bedded housing system than from a slurry based system. Different bedding materials influence ammonia emissions in many ways (Misselbrook and Powell, 2005). The physical structure of the bedding material is important, influencing the extent to which urine drains through the bedding. Ammonia emissions will be reduced if the urine is absorbed or protected from air flow by a physical bedding layer.
Because ammonia holding capacity of bedding materials is quite important, there have been studies on the influence of bedding materials used in animal barns on ammonia emissions (Scholtens, 1990; Swierstra et al., 1995). However, on-farm trials may be incorrect because external factors, such as wind, humidity and amount of fecal load, influence the emissions. Thus, a laboratory chamber system is needed to accurately estimate ammonia holding capacity of bedding materials (Misselbrook and Powell, 2005).
In vitro ammonia emissions of beddings are shown in Table 5 and total ammonia emissions are shown in Table 6. Sawdust showed higher (p<0.05) ammonia emission than cocopeat India and Vietnam at 1, 3, and 6 h experimental sampling times, meaning lower ammonia absorption capacity for sawdust compared to cocopeat treatments. The ammonia emissions at 1 h were 7.37, 5.02, and 5.04 mg/m2/h for sawdust, cocopeat India, and Vietnam, respectively. The ammonia emissions were decreased dramatically from 1 to 3 h (7.37 to 4.12, sawdust; 5.02 to 1.70, cocopeat India; 5.04 to 0.81, cocopeat Vietnam), then decreased steadily. No significant differences among beddings were observed at 24 and 36 h. Average ammonia emissions from 1 to 36 h experimental times showed in order of sawdust>cocopeat India = Vietnam (sawdust, 2.71 mg/m2/h; cocopeat India, 1.59 mg/m2/h; cocopeat Vietnam, 1.22 mg/m2/h). There were no significant differences between cocopeat treatments, except at 12 h. Therefore, cocopeat showed higher (p<0.05) ammonia absorption capacity than sawdust.
Total ammonia emission values, meaning the total amount of ammonia emission from initial to each sampling time were higher (p<0.05) in sawdust than cocopeat India and Vietnam during the whole experimental times. Final ammonia emissions at 36 h were 37.02, 22.51, and 13.60 mg/m2 for sawdust, cocopeat India and Vietnam, respectively (p<0.05). Cocopeat Vietnam showed lower (p<0.05) ammonia emission values after 12 h than cocopeat India, probably because cocopeat Vietnam had almost double proportion of extremely fine particles (below 250 μm) than cocopeat India, thus having more surface area for ammonia absorption.
Cocopeat had higher proportions of fine particles and water absorption rates than sawdust, resulting in higher ammonia absorption capacity than sawdust. In addition, data from total ammonia emission also indicate that cocopeat has higher ability of ammonia absorption than sawdust.
Summarizing physicochemical properties of bedding materials, cocopeat treatments showed higher water absorption rate and ammonia absorption capacity than sawdust. In addition, cocopeat Vietnam showed the highest moisture evaporation rate among treatments, having outstanding characteristics for bedding materials. In contrast, bedding cost per pen was 4.4 times higher in cocopeat treatments than sawdust, and cocopeat treatments may not be free from dust generation problem, because of the high distribution of small particles (250 μm+<250 μm). Therefore, an on-farm trial (Experiment II) was needed to evaluate efficiencies of sawdust and cocopeat India and Vietnam for bedding materials.
Concentrations of moisture in bedding materials are presented in Table 7. Moisture concentrations were significantly different (p<0.01) by type of bedding materials, fan effect and location within a pen during the whole 8-week experimental periods. However, there were no significant 2-way and 3-way interactions among effects of bedding type, fan and pen location. The initial moisture concentrations were 10.3%, 18.3%, and 13.0% for sawdust, cocopeat India and Vietnam, respectively. Dramatic increase of moisture concentrations were observed from initial to week 1, moisture concentrations of sawdust and cocopeat India and Vietnam were 49.32%, 62.55%, and 59.04%, respectively.
Beddings were replaced with fresh bedding materials when moisture concentrations were over 65%, thus sawdust-fan-FB and the whole no-fan-FB were replaced with fresh bedding materials between 4 and 5 experimental weeks. Cocopeat-fan treatments did not reach 65% of moisture concentrations at 4 week. Therefore, cocopeat can be used twice longer than sawdust for bedding materials when using a blowing fan, and cocopeat Vietnam (54.4%) showed lower (p<0.01) average moisture concentrations than cocopeat India (60.9%).
Moisture concentrations of FB within a pen were higher (p<0.01) than those of WS during the whole experimental period. The differences of average moisture concentrations between FB and WS for fan treatments were 18.7%, 15.1%, and 13.3% unit, and no-fan treatments were 12.4%, 15.5%, and 13.5% unit for sawdust and cocopeat India and Vietnam, respectively (p<0.01). Thus, for maintaining low moisture concentrations of beddings within a pen, management of FB is more important than WS. Because cattle spent most of their time in FB within a pen for feeding, FB showed higher (p<0.01) moisture concentrations than WS regardless of bedding type.
Moisture concentrations of fan vs no fan treatment also showed significant differences (p<0.01) in all beddings, and all of no fan-FB treatments replaced with new bedding materials between 4 to 5 experimental weeks, while fan-FB except for sawdust did not reach 65% of moisture concentrations. Moreover, moisture concentrations of WS-fan treatments were kept below 55% regardless of type of bedding materials until 7 weeks.
Overall, cocopeat India showed higher moisture concentration than sawdust and cocopeat Vietnam, although sawdust-fan-FB was replaced with fresh new bedding materials between 4 to 5 weeks. These results are probably associated with the physical characteristics of bedding materials, considering that sawdust and cocopeat India showed lower moisture evaporation rates than cocopeat Vietnam (sawdust 71.2%, cocopeat India, 72.8%, and Vietnam, 80.4%).
According to Kweon et al. (1995), moisture concentrations of sawdust beddings for 1 week were 57.7% and 56.8% for 10 cm and 30 cm height, respectively. However to our knowledge, there are no published data on the usage of sawdust and cocopeat beddings including locations within a pen (FB and WS) and effect of a using fan.
Moisture increment rates in beddings are described in Table 8. Moisture increment rates were calculated by subtracting the moisture increment percentage from each experimental week to initial (0) week. There were no significant 2- or 3-way interactions among bedding type, fan effects, and location within a pen. However, average moisture increment rates were significantly different (p<0.01) by each treatment effect during the whole 8-week experimental periods. Average moisture increment rates of beddings for 8 weeks showed differences significantly (p<0.01) by bedding materials, fan treatment and location within a pen. The differences of moisture increment rate between FB and WS for fan treatments were 18.6%, 14.4%, and 13.1% unit and for no-fan treatments were 12.9%, 15.9%, and 13.5% unit for sawdust and cocopeat India and Vietnam, respectively (p<0.01).
During the 8 weeks of experimental period, FB showed higher (p<0.01) moisture increment rate than WS for all beddings, and fan vs no fan treatment also showed significant differences (p<0.01) in all beddings. Fan treatments showed lower moisture concentration and moisture increment rate than no fan treatment, thus using a blowing fan is essential for maximum usage of bedding materials in cattle management.
Because of the differences of particle size distribution, cocopeat India and Vietnam emitted larger amount of dust than sawdust during the on-farm trial, especially in the pen with fan. According to Hillman et al. (1992), dust often carries microbes and can absorb gases and serve as a means by which ammonia may be carried into deep lung tissue of cattle.
Summarizing moisture concentrations and increment rates, for FB within a pen, using cocopeat beddings extended twice period of bedding utilization than sawdust. Using a fan can extend twice the utilization period of bedding materials compared to no fan treatments, indicating that they are essential for maximum availability of bedding materials at farms. Between cocopeat treatments, using cocopeat Vietnam can maintain lower moisture concentrations than cocopeat India. But both cocopeat treatments showed dust problem in on-farm trial, because of the large amount of small particles.
Ammonia concentrations and pH of beddings are shown in Table 9 and 10. Ammonia concentrations of beddings indicate the capacity of bedding materials for holding ammonia emissions. Ammonia concentrations showed no significant interactions among treatments. Average ammonia levels for 8 weeks did not show significant differences for beddings, fan treatments, locations within a pen. However, fan treatment showed a tendency of lower ammonia level than no fan treatments (p<0.10). Thus, using a fan may have an effect on a ventilation of ammonia emissions.
According to Jeppsson (1999), high ammonia concentration in the bedding means low emissions of ammonia in the air. In this study, in vitro ammonia emissions and total ammonia emissions were lower in cocopeat treatments (p<0.05), but did not show any statistical difference in on-farm trial. Thus, evaluation of ammonia concentrations in the beddings at farm cannot be a suitable method for changes in ammonia situation, justifying the need of in vitro chamber trial.
Average pH levels for 8 week experimental period showed significant differences (p<0.01) for beddings, fan treatments, and location within a pen. According to Jeppsson (1999), pH of feces and urine was 7.7 to 9.8. Because feces and urine were mixed with bedding materials, the pH level of beddings in this experiment ranged from 7.0 to 8.9. There was no clear tendency in pH changes by the treatment effects, indicating pH measurement is not a recommended method for evaluation of bedding materials and (or) other effects.
Using cocopeat and a blowing fan can extend by twice the utilization period of beddings. Within a pen, WS showed twice the bedding-life compared to FB. Despite of outstanding physicochemical characteristics of cocopeat, using cocopeat bedding as an alternative for sawdust bedding is not recommended for farm management, considering 4.4 times higher bedding cost and a dust production problem.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by ‘Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ009156)’ Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Figure 1
Laboratory ammonia emission chamber system (similar to the system described by Misselbrook et al., 2005).

Table 1
Chemical composition of experimental diets1
| Items | Roughage2 | Concentrates3 |
|---|---|---|
| DM (%) | 60.0 | 88.1 |
| ———% of DM——— | ||
| CP | 4.4 | 19.1 |
| EE | 1.5 | 3.4 |
| Ash | 11.7 | 6.3 |
| CF | 36.8 | 8.2 |
| NDF | 63.8 | 22.4 |
| ADF | 37.2 | 11.0 |
| TDN | 41.6 | 71.0 |
| Ca | 0.48 | 0.43 |
| P | 0.34 | 0.10 |
Table 2
Particle size distribution and bulk density of bedding materials
| Particle size (%) | Sawdust | Cocopeat | SEM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||
| India | Vietnam | |||
| 11.2 mm | 2.43b | 5.45a | 5.50a | 1.02 |
| 3.35 mm | 27.90a | 8.10b | 6.54b | 2.87 |
| 2.00 mm | 16.33a | 6.80b | 4.27b | 1.67 |
| 1.00 mm | 21.53a | 20.90a | 14.40b | 1.28 |
| 250 μm | 24.93b | 46.57a | 46.67a | 3.24 |
| <250 μm | 6.83c | 13.13b | 22.53a | 2.56 |
| 250 μm+<250 μm | 31.76c | 59.70b | 69.20a | 4.24 |
| Bulk density (kg/m3) | 104.5c | 184.5a | 160.0b | 3.66 |
Table 3
The water absorption rate of bedding materials
| Time (h) | Sawdust (%) | Cocopeat (%) | SEM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||
| India | Vietnam | |||
| 1 | 329.3c | 514.9b | 557.9a | 1.02 |
| 2 | 361.0b | 558.8a | 588.0a | 10.04 |
| 3 | 418.8c | 604.1a | 617.2a | 9.19 |
| 4 | 444.0c | 610.9b | 664.9a | 8.29 |
| 8 | 443.8c | 702.0a | 665.0b | 7.31 |
| 12 | 443.8b | 701.7a | 678.3a | 10.11 |
| 24 | 443.9b | 697.1a | 676.8a | 15.59 |
Table 4
The moisture evaporation rate of bedding materials from water-saturation by blowing air at 2 m/s
| Time (h) | Sawdust (%) | Cocopeat (%) | SEM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||
| India | Vietnam | |||
| 1 | 20.9 | 16.8 | 16.0 | 5.03 |
| 2 | 37.8 | 32.2 | 31.6 | 5.32 |
| 3 | 48.7 | 44.4 | 45.7 | 4.24 |
| 4 | 55.0ab | 51.4b | 57.7a | 2.01 |
| 5 | 59.6b | 57.0b | 66.0a | 2.31 |
| 6 | 66.8b | 64.3b | 74.2a | 2.10 |
| 7 | 69.1b | 67.5b | 77.7a | 3.14 |
| 8 | 70.8b | 70.3b | 80.4a | 2.37 |
| 9 | 70.7b | 71.8b | 80.3a | 2.21 |
| 10 | 71.3b | 72.8b | 80.4a | 2.34 |
| 11 | 71.3b | 72.8b | 80.4a | 1.95 |
| 12 | 71.2b | 72.8b | 80.4a | 2.94 |
Table 5
Ammonia emissions of bedding materials measured by the chamber system
| Time (h) | Sawdust (mg/m2/h) | Cocopeat (mg/m2/h) | SEM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||
| India | Vietnam | |||
| 1 | 7.37a | 5.02b | 5.04b | 0.69 |
| 3 | 4.12a | 1.70b | 0.81b | 0.30 |
| 6 | 3.33a | 1.40b | 1.03b | 0.34 |
| 12 | 0.94ab | 1.24a | 0.24b | 0.24 |
| 24 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.09 |
| 36 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| Mean | 2.71a | 1.59b | 1.22b | 0.17 |
Table 6
Total ammonia emissions of bedding materials measured by the chamber system
| Time (h) | Sawdust (mg/m2) | Cocopeat (mg/m2) | SEM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||
| India | Vietnam | |||
| 1 | 7.36a | 5.02b | 5.04b | 0.69 |
| 3 | 15.61a | 8.42b | 6.64b | 0.61 |
| 6 | 25.61a | 12.63b | 9.72b | 1.03 |
| 12 | 31.23a | 20.08b | 11.17c | 1.18 |
| 24 | 34.74a | 21.70b | 12.79c | 1.34 |
| 36 | 37.02a | 22.51b | 13.60c | 1.34 |
Table 7
Effects of fan, type of beddings and pen location on moisture concentrations of beddings for Hanwoo1
| Week | Sawdust (%) | Cocopeat India (%) | Cocopeat Vietnam (%) | SE | p-values2 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Fan | No fan | Mean | Fan | No fan | Mean | Fan | No fan | Mean | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | Li | F | Lo | |||||
| 1 | 59.51 | 49.04 | 55.15 | 33.59 | 49.32 | 69.47 | 53.30 | 69.60 | 57.81 | 62.55 | 63.97 | 47.77 | 67.79 | 56.61 | 59.04 | 1.99 | 0.002 | 0.869 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 46.85 | 20.10 | 54.90 | 30.40 | 38.06 | 66.09 | 35.45 | 72.17 | 48.79 | 55.63 | 51.42 | 27.70 | 66.93 | 43.15 | 47.30 | 3.23 | 0.009 | 0.010 | <0.001 |
| 3 | 44.32 | 20.56 | 59.79 | 31.49 | 39.04 | 57.70 | 33.82 | 70.06 | 45.90 | 51.87 | 40.11 | 26.43 | 70.01 | 49.38 | 46.49 | 3.36 | 0.129 | 0.002 | <0.001 |
| 4 | 64.94 | 28.59 | 70.77 | 60.18 | 56.12 | 60.91 | 42.87 | 74.08 | 50.43 | 57.07 | 39.97 | 27.54 | 70.28 | 50.20 | 47.00 | 3.14 | 0.071 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 5 | 63.26 | 42.07 | 70.53 | 68.87 | 61.20 | 63.57 | 47.04 | 71.35 | 59.97 | 60.48 | 55.08 | 47.01 | 58.26 | 61.00 | 55.34 | 2.12 | 0.342 | 0.003 | 0.017 |
| 6 | 69.47 | 49.61 | 67.76 | 62.84 | 62.42 | 58.58 | 55.03 | 74.63 | 61.26 | 62.38 | 55.50 | 43.35 | 71.59 | 61.21 | 57.91 | 2.32 | 0.593 | 0.016 | 0.021 |
| 7 | 66.95 | 50.30 | 71.86 | 68.97 | 63.77 | 61.13 | 54.19 | 76.98 | 67.12 | 64.86 | 52.46 | 46.98 | 76.87 | 59.03 | 58.08 | 2.24 | 0.251 | 0.001 | 0.024 |
| 8 | 62.15 | 64.77 | 73.83 | 68.78 | 67.38 | 70.00 | 65.13 | 80.04 | 73.41 | 72.15 | 64.43 | 49.81 | 75.83 | 66.22 | 64.07 | 1.80 | 0.068 | 0.002 | 0.039 |
| Mean | 59.30 | 40.64 | 65.57 | 53.13 | 54.66 | 63.43 | 48.35 | 73.61 | 58.09 | 60.87 | 52.87 | 39.57 | 69.32 | 55.85 | 54.40 | 2.56 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Table 8
Effects of fan, type of beddings and pen location on moisture increment rates of beddings for Hanwoo1
| Week | Sawdust (%) | Cocopeat India (%) | Cocopeat Vietnam (%) | SE | p-values2 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Fan | No fan | Mean | Fan | No fan | Mean | Fan | No fan | Mean | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | Li | F | Lo | |||||
| 1 | 49.21 | 38.74 | 44.85 | 23.29 | 39.02 | 56.47 | 40.30 | 56.60 | 44.80 | 49.55 | 45.67 | 29.47 | 49.49 | 38.31 | 40.74 | 1.94 | <0.001 | 0.869 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 36.55 | 9.80 | 44.60 | 20.10 | 27.76 | 53.09 | 22.45 | 59.17 | 35.79 | 42.63 | 33.12 | 9.40 | 48.63 | 24.85 | 29.00 | 3.23 | <0.001 | 0.009 | <0.001 |
| 3 | 34.02 | 10.26 | 49.49 | 21.19 | 28.74 | 44.70 | 20.82 | 57.06 | 32.90 | 38.87 | 21.82 | 8.13 | 51.71 | 31.08 | 28.19 | 3.36 | 0.120 | 0.002 | <0.001 |
| 4 | 54.64 | 18.29 | 60.47 | 49.88 | 45.82 | 47.91 | 29.87 | 61.08 | 37.43 | 44.07 | 21.67 | 9.24 | 51.98 | 31.90 | 28.70 | 3.33 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 5 | 52.96 | 31.87 | 60.23 | 58.57 | 50.90 | 50.57 | 34.04 | 58.35 | 46.97 | 47.48 | 36.78 | 28.71 | 39.96 | 42.70 | 37.04 | 2.32 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.017 |
| 6 | 59.17 | 39.31 | 57.46 | 52.54 | 52.12 | 45.58 | 42.03 | 61.63 | 48.26 | 49.38 | 37.20 | 25.05 | 53.29 | 42.91 | 39.61 | 2.48 | 0.059 | 0.016 | 0.021 |
| 7 | 53.65 | 40.00 | 61.56 | 58.67 | 53.47 | 50.33 | 48.29 | 62.69 | 48.83 | 52.53 | 34.16 | 28.68 | 55.57 | 40.73 | 39.78 | 2.32 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.020 |
| 8 | 51.85 | 54.47 | 63.53 | 54.48 | 56.08 | 57.00 | 53.03 | 67.04 | 61.31 | 59.60 | 46.13 | 33.27 | 57.53 | 47.92 | 46.21 | 2.01 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.052 |
| Mean | 49.00 | 30.34 | 55.27 | 42.34 | 44.24 | 50.71 | 36.35 | 60.45 | 44.54 | 48.01 | 34.57 | 21.50 | 51.02 | 37.55 | 36.16 | 2.57 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Table 9
Effects of fan, type of beddings and pen location on ammonia concentrations of beddings for rearing Hanwoo cows1
| Week | Sawdust (mg/L) | Cocopeat India (mg/L) | Cocopeat Vietnam (mg/L) | SE | p-values2 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Fan | No fan | Mean | Fan | No fan | Mean | Fan | No fan | Mean | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | Li | F | Lo | |||||
| 1 | 219.67 | 137.72 | 190.93 | 164.52 | 178.21 | 175.78 | 188.74 | 188.10 | 188.10 | 185.18 | 244.11 | 213.56 | 180.92 | 180.92 | 204.88 | 7.24 | 0.305 | 0.331 | 0.160 |
| 2 | 129.23 | 97.69 | 158.62 | 155.80 | 135.33 | 151.28 | 157.09 | 162.58 | 234.77 | 176.43 | 251.28 | 188.21 | 200.41 | 244.52 | 221.10 | 11.07 | 0.008 | 0.134 | 0.834 |
| 3 | 171.39 | 93.69 | 166.29 | 115.57 | 136.73 | 237.54 | 152.75 | 239.62 | 49.05 | 169.74 | 210.87 | 226.77 | 218.51 | 183.43 | 209.89 | 14.15 | 0.070 | 0.408 | 0.008 |
| 4 | 231.67 | 184.17 | 210.93 | 254.00 | 220.19 | 212.22 | 237.22 | 159.90 | 242.46 | 212.95 | 247.59 | 214.44 | 210.83 | 231.18 | 226.01 | 11.45 | 0.910 | 0.911 | 0.576 |
| 5 | 318.00 | 234.92 | 494.16 | 334.93 | 345.50 | 118.43 | 134.15 | 210.05 | 116.72 | 144.84 | 220.99 | 251.08 | 210.56 | 165.44 | 212.02 | 27.75 | 0.031 | 0.452 | 0.324 |
| 6 | 427.39 | 261.23 | 134.31 | 131.74 | 238.67 | 157.64 | 249.95 | 279.01 | 229.44 | 229.01 | 144.99 | 171.49 | 274.56 | 260.72 | 212.94 | 24.43 | 0.920 | 0.743 | 0.718 |
| 7 | 279.82 | 154.97 | 153.43 | 155.20 | 185.85 | 148.61 | 192.61 | 127.64 | 141.42 | 152.57 | 179.31 | 247.60 | 121.42 | 133.12 | 170.36 | 20.16 | 0.852 | 0.202 | 0.959 |
| 8 | 245.50 | 214.67 | 145.00 | 157.50 | 153.17 | 83.56 | 235.59 | 105.19 | 17.78 | 110.53 | 400.22 | 149.11 | 148.89 | 76.48 | 193.67 | 32.03 | 0.540 | 0.047 | 0.287 |
| Mean | 206.71 | 252.83 | 164.91 | 172.38 | 199.21 | 184.01 | 160.64 | 152.47 | 193.51 | 172.66 | 195.76 | 237.42 | 184.48 | 207.78 | 206.36 | 23.54 | 0.111 | 0.067 | 0.123 |
Table 10
Effects of fan, type of beddings and pen location on pH concentrations of beddings for rearing Hanwoo cows1
| Week | Sawdust | Cocopeat India | Cocopeat Vietnam | SE | p-values2 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Fan | No fan | Mean | Fan | No fan | Mean | Fan | No fan | Mean | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | FB | WS | Li | F | Lo | |||||
| 1 | 8.33 | 8.22 | 7.91 | 7.03 | 7.87 | 8.32 | 8.29 | 7.99 | 7.96 | 8.14 | 8.31 | 8.31 | 7.84 | 8.04 | 8.13 | 0.06 | 0.007 | <0.001 | 0.043 |
| 2 | 8.79 | 8.85 | 8.51 | 8.44 | 8.65 | 8.61 | 8.67 | 8.11 | 8.32 | 8.43 | 8.75 | 8.65 | 8.10 | 8.41 | 8.50 | 0.05 | 0.120 | <0.001 | 0.415 |
| 3 | 8.75 | 8.76 | 8.59 | 8.61 | 8.68 | 8.49 | 8.26 | 8.29 | 8.20 | 8.31 | 8.63 | 8.50 | 8.30 | 8.35 | 8.45 | 0.04 | 0.008 | 0.047 | 0.458 |
| 4 | 8.91 | 8.82 | 8.68 | 8.79 | 8.80 | 8.64 | 8.38 | 8.29 | 8.32 | 8.48 | 8.79 | 8.69 | 8.60 | 8.52 | 8.65 | 0.04 | 0.006 | 0.094 | 0.114 |
| 5 | 8.51 | 8.61 | 8.81 | 8.68 | 8.65 | 8.67 | 8.47 | 8.43 | 8.08 | 8.41 | 8.89 | 8.19 | 8.75 | 8.03 | 8.47 | 0.06 | 0.200 | 0.367 | 0.004 |
| 6 | 8.75 | 8.35 | 8.63 | 8.21 | 8.48 | 8.20 | 8.17 | 8.34 | 7.86 | 8.14 | 8.57 | 8.08 | 8.74 | 8.13 | 8.38 | 0.06 | 0.040 | 0.732 | 0.001 |
| 7 | 8.32 | 8.38 | 8.26 | 8.31 | 8.32 | 8.24 | 7.81 | 8.45 | 7.25 | 8.09 | 8.56 | 8.20 | 8.63 | 8.09 | 8.37 | 0.06 | 0.088 | 0.925 | 0.013 |
| 8 | 8.31 | 8.34 | 8.43 | 8.31 | 8.35 | 8.42 | 8.06 | 8.43 | 7.79 | 8.18 | 8.38 | 8.08 | 8.62 | 7.95 | 8.26 | 0.06 | 0.381 | 0.915 | 0.002 |
| Mean | 8.58 | 8.54 | 8.48 | 8.29 | 8.47 | 8.45 | 8.27 | 8.32 | 8.05 | 8.27 | 8.61 | 8.34 | 8.46 | 8.19 | 8.40 | 0.07 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
REFERENCES
Archibeque SL, Freetly HC, Cole NA, Ferrell CL. 2007. The influence of oscillating dietary protein concentrations on finishing cattle. II. Nutrient retention and ammonia emissions. J Anim Sci 85:1496–1503.


Burkholder KM, Guyton AD, McKinney JM, Knowlton KF. 2004. The effect of steam flaked or dry ground corn and supplemental phytic acid on nitrogen partitioning in lactating cows and ammonia emission from manure. J Dairy Sci 87:2546–2553.


Chambers BJ, Williams JR, Cooke SD, Kay RM, Chadwick DR, Balsdon SL. 2003. Ammonia losses from contrasting cattle and pig manure management systems. Agriculture, Waste and the Environment. McTaggart I, Gairns L, editorsScottish Agricultural College; Edinburgh, UK: p. 19–25.
Chaney AL, Marbach EP. 1962. Modified reagents for determination of urea and ammonia. Clin Biochem 8:130–132.

Cole NA, Clark RN, Todd RW, Richardson CR, Gueye A, Greene LW, McBride K. 2005. Influence of dietary crude protein concentration and source on potential ammonia emissions from beef cattle manure. J Anim Sci 83:722–731.


Corti C, Crippa L, Genevini PL, Centemero M. 1998. Compost use in plant nurseries: Hydrological and physicochemical characteristics. Compost Sci Util 6:35–45.

Hillman P, Gebremedhin K, Warner R. 1992. Ventilation system to minimize airborne bacteria, dust, humidity, and ammonia in calf nurseries. J Dairy Sci 75:1305–1312.


Hogan JS, Smith KL, Hoblet KH, Todhunter DA, Schoenberger PS, Hueston WD, Pritchard DE, Bowman GL, Heider LE, Brockett BL, Conrad HR. 1989. Bacterial counts in bedding materials used on nine commercial dairies. J Dairy Sci 72:250–258.


Jeppsson KH. 1999. Volatilization of ammonia in deep-litter systems with different bedding materials for young cattle. J Agric Eng Res 73:49–57.

Kang HS, Hong SK, Cho WM, Paek BH, Park CH, Lee DS. 1995. Effects of sawdust and rice hulls litter on the waste management of Hanwoo (Korean native cattle). Korean Soc Livest Hous Environ 1:1–8.
Kim YS, Kim BT, Lee CH. 2007. Variations of physical properties depending on the height of reactor in vertical composting process. J KORRA 15:115–124.
Kweon DJ, Kweon UG, Jeong SG, Han JD, Jung SC, Kang SW, Kang SL, Jung HS, Chang HJ. 1995. Study on the utilization of sawdust bedding barn for dairy cows. Korean Soc Livest Hous Environ 1:117–124.
Misselbrook TH, Powell JM. 2005. Influence of bedding material on ammonia emissions from cattle excreta. J Dairy Sci 88:4304–4312.


Misselbrook TH, Powell JM, Broderick GA, Grabber JH. 2005. Dietary manipulation in dairy cattle: Laboratory experiments to assess the influence on ammonia emissions. J Dairy Sci 88:1765–1777.


National Institute of Animal Science. 2012. Korean Feeding Standard for Hanwoo. 3rd EdRural Development Administration; Jeonju, Korea:
Olson TM. 1940. Absorptive capacity of different materials ordinarily used for bedding. J Dairy Sci 23:355–360.

Potgieter FJ, Wilke PI. 1996. The dust content, dust generation, ammonia production, and absorption properties of three different rodent bedding types. Lab Anim 30:79–87.


RSPCA (Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals). 2015. The five freedoms. https://www.rspca.org.uk/servlet/Satellite?blobcol=urlblob&blobheader=application%2Fpdf&blobkey=id&blobtable=RSPCABlob&blobwhere=1210683196122&ssbinary=trueAccessed September 30, 2015
SAS User’s guide. 2002. Statistics, Version 9.01 Edition. SAS Inst, Inc; Cary. NC, USA:
Scholtens R. 1990. Measurements of ammonia emission in mechanically ventilated animal houses. In : VDI/KTBL-Symposium, Ammoniak in der Umwelt; Kreislaufe, Wirkungen, Minderung. 20.1-20.9
Swierstra D, Smits MCJ, Kroodsma W. 1995. Ammonia emission from cubicle houses for cattle with slatted and solid floors. J Agric Eng Res 62:127–132.

Tucker CB, Weary DM, Fraser D. 2003. Effects of three types of free-stall surfaces on preferences and stall usage by dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 86:521–529.


Ward PL, Wohlt JE, Zajac PK, Cooper KR. 2000. Chemical and physical properties of processed newspaper compared to wheat straw and wood shavings as animal bedding. J Dairy Sci 83:359–367.


Webster AJF. 1993. Understanding the Dairy Cow. 2nd edBlackwell; Oxford, UK:





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





