 |
 |
| Anim Biosci > Volume 29(1); 2016 > Article |
|
Abstract
This study investigated the dynamics associated with prolonged ensiling and aerobic deterioration of whole crop corn (WCC) silages and total mixed ration (TMR) silages containing WCC (C-TMR silages) to clarify the differences that account for the enhanced aerobic stability of TMR silages. Laboratory-scale barrel silos were randomly opened after 7, 14, 28, and 56 d of ensiling and were subjected to analyses of fermentation quality, microbial and temperature dynamics during aerobic exposure. WCC and C-TMR silages were both well preserved and microorganisms were inhibited with prolonged ensiling, including lactic acid bacteria. Yeast were inhibited to below the detection limit of 500 cfu/g fresh matter within 28 d of ensiling. Aerobic stability of both silages was enhanced with prolonged ensiling, whereas C-TMR silages were more aerobically stable than WCC silages for the same ensiling period. Besides the high moisture content, the weak aerobic stability of WCC silage is likely attributable to the higher lactic acid content and yeast count, which result from the high water-soluble carbohydrates content in WCC. After silo opening, yeast were the first to propagate and the increase in yeast levels is greater than that of other microorganisms in silages before deterioration. Besides, increased levels of aerobic bacteria were also detected before heating of WCC silages. The temperature dynamics also indicated that yeast are closely associated with the onset of the aerobic deterioration of C-TMR silage, whereas for WCC silages, besides yeast, aerobic bacteria also function in the aerobic deterioration. Therefore, the inclusion of WCC might contribute to the survival of yeast during ensiling but not influence the role of yeast in deterioration of C-TMR silages.
Aerobic deterioration is a critical problem affecting not only the nutritive value of feed but also the health of animals and humans (Woolford, 1990). Numerous studies have been conducted on silages to date and have reached some consensus regarding aerobic stability. According to these studies, not only fermentation products such as organic acids (Filya, 2003) and antifungal products (Wilkinson and Davies, 2013), but also yeast populations (particularly lactate-utilizing yeasts) observed at silo opening could influence the aerobic stability of silage (Woolford, 1990). The presence of yeasts is reported to be an indication of the initiation of aerobic deterioration because the growth of yeast often coincides with the heating of silages and the oxidization of the preserving acids that generally initiate aerobic spoilage. Besides, researches also indicate the role of bacteria (likely acid-tolerant bacteria) in the initial deterioration of whole crop corn (WCC) silages (Spoelstra et al., 1988).
WCC is regarded as an ideal crop for silage making due to its high yields, nutritive value, low buffering capacity and high water-soluble carbohydrates (WSC) content (McDonald, 1981). However, it is very prone to spoilage when exposed to air. It has been indicated that the aerobic stability could be greatly enhanced if formulated as total mixed ration (TMR) silage in comparison with ensiled alone (Nishino et al., 2003). There is also evidence that enhanced aerobic stability could be detected with prolonged ensiling, and yeast seemed to play less role in aerobic deterioration of TMR silages formulated with peach pomace, which had a high WSC content of 25.9% on dry matter (DM) basis (Hu et al., 2015). However, little information could be found for TMR silage, particularly regarding the mechanisms resulting in its enhanced aerobic stability compared with that of common silage. It is necessary to clarify the dynamics associated with aerobic deterioration of common silages and TMR silages to have a deep understanding on aerobic stability of TMR silages. Considering the enhanced aerobic stability of TMR silage with prolonged ensiling and the aerobically unstable WCC, this study was conducted on TMR silages inclusive of WCC. WCC silages were also used to reveal the dynamics associated with prolonged ensiling and aerobic deterioration of TMR silages containing WCC (C-TMR silages) and clarify the differences that account for the enhanced aerobic stability in TMR silages.
The WCC and agro-industry by-products used in this study were all available local materials obtained from Hebei Province in China. WCC (Zhongke 11, a high yield corn) was harvested at the milk stage, chopped to a length of 2 to 3 cm, formulated as a C-TMR by a TMR mixer (Labrador, Storti, Italy) and then ensiled within the day of production. The C-TMR was prepared using WCC, soybean curd residue, soy sauce residue, corn starch residue, rice bran, corn meal, alfalfa, cotton meal, wheat bran, soybean meal, and a vitamin-mineral supplement at a ratio of 20:10:2.5:9:27:10:8:5:4:2:2.5 on a DM basis. WCC and C-TMR were packed tightly into high-density polyethylene barrels (60-L capacity), and each barrel was sealed with a polyethylene cover using a gasket fixed by a steel circlip. Triplicate barrels were randomly opened after 7, 14, 28, and 56 d of ensiling at ambient temperature.
Non-fermented WCC and C-TMR samples were collected immediately after thorough mixing, and silage samples were collected at the time of silo opening and during the aerobic exposure periods. The DM content was determined by drying the material in an oven at 60°C for 48 h and grinding the dried material to pass through a 1-mm screen. The DM, crude protein (CP) and crude ash were analysed according to methods 934.01, 976.05 and 942.05, respectively, of the AOAC (1990). The organic matter (OM) was calculated as the weight loss upon ashing. The acid detergent fiber (ADF) and neutral detergent fiber (aNDF) are analysed by the methods described by Van Soest et al. (1991) with amylase and sodium sulphite, and the results were expressed inclusive of residual ash. The WSC concentration was determined using the method of Owens et al. (1999).
The fermentation qualities were determined from water extracts of the silage. The pH was measured using a glass electrode pH meter (S20K, Mettler Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland), and the organic acid content was determined by HPLC using the procedures described by Xu et al. (2007a).
The numbers of microorganisms in the fresh material and silage samples were measured through the plate count method (Hu et al., 2015). Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) were counted from MRS agar prepared using MRS broth (Difco, Detroit, MI, USA) with 1.6% agar, after incubation in an anaerobic incubator at 35°C for 3 d. The microbial counts for aerobic bacteria were determined on Nutrient Agar (Nissui, Tokyo, Japan), whereas for enterobacteria using Blue Light Broth (Nissui) with additional 1.6% agar, and incubated at 30°C for 2 d. Yeast were enumerated on spread plates of Potato Dextrose Agar (Nissui) that had been acidified to pH 3.5 with sterilized tartaric acid. The plate cultures were incubated at 25°C for 3 to 5 d. The colonies were counted from the plates at appropriate dilutions, and the number of colony forming units (cfu) is expressed per gram of fresh matter (FM).
Non-fermented WCC and C-TMR were used as controls for comparing aerobic stability with the corresponding silages promptly after preparation. Silages ensiled for 7, 14, 28, and 56 d were used for aerobic stability tests immediately following silo opening. After silo opening, the surface silage layers were removed, and the underlayers were scattered thoroughly. After emptying a silo, about 10 kg of the thoroughly mixed contents were placed loosely back into the barrel without compaction. A thermocouple thermometer (Datataker, Victoria, Australia) was inserted into the core of the sample mass to obtain temperature data. The changes in the ambient temperature and sample temperature were monitored every 10 min, and the recording duration varied from 5 to 25 d depending on the extent of aerobic deterioration. All of the barrels were maintained at room temperature of approximately 20°C and partly covered to avoid water loss and allow air penetration.
The aerobic stability was distinguished by the length of time expended once the difference between the sample temperature and surrounding temperature reached 2°C. Silage was considered to have deteriorated when its temperature was 2°C above the ambient temperature.
All of the microbial counts were log10-transformed to obtain normally distributed data and are presented on a wet basis. The counts that below the detection limit (500 cfu/g FM) were assigned a value corresponding to half of the detection limit for subsequent statistical analysis. The fermentation characteristics, microbial counts, aerobic stability and chemical compositions during ensiling were statistically analysed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s test for the post hoc analysis using the IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows ver. 20.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). The statistical significance was set as p<0.05.
The chemical and microbial compositions of WCC and C-TMR prior to ensiling are shown in Table 1 and 2. The values for WCC are typical of graminaceous plants, with high WSC levels, a high moisture content and a low CP content. When incorporated into TMR, both the DM and CP contents improved. The microbial compositions of both WCC and C-TMR were detected at levels exceeding 106 cfu/g FM, particularly for C-TMR.
Irrespective of ensiling periods, all of the silages were well-preserved with relatively low pH and high lactic acid content (Table 2). As observed for the main fermentation acids, lactic acid increased markedly within the first 7 d and reached peak values of 130 g/kg DM at day 28 post-ensiling for WCC silage and 86 g/kg DM at day 14 for C-TMR silage. Both the lactic and acetic acid (on DM basis) levels were higher in WCC silage than the acid levels in C-TMR silage during the same ensiling period, whereas, high ratio of lactic acid to acetic acid was detected in C-TMR silage. Furthermore, the ratio decreased significantly (p<0.001) with prolonged ensiling of WCC silages, whereas for C-TMR silages, the ratio tended to increase with the extension of ensiling.
Microorganisms of both silages were inhibited to different extents. Yeast became undetected within 28 d of ensiling, whereas enterobacteria were not detected after less than seven days. Aerobic bacteria were also inhibited within 7 d of ensiling. In addition, LAB that were detected at high levels of over 106 cfu/g in WCC and C-TMR, were also inhibited with prolonged ensiling. Significant differences were also detected in the chemical components, with the exception of the content of aNDF in WCC silages and the contents of OM and ADF in C-TMR silages, which remained stable throughout the ensiling periods. The OM content of WCC decreased with prolonged ensiling. The DM contents of both WCC and C-TMR silages decreased by approximately 20 g/kg during the 56-d ensiling period and approximately 15 g/kg occurred within the first 7 d of ensiling. The WSC in fresh WCC was consumed by more than 75%, mostly during first 7 d of ensiling. The content of CP increased for both silages, and aNDF decreased with ensiling, particularly for C-TMR silage. The content of ADF increased in WCC silage, whereas in C-TMR, the content tended to decrease.
For non-fermented WCC and C-TMR, deterioration occurred within 6 h of aerobic exposure. However, the aerobic stability was greatly enhanced (p<0.001) with prolonged ensiling, particularly for C-TMR silages (Table 2). When the ensiling period was prolonged to 56 d, WCC silage resisted deterioration for as long as 144 h, whereas C-TMR silage resisted deterioration for 411 h. Overall, the aerobic stability of C-TMR silages were approximately two-fold greater than that of WCC silages during the same ensiling period.
The changes of fermentation quality in non-fermented WCC and C-TMR after exposure to air are shown in Figure 1. Similarities were observed during the first 24 h of exposure. During the initial 6 h, both materials exhibited an increased lactic acid content and a reduction in pH. After 24 h of exposure, the lactic and acetic acid in both WCC and C-TMR started to decrease and were reduced to a lower level in WCC (until 120 h of exposure), whereas in C-TMR, the acid levels increased again after 48 or 72 h of exposure, and pH decreased accordingly from 7.1 to 5.8.
After silo opening, all of the silages experienced a longer and more stable period before silage heating (2°C above room temperature) occurred. During the deterioration of WCC silages, all of the acids decreased throughout the detection periods, and the pH increased accordingly from 3.6 to levels above 7.0 (Figure 2). Similar tendency was also observed in C-TMR silages, which encountered a pH increase from 4.0 to above 6.7 after exposure (Figure 3). Thereafter, pH changes differed by ensiling periods. For the short-ensiled (7 and 14 d) C-TMR silages, the pH decreases to levels below 6.0 and later increased again to higher levels. However, the long-ensiled (28 and 56 d) C-TMR silages encountered a pH increase throughout the deterioration periods, except for a likely decrease of pH in the 28-d C-TMR silage (at 432 h).
The microbial dynamics of non-fermented WCC and C-TMR after exposure are shown in Figure 4. Similar changes were detected in both materials. The yeast levels decreased during the first 6 h, increased to higher levels until 48 h and then decreased again. Other microorganisms in C-TMR exhibited changes similar to those found for yeast during the first 24 h. The microorganisms in WCC other than yeast exhibited an opposite trend during the first 12 h of exposure.
The microbial dynamics of WCC and C-TMR silages after aerobic exposure are shown in Figure 5 and 6. The LAB counts of WCC silages mostly remained at approximately 108 cfu/g FM before aerobic deterioration. However, the aerobic bacteria and yeast levels both increased before deterioration, particularly the yeast, which exhibited a earlier and greater increase before aerobic deterioration. For WCC silages that were ensiled for 7, 14, 28, and 56 d, the maximum yeast counts (about 108 cfu/g FM) occurred at about 72, 96, 120, and 168 h after exposure, respectively. Irrespective of ensiling periods, enterobacteria started to proliferate after deterioration. Similar results were found for C-TMR silages, irrespective of the ensiling periods. The yeast levels increased significantly before silage heating, and this was particularly true for the long-ensiled C-TMR silages, in which the yeast levels were below the detection limit at silo opening. Irrespective of ensiling periods, the peak value of yeast counts is equivalent (about 108 cfu/g FM). In addition, for C-TMR silages ensiled for 7, 14, 28, and 56 d, the maximum yeast counts occurred after about 144, 168, 360, and 456 h of exposure, respectively. LAB counts all kept at lower level of 106 cfu/g FM before deterioration, which is similar to the level of aerobic bacteria. Aerobic bacteria counts were detected to increase in deteriorated C-TMR silages. Whereas, LAB and enterobacteria occasionally increased prior to deterioration but never before the proliferation of yeast.
The temperature of non-fermented WCC and C-TMR increased to 30°C within 6 h of exposure, reached 40°C after 9 h and 16 h, respectively, and then remained above 40°C until the end of the monitoring period (120 h). WCC and C-TMR silages exhibited different temperature dynamics during aerobic exposure. Only one temperature peak was detected in WCC silages after exposure, ignoring the temperature variations caused by periodic mixing (Figure 7). The peak values of WCC silages ensiled for 7, 14, 28, and 56 d were observed after about 128, 109, 162, and 166 h of exposure, respectively, which were varied from 48°C to 42°C. However, two peaks were detected in C-TMR silages during the monitoring periods, ignoring the periodic temperature variations (Figure 8). The first peak temperature of C-TMR silages ensiled for 7, 14, 28, and 56 d were detected at approximately 162, 173, 323, and 438 h, respectively, and the peak values decreased from 54°C to 45°C with prolonged ensiling periods. Furthermore, the first temperature peak tended to be lower with the extension of ensiling, particularly C-TMR silages. The duration of the first heating was decreased with prolonged ensiling, especially for that of WCC silages. It is notable that the temperature minimum of C-TMR silages after the first peak was concomitant with a pH decrease for the short-ensiled silages, whereas with a pH increase for the long-ensiled C-TMR silages, which has no pH decrease during the entire monitoring periods.
TMR silages incorporated with locally available byproducts and WCC obtained good fermentation quality and aerobic stability in this study. The result is consistent with our previous studies (Xu et al., 2007a,b; Hu et al., 2015), which indicated that high-moisture food by-products can be formulated as TMR silage. This may be attributed to the sufficient WSC contents in WCC and C-TMR (144 and 63.2 g/kg) to meet the requirement for obtaining well-preserved silage (Smith, 1962). Therefore, good fermentation quality could be expected even though high numbers of aerobic bacteria and yeast were detected in non-fermented WCC and C-TMR.
It has been confirmed by many researches that yeasts are primarily responsible for the onset of the aerobic spoilage of silage (McDonald et al., 1991). In this study, the microbial dynamics of WCC and TMR silages after opening also verified the role of yeast in the initiation of deterioration, as indicated by the fact that yeast were the first to propagate and the increase in yeast levels is greater than that of other microorganisms in silages before deterioration. Besides, aerobic bacteria also played important role in the deterioration of WCC silages because increased levels of aerobic bacteria were also detected before heating. Moreover, the first temperature peak of C-TMR silages almost coincided with the maximum yeast count, while for WCC silages, comparable numbers of aerobic bacteria and yeast were detected when the silages reached their temperature peak. Therefore, yeast probably initiated the deterioration of C-TMR silages, whereas for WCC silages, yeast and aerobic bacteria both functioned in aerobic deterioration. The results are inconsistent with previous studies on maize silages the first temperature peak is associated with the development of yeasts and aerobic acetic acid bacteria and the second temperature increase is a reflection of mold development (Wilkinson and Davies, 2013). The detection of high levels of aerobic bacteria in aerobically deteriorated WCC and C-TMR silages indicated the role of aerobic bacteria in the late deterioration, which agreed with the studies conducted by McDonald et al. (1991) and Seppala et al. (2013). Furthermore, enterobacteria played less role in silages with low pH as they were mostly observed in deteriorated silages. It is consistent with the results that enterobacteria do not proliferate and their viability decreases at pH values lower than 4.5 to 5.0 (Heron et al., 1993). Overall, multiple microorganisms contribute to the dynamic changes observed after aerobic exposure, and yeast were closely associated with the onset of aerobic deterioration of silages, particularly C-TMR silages.
In this study, the LAB of over 106 cfu/g detected in fresh WCC and C-TMR contributed to good fermentation quality in silages, whereas for aerobic exposed WCC and C-TMR, caused an accumulation of lactic acid, decrease in pH and inhibition of yeast at the initial period, however, coincided with a notable heat and followed by increased pH. The properties (residue or meal) of TMR ingredients, which could easily form a relatively anaerobic condition after put back without compaction, might also account for the lactic acid fermentation. In this study, the microbial populations of WCC and C-TMR were all above 106 cfu/g FM and deteriorated within 6 h of aerobic exposure. It is consistent with previous studies that silages with over 105 cfu/g of yeast are prone to spoil when exposed to air (McDonald et al., 1991). With prolonged ensiling, the yeast counts fell below the detectable level, further improving the aerobic stability due to the absence of undesirable microorganisms. Similar results were also obtained in our previous study on TMR silages with different moisture contents (Hao et al., 2015), which also indicates that TMR silages with higher moisture content are relatively unstable (Hao et al., 2015). In this study, C-TMR silages were more aerobically stable than WCC silages for the same ensiling period. Besides the high moisture content, the weak aerobic stability in WCC silage is likely attributable to the high lactic acid content and high yeast count, which result from the high WSC content. This finding conforms to conclusions that well-fermented silages with high residual sugars and lactic acid are prone to spoil because they can be used as substrates by yeasts (McDonald et al., 1991). Furthermore, the high WSC content appeared to favor high levels of yeast in the resulting silage, as the fermentation of sugars (the only source of energy for yeast under anaerobic conditions) could provide energy to export the H+ ions that will reduce the intracellular pH and kill the cell, thereby, counteract the harmful effect of H+ ions on yeast (McDonald et al., 1991; Pahlow et al., 2003). It is similar to the conclusion that yeasts are favored by the addition of formic acid because increased amounts of residual sugars contributed to its survival (Henderson et al., 1972). In our previous laboratory experiments, even longer aerobic stability has been observed in TMR silage with materials other than WCC (Hao et al., 2015). Therefore, the inclusion of WCC in C-TMR might contribute to the survival of yeast in this study.
It is common that aerobic deterioration is accompanied by a temperature increase, pH changes, and an increase in yeast counts. The increase in temperature by 2°C above the ambient temperature is mostly adopted to evaluate aerobic deterioration. It has been indicated that the temperature increase in silage is associated with the microbial oxidation of acids and WSC to carbon dioxide and water (Ranjit and Kung, 2000). Results also indicated that the rise in temperature is greater in crops of higher DM concentration than in those of lower DM concentration, because more heat is required to raise the temperature of wetter material than is needed for drier material (Wilkinson and Davies, 2013). This might account for the higher peak temperature in C-TMR silages than that of WCC silages during the same ensiling period. In this study, a rise in silage pH was concomitant with heating, which is attributed to that lactic and other acids can be used as substrate by acid-resistant microorganisms. The metabolism of antifungal organic acids and the increase in silage pH facilitate the development of other less acid-tolerant aerobic microorganisms (e.g., molds, bacilli) (Woolford, 1990). In addition, the catabolism of protein to NH3 also contributes to the increase in pH (Rooke and Hatfield, 2003). However, for short-ensiled C-TMR silages, a decline in pH was observed after it increased to approximately 7.0. The slowly decreased lactic acid and increased acetic acid contents (on DM basis) that were probably caused by DM losses in the late deterioration may partly account for the pH decrease. No other suitable explanation could be made based on the current data. Decreased pH during deterioration were also reported in silages with high original pH (higher than 5.0), which presumably because of the restricted fermentation due to high DM contents (Ohyama et al., 1975). However, no pH decline was observed for the long-ensiled C-TMR silages during exposure. This probably due to the length of deterioration, which was not sufficiently long to reach the peak value, or the fact that no pH decrease would be observed during exposure.
As indicated by Seppala et al. (2013), a small quantity of sample would increase the rate of heat loss of the sample relative to heat production, thus hindering heat accumulation. Furthermore, the small sample size likely also contributed to the variable results obtained for DM-loss measurements during the aerobic exposure. Approximately 10 kg of sample were used for aerobic stability test in this study. Therefore, analysis of aerobic deterioration will be more representative. In this study, enhanced aerobic stability was observed in both WCC and C-TMR silages with prolonged ensiling and C-TMR silages were more aerobically stable than WCC silages. Besides, a decreased temperature peak and a compressed heat period were also observed in both silages with prolonged ensiling. In addition to the inhibition of undesirable microorganisms and the differences in characteristics of materials and silages, the microbial diversity also contributed to the differences in aerobic stability of silages. As discussed above, yeast are closely associated with the onset of the aerobic deterioration of C-TMR silage. To clarify the mechanisms underlying the enhancement in aerobic stability and thereby prevent deterioration, further studies on the yeast profiles associated with aerobic deterioration should be performed.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31172240), the National Scientific and Technological support projects (2011BAD17B02) and the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund (2012YJ100).
Figure 1
Changes in lactic acid (▲), acetic acid (▽), propionic acid (■), butyric acid (◇) and pH (×) during aerobic deterioration of non-fermented WCC (a) and C-TMR (b). DM, dry matter; WCC, whole crop corn; C-TMR, total mixed ration containing WCC.

Figure 2
Changes in lactic acid (▲), acetic acid (▽), propionic acid (■), butyric acid (◇) and pH (×) during aerobic deterioration of WCC silages ensiled for 7 (a), 14 (b), 28 (c), and 56 d (d). DM, dry matter; WCC, whole crop corn.
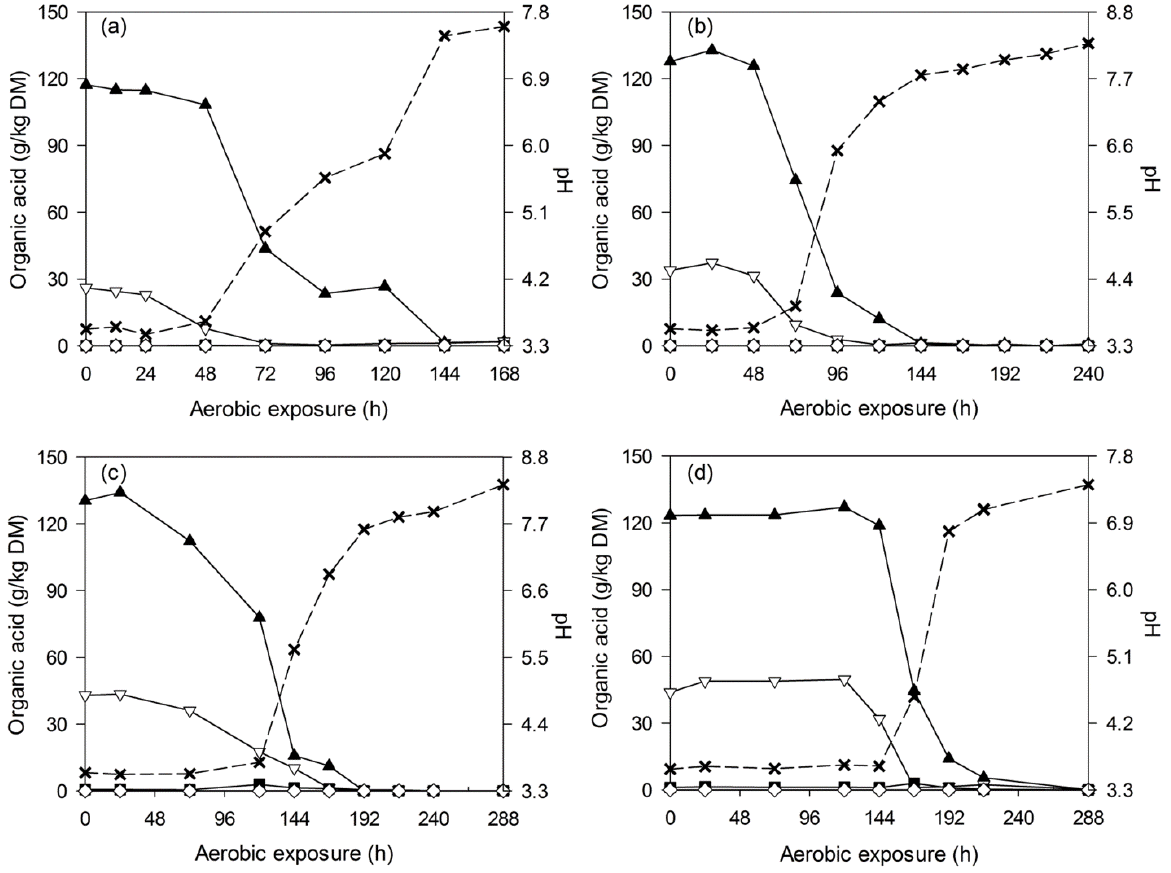
Figure 3
Changes in lactic acid (▲), acetic acid (▽), propionic acid (■), butyric acid (◇) and pH (×) during aerobic deterioration of C-TMR silages ensiled for 7 (a), 14 (b), 28 (c), and 56 d (d). DM, dry matter; C-TMR, total mixed ration containing whole crop corn.
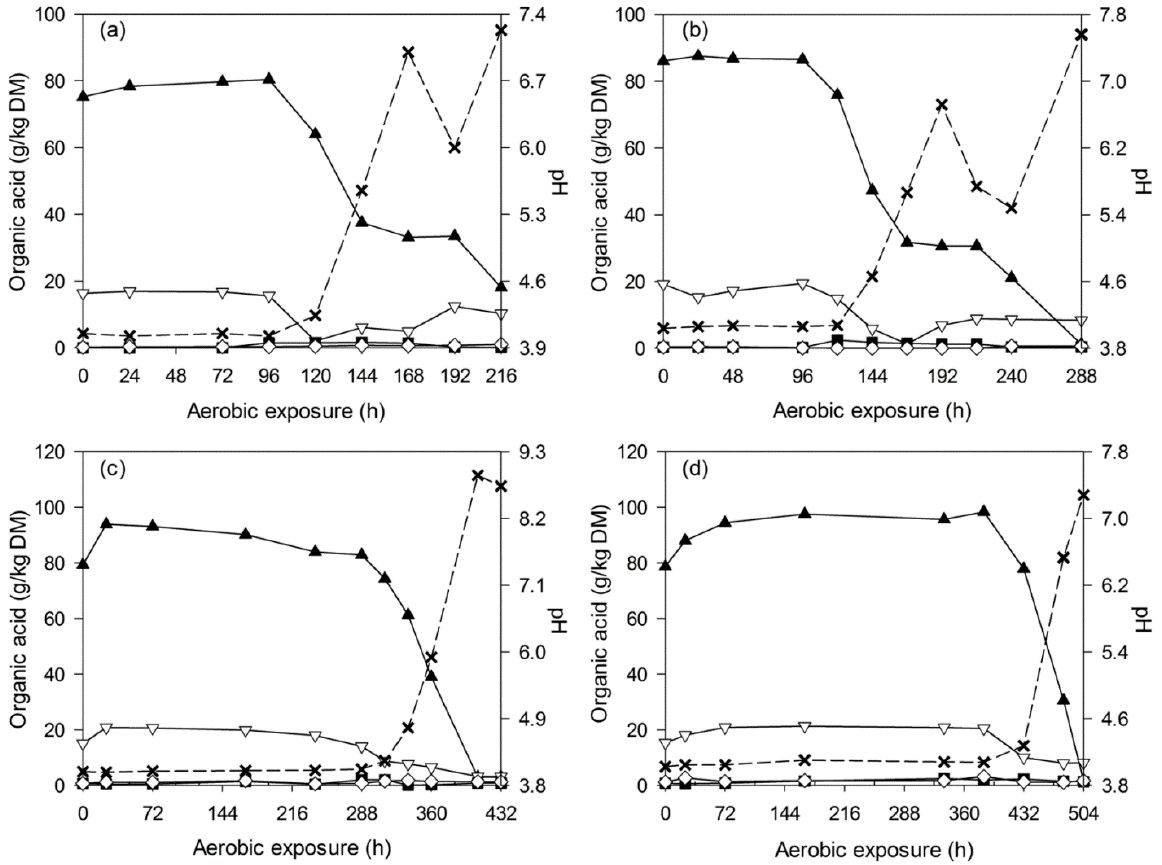
Figure 4
Changes in lactic acid bacteria (●), yeast (○), aerobic bacteria (▼) and enterobacteria (△) counts during aerobic deterioration of non-fermented WCC (a) and C-TMR (b). cfu, colony forming units; FM, fresh matter; WCC, whole crop corn; C-TMR, total mixed ration containing WCC.

Figure 5
Changes in lactic acid bacteria (●), yeast (○), aerobic bacteria (▼) and enterobacteria (△) counts during aerobic deterioration of WCC silages ensiled for 7 (a), 14 (b), 28 (c), and 56 d (d). AS, aerobic stability; *, 2.40, i.e., log10 250 cfu/g, a microbial count below the detection limit was assigned a value corresponding to half of the detection level. The reported values represent the averages from triplicate analyses. cfu, colony forming units; FM, fresh matter; WCC, whole crop corn.
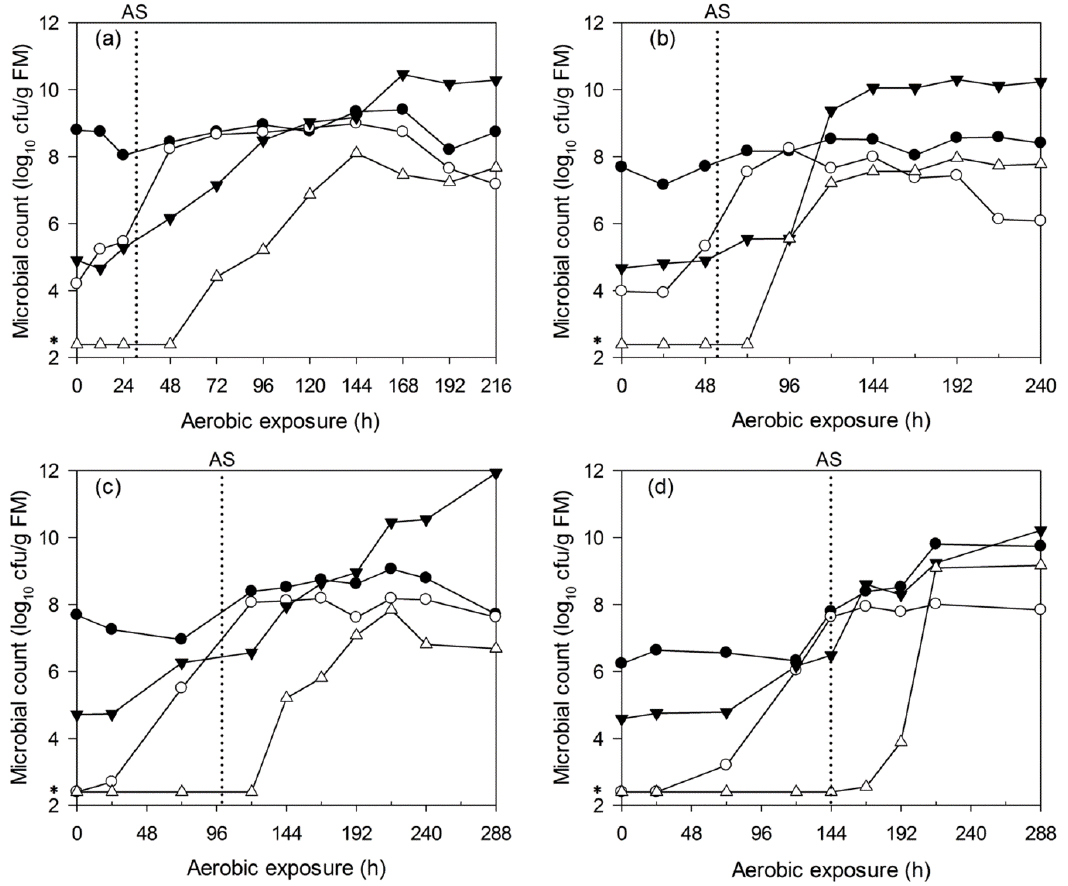
Figure 6
Changes in lactic acid bacteria (●), yeast (○), aerobic bacteria (▼) and enterobacteria (△) counts during aerobic deterioration of C-TMR silages ensiled for 7 (a), 14 (b), 28 (c), and 56 d (d). AS, aerobic stability; *, 2.40, i.e., log10 250 cfu/g, a microbial count below the detection limit was assigned a value corresponding to half of the detection level. The reported values represent the averages from triplicate analyses. cfu, colony forming units; FM, fresh matter; C-TMR, total mixed ration containing whole crop corn.
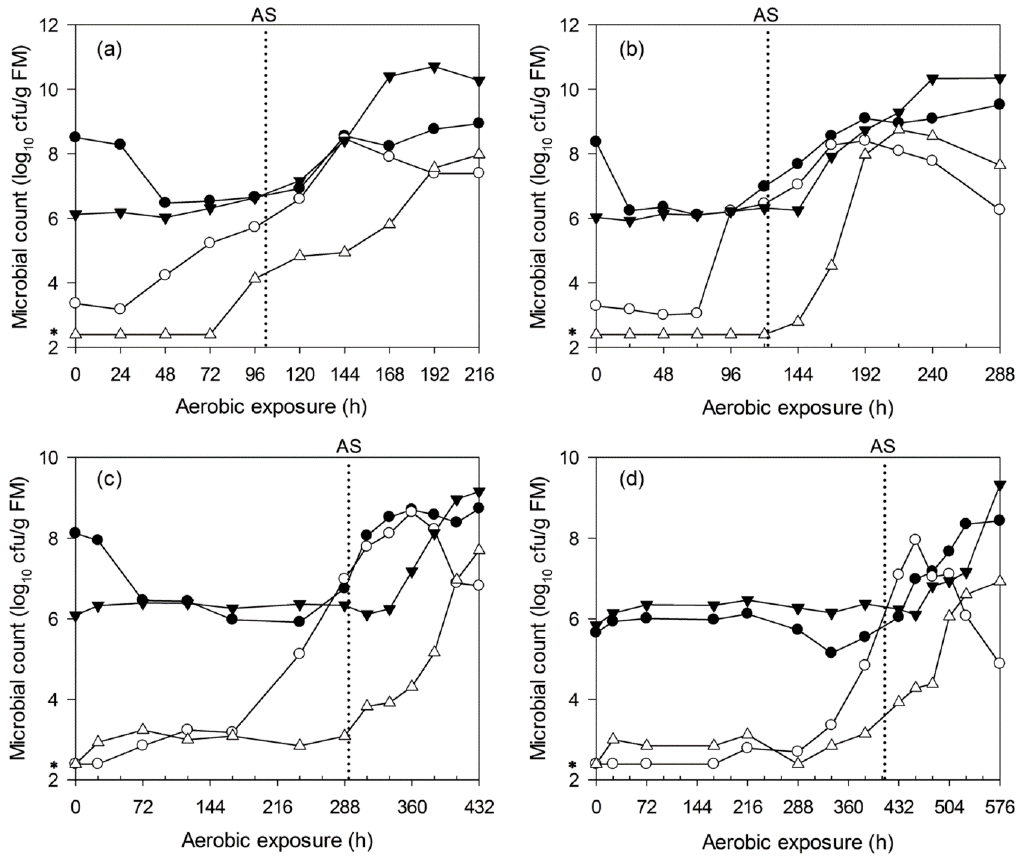
Figure 7
Changes in the core temperature (—) and ambient temperature (---) during the aerobic exposure of WCC silages ensiled for 7 (a), 14 (b), 28 (c), and 56 d (d). The reported values represent the averages from triplicate analyses. WCC, whole crop corn.
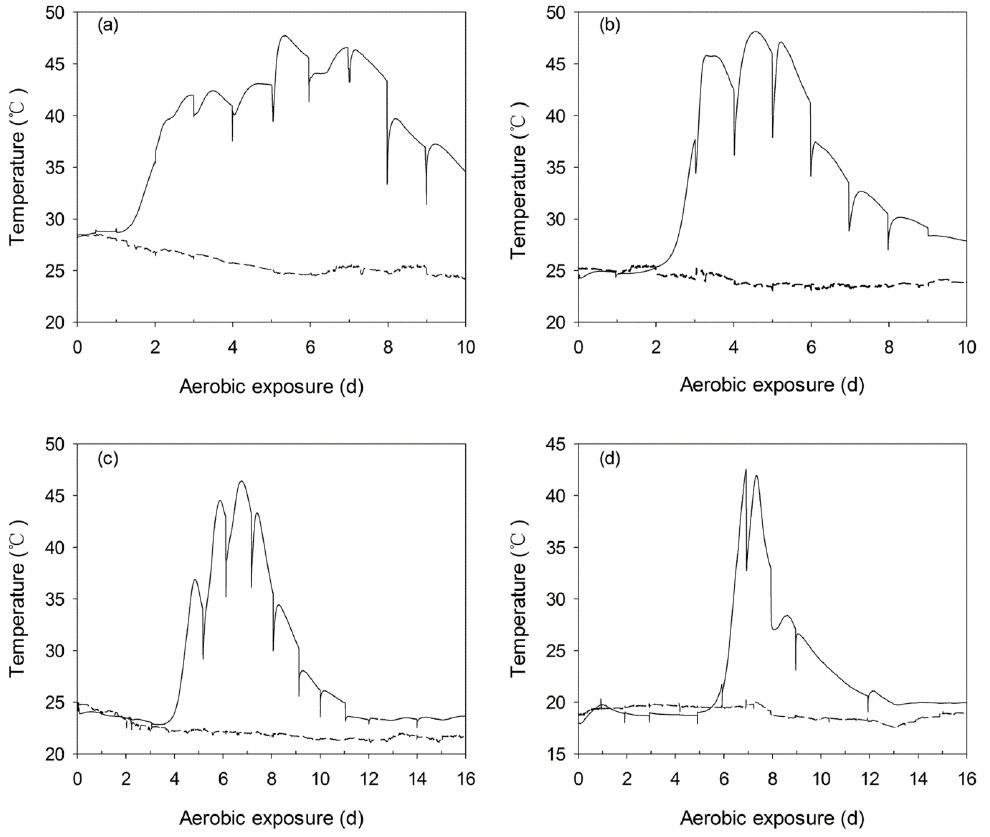
Figure 8
Changes in the core temperature (—) and ambient temperature (---) during the aerobic exposure of C-TMR silages ensiled for 7 (a), 14 (b), 28 (c), and 56 d (d). The reported values represent the averages from triplicate analyses. C-TMR, total mixed ration containing whole crop corn.
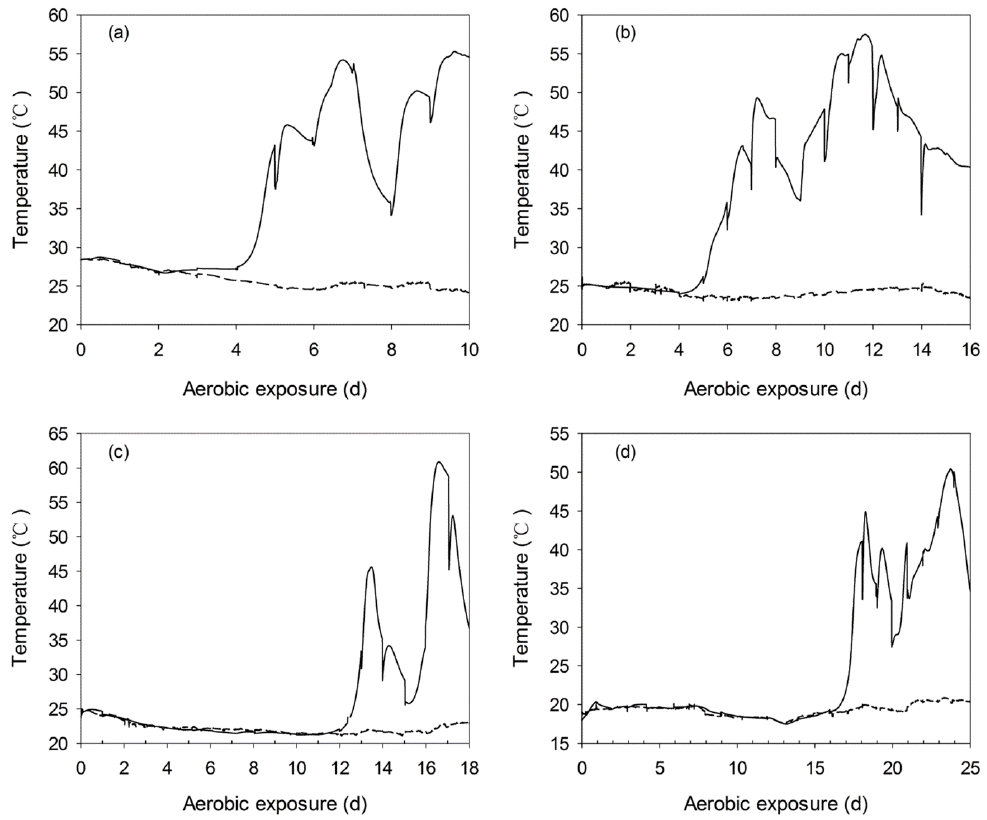
Table 1
Changes in chemical components during ensiling of WCC and C-TMR silages
| Parameters | WCC (d) | C-TMR (d) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 0 | 7 | 14 | 28 | 56 | SEM | Sig. | 0 | 7 | 14 | 28 | 56 | SEM | Sig. | |
| DM (g/kg FM) | 198a | 183b | 184b | 178bc | 176c | 2.11 | <0.001 | 444h | 428i | 428i | 420j | 425i | 2.21 | <0.001 |
| OM (g/kg DM) | 931a | 930ab | 928bc | 928bc | 926c | 0.59 | 0.001 | 902 | 901 | 901 | 901 | 901 | 0.29 | 0.611 |
| CP (g/kg DM) | 91.1c | 94.2bc | 98.2ab | 98.2ab | 102.3a | 1.12 | 0.001 | 142j | 144hij | 143ij | 145hi | 145h | 0.38 | 0.006 |
| WSC (g/kg DM) | 144a | 32.3b | 31.4b | 26.1b | 29.2b | 12.2 | <0.001 | 63.2h | 27.3i | 27.2i | 26.6i | 29.5i | 3.82 | <0.001 |
| aNDF (g/kg DM) | 522 | 520 | 515 | 520 | 508 | 2.53 | 0.497 | 464h | 445i | 437i | 433i | 431i | 3.49 | 0.001 |
| ADF (g/kg DM) | 287c | 291bc | 308a | 309a | 304ab | 2.79 | 0.003 | 275 | 273 | 272 | 271 | 269 | 1.38 | 0.751 |
WCC, whole crop corn; C-TMR, total mixed ration containing whole crop corn; SEM, standard error of mean; Sig., significance; DM, dry matter; OM, organic matter; CP, crude protein; WSC, water-soluble carbohydrates; aNDF, neutral detergent fiber assayed with a heat stable amylase and expressed inclusive of residual ash; ADF, acid detergent fiber expressed inclusive of residual ash.
Table 2
Changes in fermentation characteristics, microbial components and aerobic stability during ensiling of WCC and C-TMR silages
| Parameters | WCC (d) | C-TMR (d) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 0 | 7 | 14 | 28 | 56 | SEM | Sig. | 0 | 7 | 14 | 28 | 56 | SEM | Sig. | |
| Fermentation characteristics | ||||||||||||||
| pH | 6.15a | 3.51b | 3.58b | 3.60b | 3.58b | 0.28 | <0.001 | 5.04h | 4.05i | 4.04i | 4.03i | 4.03i | 0.11 | <0.001 |
| Lactic acid (g/kg DM) | 2.32e | 117d | 128b | 130a | 123c | 13.1 | <0.001 | 13.6j | 75.2i | 86.0h | 79.3i | 78.7i | 7.15 | <0.001 |
| Acetic acid (g/kg DM) | 0.31d | 26.0c | 33.9b | 42.9a | 43.9a | 4.26 | <0.001 | 4.02k | 16.3i | 19.2h | 15.1j | 15.3j | 1.39 | <0.001 |
| Lactic acid/acetic acid ratio | - | 4.51a | 3.77b | 3.04c | 2.81d | 0.20 | <0.001 | - | 4.61i | 4.48i | 5.27h | 5.16h | 0.11 | <0.001 |
| Microbial components | ||||||||||||||
| LAB (log10 cfu/g FM) | 6.60c | 8.80a | 7.69b | 7.68b | 6.23c | 0.25 | <0.001 | 9.47h | 8.50i | 8.36i | 8.12j | 5.65k | 0.34 | <0.001 |
| Yeast (log10 cfu/g FM)1 | 6.44a | 4.20b | 3.98b | 2.40c | 2.40c | 0.40 | <0.001 | 7.71h | 3.36i | 3.28i | 2.40j | 2.40j | 0.53 | <0.001 |
| Aerobic bacteria (log10 cfu/g FM) | 7.79a | 4.91b | 4.67b | 4.72b | 4.59b | 0.33 | <0.001 | 8.36h | 6.13i | 6.03i | 6.09i | 5.84j | 0.25 | <0.001 |
| Enterobacteria (log10 cfu/g FM)1 | 6.65a | 2.40b | 2.40b | 2.40b | 2.40b | 0.45 | <0.001 | 7.35h | 2.40i | 2.40i | 2.40i | 2.40i | 0.53 | <0.001 |
| Aerobic stability (h) | 5.5e | 31d | 55c | 100b | 144a | 13.3 | <0.001 | 5.0l | 102k | 122j | 292i | 411h | 38.9 | <0.001 |
WCC, whole crop corn; C-TMR, total mixed ration containing WCC; SEM, standard error of mean; Sig., significance; DM, dry matter; LAB, lactic acid bacteria; cfu, colony forming units; FM, fresh matter; Aerobic stability, was measured as hours to reach 2°C above ambient temperature.
REFERENCES
AOAC. 1990. Offcial Methods of Analysis. 15th EdnAssociation of Official Analytical Chemists; Arlington, VA, USA:
Filya I. 2003. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri, with or without homofermentative lactic acid bacteria, on the fermentation, aerobic stability and ruminal degradability of wheat, sorghum and maize silages. J Appl Microbiol 95:1080–1086.


Hao W, Wang HL, Ning TT, Yang FY, Xu CC. 2015. Aerobic stability and succession of yeasts during deterioration of non-fermented and fermented total mixed ration with different moisture levels. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 28:816–826.



Henderson AR, McDonald P, Woolford MK. 1972. Chemical changes and losses during the ensilage of wilted grass treated with formic acid. J Sci Food Agric 23:1079–1087.

Heron SJE, Wilkinson JF, Duffus CM. 1993. Enterobacteria associated with grass and silages. J Appl Bacteriol 75:13–17.

Hu X, Hao W, Wang H, Ning T, Zheng M, Xu C. 2015. Fermentation characteristics and lactic acid bacteria succession of total mixed ration silages formulated with peach pomace. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 28:502–510.



McDonald P. 1981. The biochemistry of silage. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; New York, NY, USA:
McDonald P, Henderson AR, Heron SJE. 1991. The biochemistry of silage. 2nd EdChalcombe Publications; Welton, UK:
Nishino N, Harada H, Sakaguchi E. 2003. Evaluation of fermentation and aerobic stability of wet brewers’ grains ensiled alone or in combination with various feeds as a total mixed ration. J Sci Food Agric 83:557–563.

Ohyama Y, Masaki S, Hara SI. 1975. Factors influencing aerobic deterioration of silages and changes in chemical composition after opening silos. J Sci Food Agric 26:1137–1147.

Owens VN, Albrecht KA, Muck RE, Duke SH. 1999. Protein degradation and fermentation characteristics of red clover and alfalfa silage harvested with varying levels of total nonstructural carbohydrates. Crop Sci 39:1873–1880.

Pahlow G, Muck RE, Driehuis F, Elferink SJ, Spoelstra SF. 2003. Microbiology of ensiling. Silage science and technology. Buxton DR, Muck RE, Harrison JH, editorsAmerican Society of Agronomy; Madison, Wi, USA: p. 31–93.

Ranjit NK, Kung L. 2000. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri, Lactobacillus plantarum, or a chemical preservative on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silage. J Dairy Sci 83:526–535.


Rooke JA, Hatfield RD. 2003. Biochemistry of ensiling. Silage Science and Technology. Buxton DR, Muck RE, Harrison JH, editorsAmerican Society of Agronomy; Madison, WI, USA: p. 95–139.

Seppälä A, Heikkilä T, Mäki M, Miettinen H, Rinne M. 2013. Controlling aerobic stability of grass silage-based total mixed rations. Anim Feed Sci Technol 179:54–60.

Smith LH. 1962. Theoretical carbohydrates requirement for alfalfa silage production. Agron J 54:291–293.

Spoelstra SF, Courtin MG, Van Beers JAC. 1988. Acetic acid bacteria can initiate aerobic deterioration of whole crop maize silage. J Agric Sci 111:127–132.

Van Soest PJ, Robertson JB, Lewis BA. 1991. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and non-starch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J Dairy Sci 74:3583–3597.


Wilkinson JM, Davies DR. 2013. The aerobic stability of silage: Key findings and recent developments. Grass Forage Sci 68:1–19.






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





