Polymorphism, Genetic Effect and Association with Egg Production Traits of Chicken Matrix Metalloproteinases 9 Promoter
Article information
Abstract
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) are key enzymes involved in cell and tissue remodeling during ovarian follicle development and ovulation. The control of MMP9 transcription in ovarian follicles occurs through a core promoter region (−2,400 to −1,700 bp). The aim of this study was to screen genetic variations in the core promoter region and examine MMP9 transcription regulation and reproduction performance. A single cytosine deletion/insertion polymorphism was found at −1954 C+/C−. Genetic association analysis indicated significant correlation between the deletion genotype (C−) with total egg numbers at 28 weeks (p = 0.031). Furthermore, luciferase-reporter assay showed the deletion genotype (C−) had significantly lower promoter activity than the insertion genotype (C+) in primary granulosa cells (p<0.01). Therefore, the identified polymorphism could be used for marker-assisted selection to improve chicken laying performance.
INTRODUCTION
In adult females, the reproductively active ovary goes through dramatic tissue remodeling, along with structural and functional alterations. These changes involve the remodeling of extracellular matrix (ECM) in the ovarian follicles throughout reproductive cycles (Rodgers et al., 2003). Previous studies have established that matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) play key roles in the degradation and re-synthesis of ECM (Page-McCaw et al., 2007). These proteinases are also involved in regulating basic cellular functions by processing other important biofactors in the ovary (Curry and Osteen, 2003).
The MMP9 (gelatinase B) represents the largest and most complex member of the MMP enzyme family and has been extensively studied in different species (Van den Steen et al., 2002). The MMP9 expression is highly regulated during follicle development, ovulation, luteinization and regression in rat (Curry et al., 2001), pig (Ribeiro et al., 2006), cattle (Imai et al., 2003), monkey (Peluffo et al., 2011) and human (Oksjoki et al., 2004). It has also been employed as a genetic marker for assessing follicular health in cattle (McCaffery et al., 2000). The MMP9 levels in the follicular fluid (Shalev et al., 2001; Baka et al., 2009; Baka et al., 2010) and serum (Lewandowski et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2008) were remarkably higher in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) women than healthy women, suggesting that elevated levels of follicular proteinase activity could cause the anovulation in PCOS ovaries (Henmi et al., 2001). The MMP9 mRNA expression and protein activity were also increased significantly in different types of human ovarian cancer cells (Tamakoshi et al., 1994; Kikkawa et al., 1997; Furuya et al., 2000; Sakata et al., 2000), which suggested MMP9 could also serve as a diagnosis and prognosis marker for ovarian cancer. The cause of the abnormal MMP9 regulation remains unclear and thus increasing investigation of MMP9 expression regulation in the ovary may contribute to the better understanding of the biology of PCOS and ovarian cancer.
Like humans, the domestic laying hen ovulates regularly, makes it a suitable animal model for investigating the biology of follicle growth and ovulation. Hen is the only non-human animal that spontaneously develops ovarian cancer with a high prevalence (Johnson and Giles, 2013). The irregular MMP3 expression associated with human ovarian cancer was also found in chicken ovarian cancer tissue (Choi et al., 2011) indicated that a tightly controlled MMP system is important for the normal functioning of the chicken ovary. We have recently analyzed the expression patterns and the core promoter region of MMP9 gene in chicken ovary (Zhu et al., 2014). Here in current study, in order to determine whether the ovarian MMP9 expression could affect the chicken follicle growth and ovulation, we examined the genetic variations of MMP9 promoter in layer populations and performed further transcriptional regulation and genetic association analysis.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
Animals and DNA preparation
Xinyang Brown layers (Kang et al., 2012) is a hybrid line of brown shell layer, which was bred from Rhode Island Red and Rhode Island White with continuous selection by Shanghai Poultry Breeding Co. Ltd. The complete production population consists of the grandparent, the parent and the commercial layer chickens. About 330 Xinyang Brown Layers were randomly selected from the population of commercial generation layers in the same farm and used in the association study. The laying pattern of each hen was recorded daily. Egg production traits including age at first egg (AFE) and total number of eggs at 28 weeks of age (E28) were used for polymorphism–trait association analysis. A Chinese indigenous breed (Wenchang) and a hybrid line (Hy-line Brown) were also included in the genotyping analysis. Genomic DNA from birds was extracted from blood samples using the TIANamp Genomic DNA kit (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China). The hens were handled and treated according to the Animal Care and Use Committee of Shandong Agricultural University.
Polymerase chain reaction and sequencing
Primer pair was designed to amplify a fragment of the promoter region according to chicken MMP9 gene sequence (GenBank accession NC_006107.3). The primer sequences were as follows: forward 5′-TTGGCGGCCAGTGGGCCC -3′ and reverse 5′-ACACAGCTGGCTCCAGGGTG -3′. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed by mixing 1 μL (50 to 100 ng) of genomic DNA, 2 μL of dNTPs (2.5 mM each), 2 μL of MgCl2 (25 mM), 1 μL of each primer (25 μM), 0.2 μL of Taq polymerase (5 U/μL, TaKaRa Bio, Dalian, China), and 2.5 μL of 10×Taq buffer in a 25 μL volume, and running according to the following program: 95°C for 4 min, 35 cycles of 95°C for 40 s, 58°C for 40 s, and 72°C for 40 s and final extension at 72°C for 5 min. The PCR products were electrophoresed on 1% agarose gel, purified with AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biotechnology, Hangzhou, China) and sequenced using the reverse primer. Sequences were edited and aligned using DNAMAN program.
Plasmid construction
Based on the sequencing analysis, three genotypes (C+C+, C+C−, C−C−) at the −1,954 of MMP9 promoter region were discovered. Using the following primers: forward 5′-TTTCTCGTGCCGCATTGTTCCT-3′ and reverse 5′-CAGAGGAGGGTGAAGCTGTGCC-3, the 5′-regulatory region from −3,842 to −14 bp of the chicken MMP9 gene, where +1 is the transcription initiation site, was cloned. The PCR fragments contain each of the alleles were cloned into the pGL-3 basic luciferase reporter vector (Promega, Madison, WI, USA).
Granulosa cell culture and plasmid transfection
The granulosa cell isolation and transfection procedures were according to previous protocol (Zhu et al., 2012). The hen ovaries were isolated and placed in phosphate buffered saline (HyClone, Logan, UT, USA). The granulosa layer from F2 to F4 follicles were separated from the follicle and the granulosa cells were dispersed by treatment with 0.3% collagenase at 37°C for 10 min with gentle agitation in a flask. After centrifugation, the cells were suspended in culture medium (M199 with 2.5% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin) and subsequently seeded in 24-well culture plates at a density of 2×105/well. The number of viable cells (>90%) was estimated using Trypan blue. Cells were cultured at 39°C in a water-saturated atmosphere of 95% air and 5% CO2. The cells were transfected with the luciferase reporter plasmids (800 ng/well) using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Transfection efficiency was normalized by co-transfection of 30 ng of the Renilla luciferase reporter plasmid (pRL-CMV vector, Promega, Madison, WI, USA). At 48 h after transfection, the cells were lysed and assayed for luciferase activity using the dual-luciferase reporter assay system (Promega, USA). The enzymatic activity of luciferase was measured with a Modulus Luminometer (Turner Biosystems, Sunnyvale, CA, USA).
Statistical analysis
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was tested employing the exact probability test in POPGENE version 1.32. The associations of MMP9 promoter genotypes with egg production traits including AFE and E28 were analyzed in Xinyang Brown chicken populations using the general linear model of SAS (SAS Institute Inc). The estimated genotype values were compared by Duncan’s Multiple Range Test of SAS. The statistical model was shown as following:
where Yij was phenotypic value of traits, μ was the population mean, Gi was the fixed effect of genotypes (include additive effect and dominance effect), Tj was the fixed effect of tier floor of the farm house, and eij was the random residual error. The difference between genotypic effects were considered as significant when p<0.05. The additive effects and dominance effects of the MMP9 gene promoter polymorphism were estimated using the REG procedure of the SAS version 8.0 (Liu, 1998). In short, Additive = (AA − BB)/2, Dominance = AB − (AA+BB)/2, where AA, AB, and BB are the least squares means of genotype C+C+, C+C−, and C−C− groups, respectively. One-way analysis of variance was used to examine the difference of the luciferase activity of different genotypes C+C+ and C−C− of MMP9 promoter-reporters and when p<0.05 the difference was considered as significant.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The MMP9 is the least conserved member of the MMP family during evolution (Hahn-Dantona et al., 2000). Comparing the MMP9 protein sequences of different species revealed that MMP9s of fish, amphibian and chicken are markedly different from mammalian MMP9s (Takeuchi et al., 2002; Yeh and Klesius, 2008). However, the cis-regulatory elements of the MMP9 promoter in chicken and other species suggested a certain level of conservation (Zhu et al., 2014). We have previously identified the −2,400 to −1,700 bp region of the chicken MMP9 promoter that is necessary for the basal transcription of MMP9 gene in the ovary. To further investigate the MMP9 transcription regulation, we screened for genetic variations located in the core promoter region by sequencing different individuals and identified a cytosine insertion/deletion polymorphism at −1,954 bp (Figure 1).

Sequencing analysis of the −1954 (C+/C−) polymorphism of chicken matrix metalloproteinases 9 promoter. Partial sequencing results, arrows indicate the polymorphism sites. We designated the cytosine deletion as −1954 (C+/C−) polymorphism but the deletion could be one of the three consecutive cytosines.
More than four hundred hens from three populations representing Chinese indigenous breed and hybrid lines were genotyped in regards to the cytosine insertion/deletion polymorphism at −1,954 bp using PCR based assay. The allele and genotype frequencies of the (−1,954 C+/C−) polymorphism in different populations are shown in Table 1. In Xinyang Brown hens, the genotypes of the (−1,954 C+/C−) polymorphism were evenly distributed between the C+ and C− alleles. In each of the other populations, the (−1,954 C+/C−) polymorphism locus was dominated by the insertion allele (C+).
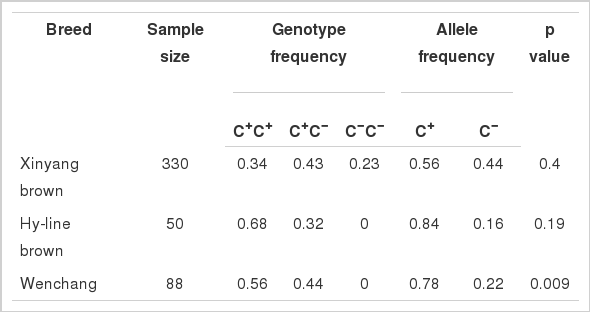
Allele and genotype frequencies of the −1,954 (C+/C−) polymorphism in the promoter region of chicken MMP9 gene and the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium test
The relationship between the (−1,954 C+/C−) polymorphism and the reproduction traits were analyzed in Xinyang Brown chicken population (Table 2). Hens with C+C− and C−C− genotypes had higher total number of E28 and shorter age AFE than the individuals with the C+C+ genotype, although the AFE did not reach a statistical significance with the present sample size. Our results showed that C− allele has positive effects on egg production and the (−1,954 C+/C−) polymorphism could be used as a selection marker in chicken breeding to improve laying performance. Comparatively, MMP9 gene polymorphisms were also associated with the litter size traits in pig populations (Niu et al., 2013). Many of the biological aspects of MMP9, including catalytic and non-catalytic activities, as well as specific MMP9 substrates have been implicated in reproduction biology (Vandooren et al., 2013). These results together indicated that genetic variations of MMP9 could lead to abnormal follicle development and ovulation in different species.
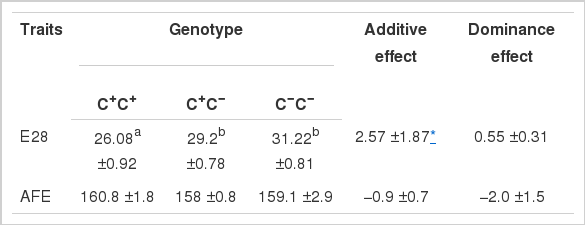
Least square means±standard errors of AFE and E28 according to genotypes at the −1954 (C+/C−) polymorphism of MMP9 promoter region in Xinyang Brown chicken
Next, we tried to determine the functional significance of the polymorphism in the MMP9 promoter. The MMP9 was expressed predominantly in follicular granulosa cells of chicken ovary (Zhu et al., 2014). To test whether the two alleles of the (−1,954 C+/C−) polymorphism in the core promoter region have different transcriptional activities in ovarian tissues, we transfected chicken granulosa cells with pGL3-MMP9-(C+)-promoter-reporter vectors, pGL3-MMP9-(C−)-promoter-reporter vectors or the control pGL3-basic reporter vectors, respectively. In chicken granulosa cells, both constructs containing either one of the MMP9 promoter variants showed much higher luciferase activity than the promoterless vector, and the promoter with the insertion allele (C+) displayed significant greater luciferase activity than the promoter with deletion allele (C−) (Figure 2). This indicates that the polymorphism (C+) could cause an increase in MMP9 expression by changing the affinity of the core promoter region to different transcriptional activators or repressors.
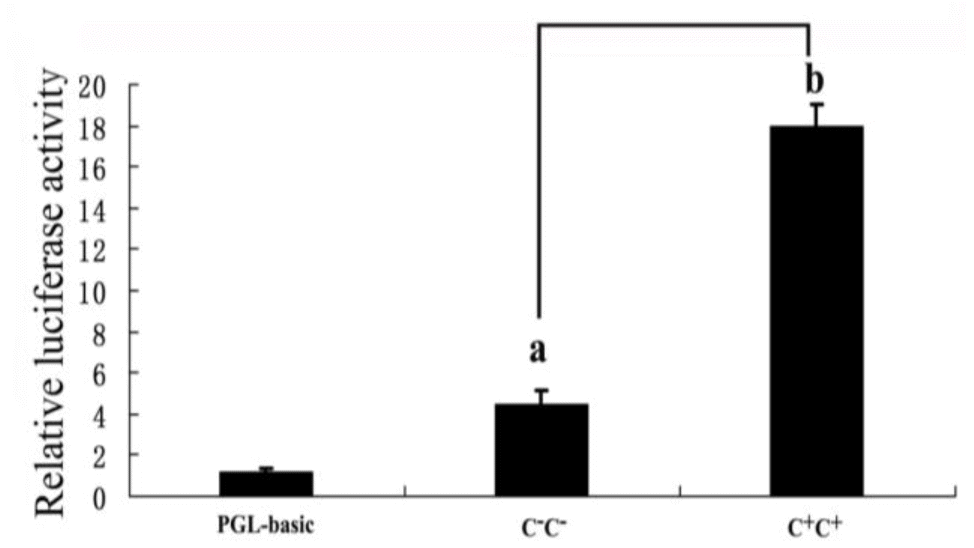
Analysis of the promoter activity of the two constructs in the chicken granulosa cells. The pGL3-basic vector was used as a control. A renilla luciferase reporter plasmid was used as an internal control to correct the transfection efficiency. Bars with different superscript letters are significantly different (p<0.01). Data are presented as mean±SEM from at least 4 independent experiments. SEM, standard error of the mean.
Using the TFSEARCH online tool (Heinemeyer et al., 1998), we sought to establish those transcription factors that can bind to the cis-elements containing either allele of the polymorphism. In the presence of C+ allele, a binding site for the nuclear factor-1 (NF-1) was abolished, and therefore, the two alleles of the (−1,954 C+/C−) polymorphism may have different binding affinity for NF-1 at this locus. The NF-1 family members can either activate or repress gene transcription in different cells (Liu et al., 1997; Pjanic et al., 2011). These data indicate that the higher transcriptional activity of the MMP9 promoter containing the C+ allele at the polymorphic locus may be caused by the loss of NF-1 binding, which represses MMP9 transcription in chicken granulosa cells, but further investigation is required to confirm the role of NF-1 in MMP9 transcriptional regulation.
Reproductive traits are complex quantitative traits involving multiple genes, loci and interactions. Hence, it cannot be ruled out that the identified genetic-traits associations could be caused by SNPs in linkage with the MMP9 promoter and not by the MMP9 gene expression itself. Whether the decreased MMP9 expression in follicle cells can contribute to the improved egg production still requires further physiological and biochemical evidence. Nevertheless, MMP9 deficiency in mice significantly reduced the litter size indicated that MMP9 expression is necessary for normal mammalian reproduction (Dubois et al., 2000). We propose that the fine-tuning of MMP9 expression in the chicken ovary could contribute to efficient follicle maturation and ovulation. In summary, our results not only demonstrated that the chicken MMP9 gene promoter (−1954 C+/C−) polymorphism is associated with the egg production traits, but also provided first evidence of the transcriptional regulation on this polymorphic locus. Further investigations will be performed to determine whether (−1,954 C+/C−) in MMP9 promoter is causative for the variation in reproductive performance.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31272435, 31301974), the Agricultural Elite Breeds Project of Shandong Province and the Innovation and Application Research of Poultry Grant of Shandong province. We appreciate the help from Huaxiang Yan and Changsuo Yang for collecting Xinyang Brown chicken samples.